CHAPTER 6: A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE
22 Slides5.80 MB

CHAPTER 6: A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE

SES FOR THE GROWTH F INDUSTRIALIZATION Wealth of natural resources Government support for Business A growing urban population cheap labor and markets for new products Ex: oil boom Now a modern urban- industrial state economy PA Rock Oil Company of Connecticut drilled the first oil well at 69 ft. in 1859
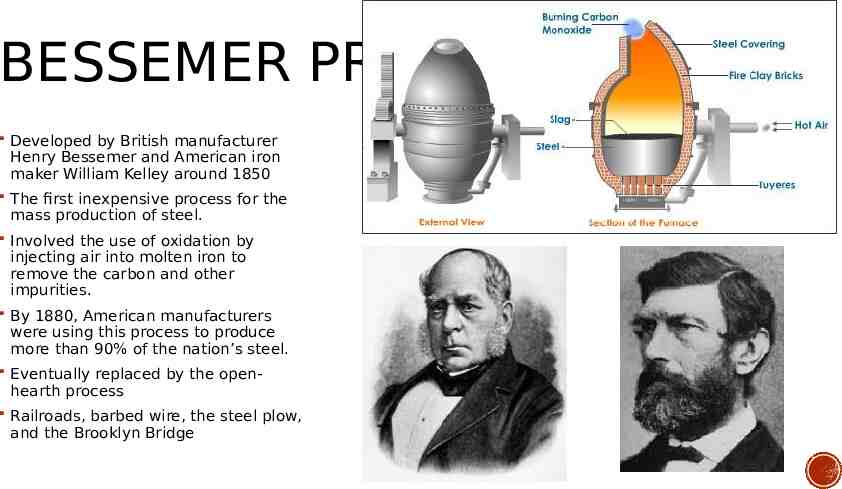
BESSEMER PROCESS Developed by British manufacturer Henry Bessemer and American iron maker William Kelley around 1850 The first inexpensive process for the mass production of steel. Involved the use of oxidation by injecting air into molten iron to remove the carbon and other impurities. By 1880, American manufacturers were using this process to produce more than 90% of the nation’s steel. Eventually replaced by the open- hearth process Railroads, barbed wire, the steel plow, and the Brooklyn Bridge

WILLIAM LE BARON JENNEY“FATHER OF THE AMERICAN SKYSCRAPER” Designed the first skyscraper with a steel frame in 1884 Before, buildings were supported by their walls or iron frames With steel frames workers could build as high as they wanted

THOMAS ALVA EDISON Establishes the world’s first research laboratory in Menlo Park, NJ Perfected the incandescent lightbulb in 1880 and later invented an entire system for producing and distributing electrical power Now electricity can run numerous machines and cities no longer need to be near rivers to power their machinery.

ALEXANDER GRAHAM BELL Bell invented the telephone along with Thomas Watson in 1876 Opened the doors for a worldwide communications network Transformed the workplace Created new jobs for women(40% in 1910 made up the clerical work force)
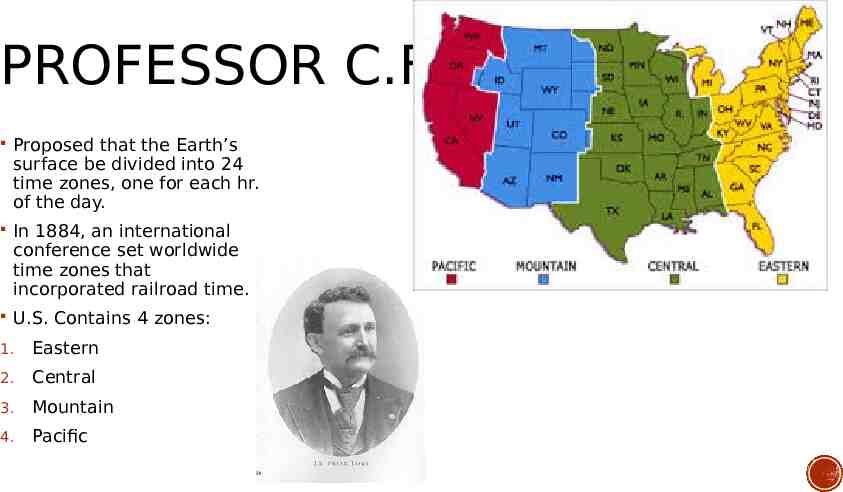
PROFESSOR C.F. DOWD Proposed that the Earth’s surface be divided into 24 time zones, one for each hr. of the day. In 1884, an international conference set worldwide time zones that incorporated railroad time. U.S. Contains 4 zones: 1. Eastern 2. Central 3. Mountain 4. Pacific

RAILROAD ABUSES Farmers demand governmental control over the railroad industry Misuses of government land grants Railroads sold to other businesses rather than to settlers Railroads fixed prices; no competition keeps farmers in their debts. These three giants formed a Railroad “giants”: William Vanderbilt (top), Jay Gould (bottom right), and Cyrus W. Fields (bottom left) railroad trust out of their three railroad companies- Union Pacific, New York Central, and Lake Shore & Dependence lines

MUNN V. ILLINOIS (1877) The Grange begins to take political action against the Railroad companies The Grange calls for new railroad legislation they soon called “Granger Laws.” Railroad companies challenged the constitutionality of those regulations In 1877, the Supreme Court ruled to uphold the Granger Laws. Outcome: Therefore, the states won the right to regulate the Railroads to benefit the farmers and consumers. Importance: establishes the principle that the federal government has the right to regulate private industries for the good of the people.

INTERSTATE COMMERCE ACT (1887) Almost 10 years after Munn v. Illinois the supreme court ruled that states could not set rates on interstate commerce-traffic coming or leaving among the states. In response, the Supreme Court passed the Interstate Commerce Act to reestablish their right as the federal government to supervise Railroad activities Establishes a 5 member interstate commerce commission (ICC) as a regulatory body.

ANDREW CARNEGIE Scottish immigrant who came to America in 1848 at age 12. Rises to become the private secretary to the local superintendent of the PA Railroad He is one of the first industrial moguls to make his own fortune (from rags to riches). Embodies the American Dream Enters the steel industry in 1873 after seeing the Bessemer process in a British Mill. By 1899, Carnegie’s Steel Company manufactured more steel than all the factories of Great Britain.

VERTICAL INTEGRATION AND HORIZONTAL INTEGRATION Vertical Integration The process of buying out one’s suppliers in order to control the raw materials and transportation systems. Untied through a hierarchy and share a common owner Each member of the hierarchy produces a different product or service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. Vertical integration was used by Andrew Carnegie Horizontal Integration A process in which companies producing similar products merge together. It is used by Businesses who seek to sell a type of product in numerous markets. Horizontal Integration occurs when a company in the same industry and in the same stage of production is being taken-over or merged with another company at the same stage of production Example: when one steel company take over another steel

SOCIAL DARWINISM A Philosophy that grew out of Charles Darwin’s theory of biological evolution. Darwin’s theory revolved around the idea that some species flourish while other do not- “natural selection.” Natural selection was known to “weed-out” less suited individuals. This theory supports individual responsibility & blame. Appealed to the protestant work ethic- Riches were a sign of Gods Favor

ROCKEFELLER & THE “ROBBER BARONS” John D. Rockefeller owned the Standard Oil Company and used trusts to gain control of the oil industry in America. Rockefeller paid his employees low wages and drove his competitors out of business by selling his oil at lower prices than it cost to produce it. This tactic led to industrialists like Rockefeller to be seen as the “Robber Barons”- capitalist men in the 1900s that became rich by using ruthless tactics against their competition “Monopolization”-exclusive possession or control of the supply or trade in a commodity or service

THE NOBLE ORDER OF THE KNIGHTS OF LABOR Emerged out of the National Labor Union (NLU) in 1869 led by Uriah Stephens when he began to focus on individual workers. Membership was open to all workers regardless of race, gender, or skill level. Support an 8 hr. workday and equal pay for equal work Used strikes and refusals to work as a last resort. Instead, they advocate for arbitration. At their height, the Knights had about 700,000 members and led to more unions forming diverse organizations.

AFRICAN AMERICANS AND THE LABOR MOVEMENT Isaac Meyers forms the Colored National Labor Union (CNLU) in 1869. CNLU emphasized cooperation between management and labor and the importance of political reform Disbanded in the early 1870s- many went to join the Knights, but the movement still remained racially divided. Management often hires African Americans to be strikebreakers, which only polarized them more from White unions’ acceptance. National Colored Convention in 1869

Craft Unionism: skilled workers from one or more trades in the SAME union AMERICAN FEDERATION OF LABOR (AFL) Led by Jewish immigrant, Samuel Gompers. focused on collective bargaining or negotiation between representatives of labor and management, to reach agreements on wages, work hours, and working conditions Used strikes as a major tactic to win higher wages and shorter work weeks Example of craft unionism

INDUSTRIAL WORKERS OF THE WORLD (IWW) A group of radical unionists and socialists in Chicago who start the Industrial Workers of the World in 1905 headed by William “Big Bill” Haywood They’re also known as the Socialism- A political system based on government control of business and property and equal distribution of the wealth. Results in overpowering capitalism, and the extreme side leads to communism. “Wobblies” The Wobblies included miners, lumberers, and cannery & dock workers. The IWW also welcomed African Americans.

HAYMARKET AFFAIR (MAY 4, 1886) 3,000 gather in Haymarket Square in Chicago to protest police brutality. The aftermath of a bombing that took place at a labor demonstration in Haymarket Square in Chicago. 7 officers and several workers die in the chaos. The 3 speakers at the demonstration and 5 others are charged with inciting a riot. 4 are hanged, and 1 commits suicide in prison Result of the affair: The public begins tot turn against the labor movement

EUGENE V. DEBS Attempted to form an industrial union- The American Railway Union (ARU). When the Pullman Co. strike ensues Debs tries to call for an arbitration, but when the Railroad co. refuses the ARU boycotts Pullman trains. Debs is jailed, but while in jail he reads the works of Karl Marx and becomes an advocate for the Socialist Party and was their Presidential candidate 5 times. Industrial Union- The belief that unions should include all laborers-skilled and unskilledin a specific industry.

TRIANGLE SHIRTWAIST F (MARCH 25, 1911) A fire breaks out in the Triangle Shirtwaist factory in New York City and engulfs the 8th, 9th, and 10th floors of the building Workers could not escape the fire, and there were no sprinklers in buildings yet. 146 women died in the fire The public could no longer ignore the conditions in garment factories, and were outraged after the jury acquitted the factory owners of manslaughter.

LLOW-DOG CONTRACTS” Employers began to fear the power of the unions Employers forbade union meetings, and forced employees to sign “yellowdog contracts,” swearing not to join a union. Protected employers from strikes breaking out in their factories, mills, workshops and sweatshops, and put workers on a tight leash.