Conditional Sentences
15 Slides422.00 KB

Conditional Sentences

Conditional Sentences Structure : A conditional sentence has 2 parts : If-clause Example : Main Clause If it rains tomorrow, we will not come. If-clause Main Clause

Conditional Sentences The order of the two clauses is flexible, it’s not important. But if the if-clause comes first, it must be followed by a comma. If it rains, I’ll stay at home TYPES: There are 4 types of conditional sentences. They are classified according to the degree of probability that they express. Each type of conditional sentences uses different tenses to show the difference in the degree of

Conditional Sentences Zero Conditional: If /when present simple / present simple. First Conditional: If/unless present simple,/ Willfuture If I study, I’ll pass Second Conditional: If past, / would base form. Water boils if it reaches 100º If I studied, I would pass Third Conditional: If past perfect / would have pp If I had studied, I would have passed

Zero Conditional Tense : Present tense in both clauses Exampl e: Present Tense Present Tense If you heat water to 100 C, it boils. If you pour oil into water, it floats.

Zero Conditional Use : Talk about universal truths. If you heat ice, it turns into water To give commands If you are tired, go to bed! In this case the verb in the main clause is an Imperative, not a Present Simple.
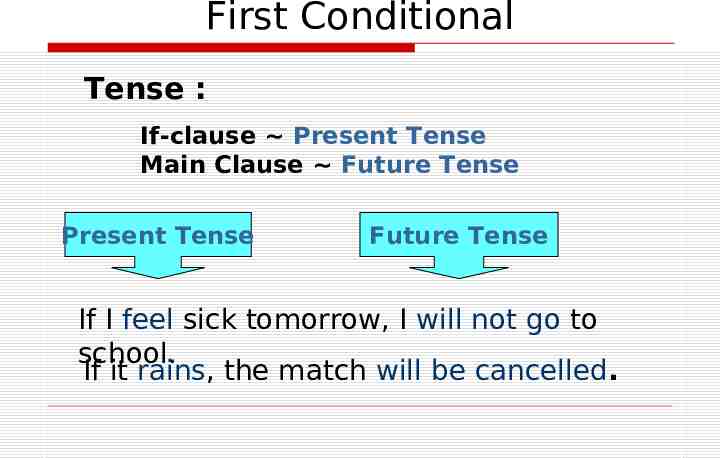
First Conditional Tense : If-clause Present Tense Main Clause Future Tense Present Tense Future Tense If I feel sick tomorrow, I will not go to school. If it rains, the match will be cancelled.

First Conditional Use : To speak about possible or probable future events. If the weather is as sunny tomorrow as it was today, we will go surfing. To make promises or warnings If you forget my birthday, I’ll never speak to you again. Unless is used in negative conditionals (si no) Unless we recycle more, we won’t have a better world.

Exercise One. First Conditional do not come (not come), 1. If you will miss (miss ) the show. You will buy 2. John (buy)a car if he gets (get) a job. will get 3. Mary (get) a toothache if eats she (eat) too many sweets.

Second Conditional Tense : If-clause Past Tense Example : Main Clause would base form Past Tense Would base form If he were a bird, he would fly across the harbour. If I had 200,000 now, I would buy a car.

Second Conditional Use : To speak about present and future situations which are unlikely to happen or hypothetical or unreal. If I had any money I would lend it to you. ( I don’t have) If I were you I wouldn't do this ( I can’t be you) MIND Were is often used instead of was in the 1st and 3rd person singular
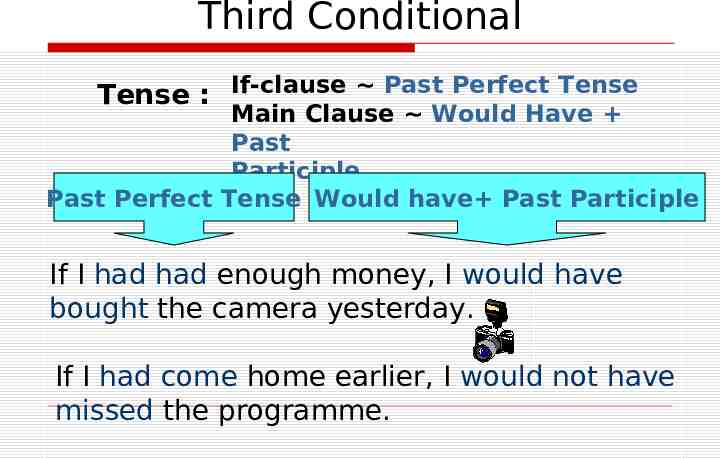
Third Conditional Tense : If-clause Past Perfect Tense Main Clause Would Have Past Participle Past Perfect Tense Would have Past Participle If I had had enough money, I would have bought the camera yesterday. If I had come home earlier, I would not have missed the programme.

Third Conditional Use : To speak about impossible past events. If they’d gone by bus, they would have arrived much later. (They didn’t go by bus) he He would have travelled around the world if had had more money. (Impossible to change, because he didn’t have the money)

Exercise Two were 1. If I (be) four years old, I would learn (learn) to play the piano. had not failed(not fail) in the 2. If I would have bought examination, my mother (buy) me a would new computer. have finished (finish) if we 3. We had had (have) better preparation.

Conditional Sentences Other connectors: Type 1 : UNLESS If you don’t phone John, he’ll get very angry. Unless you phone John, he’ll get very angry. Unless can replace If in negative conditionals






