CH. 3 DOING BUSINESS IN GLOBAL MARKETS
48 Slides2.93 MB

CH. 3 DOING BUSINESS IN GLOBAL MARKETS

OBJECTIVES LO 3-1 Discuss the importance of the global market and the roles of comparative advantage and absolute advantage in global trade. LO 3-2 Explain the importance of importing and exporting, and understand key terms used in global business. LO 3-3 Illustrate the strategies used in reaching global markets and explain the role of multinational corporations. LO 3-4 Evaluate the forces that affect trading in global markets. LO 3-5 Debate the advantages and disadvantages of trade protectionism. LO 3-6 Discuss the changing landscape of the global market and the issue of offshore outsourcing.

3-1 Discuss the importance of the global market and the roles of comparative advantage and absolute advantage in global trade.

WHY TRADE WITH OTHER NATIONS No country can produce all the products that its people want and need Free-trade: movement of goods and services among countries without political or economic barriers
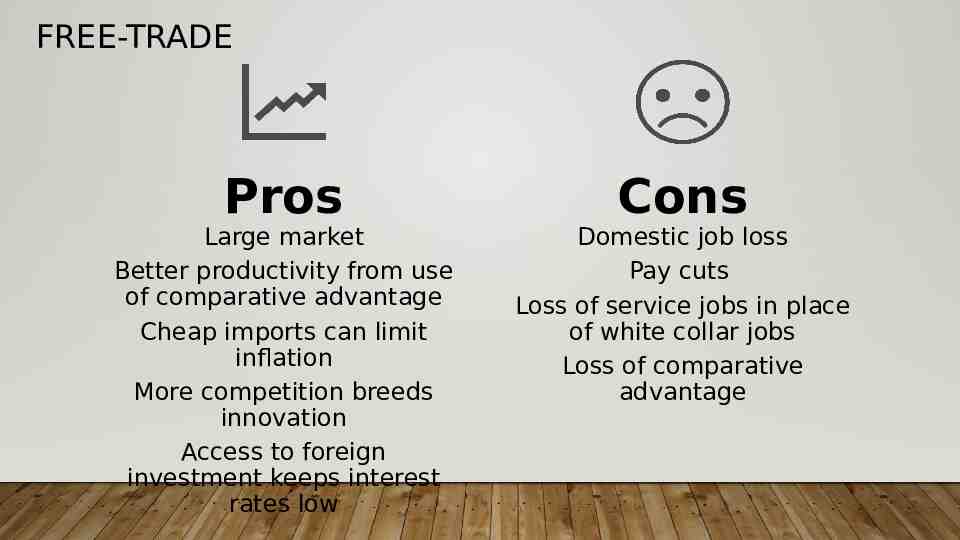
FREE-TRADE Pros Large market Better productivity from use of comparative advantage Cheap imports can limit inflation More competition breeds innovation Access to foreign investment keeps interest rates low Cons Domestic job loss Pay cuts Loss of service jobs in place of white collar jobs Loss of comparative advantage

COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE THEORY a country should sell to other countries those products it produces most effectively and efficiently, and buy from other countries those products it cannot produce as effectively or efficiently

ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE can produce a specific product more efficiently than all other countries Do not last long Manufacturing in China

3-2 Explain the importance of importing and exporting, and understand key terms used in global business.

IMPORTING Buying products from another country

EXPORTING Selling products to another country

MEASURING GLOBAL TRADE Balance of trade: value of exports compared to imports measured over a period of time Trade surplus Exports Imports Trade deficit Imports Exports

EXAMPLE Imported 1.5 trillion worth of goods and service Exported 1 trillion worth of goods and services

TOP EXPORTING COUNTRIES https://www.statista.com/statistics/264623/leading-export-countries-wo rldwide/ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2 078rank.html

BALANCE OF PAYMENTS Difference between money coming into a country and money leaving the country Money flows come from: Imports Exports Tourism Foreign investment Foreign aid Military expenditures Favorable Surplus Unfavorable Deficit
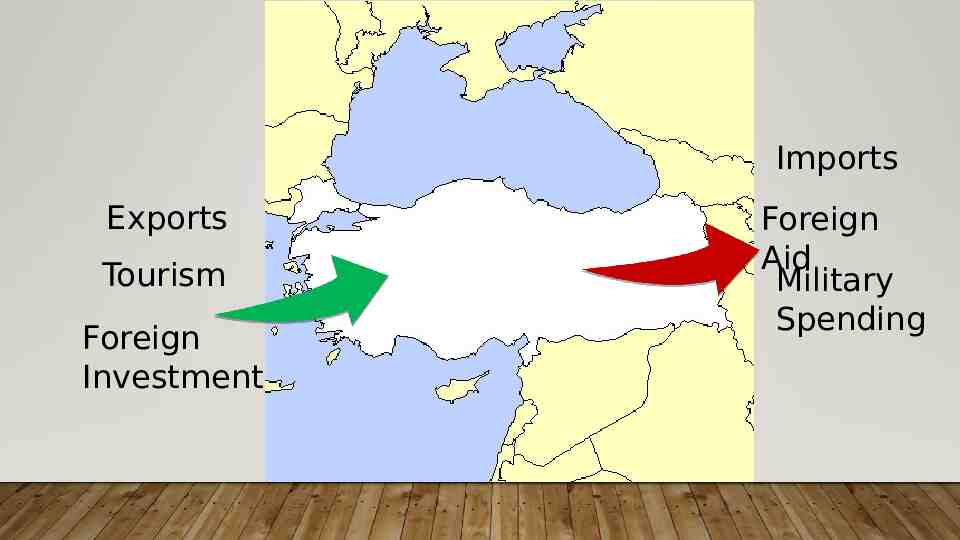
Imports Exports Tourism Foreign Investment Foreign Aid Military Spending

3-3 Illustrate the strategies used in reaching global markets and explain the role of multinational corporations.

STRATEGIES FOR REACHING GLOBAL MARKETS Licensing Exporting Franchisin g Contract Manufactu r-ing Internation al Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances Foreign Direct Investmen t LEASTAmount of commitment, control, risk, and profit potential MOST
Licensing LICENSING Allowing a foreign company to produce your product for a fee Licensor Licensee Royalty 2017 Top Licensors: https://www.statista.com/statistics/294111/leading-organizations-in-licensed-merchandise-wo rldwide/

The Walt Disney Company - 53B Meredith Corporation - 23.2B PVH Corp. - 18B Universal Brand Development - 7.3B Hasbro - 7.1B

Licensing LICENSING PRO CON Revenue Long-term deals Low start up costs Most of profit goes to licensee Low marketing and production costs Theft of trade secrets

Exporting EXPORTING Direct Indirect Through specialist company Deals with establishing trade relationships, customs, documentation

FRANCHISING Franchisin g Franchisee sells products and services under the name of the Franchiser Franchiser keeps significant control of or provides assistance with operational methods https://www.fr anchisedirect. com/top100gl obalfranchises /

CONTRACT MANUFACTURING Contract Manufacturin g Within the concept of outsourcing A foreign company produces private-label goods to which a domestic company then attaches its own brand name or trademark Often subcontracted for component parts
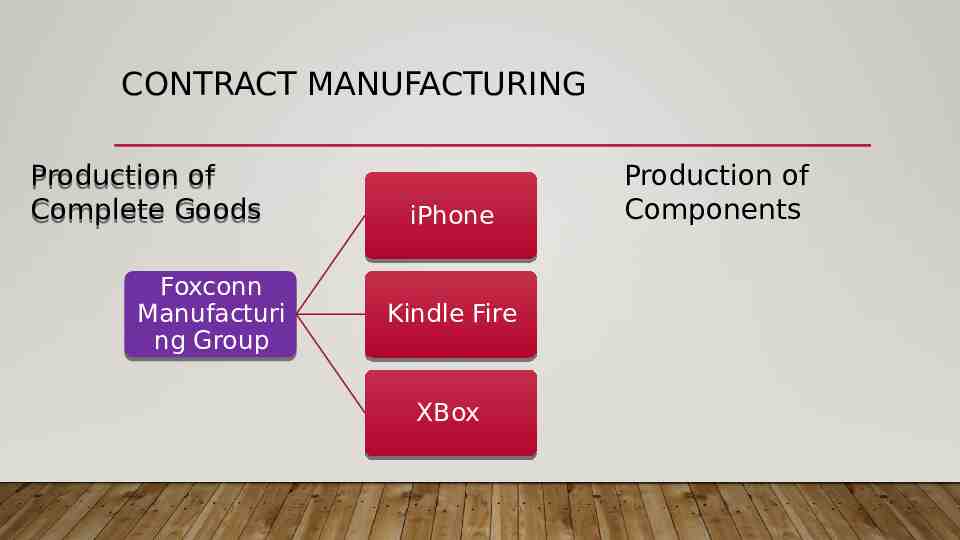
CONTRACT MANUFACTURING Production of Complete Goods Foxconn Manufacturi ng Group iPhone Kindle Fire XBox Production of Components

INTERNATIONAL JOINT a partnership in which two or more companies (often from different countries) join to undertake a major project. International Joint VENTURES Ventures and Strategic Alliances

INTERNATIONAL JOINT VENTURES Share technology Share risk Shared marketing and management expertise Entry to markets closed off to solely foreign firms
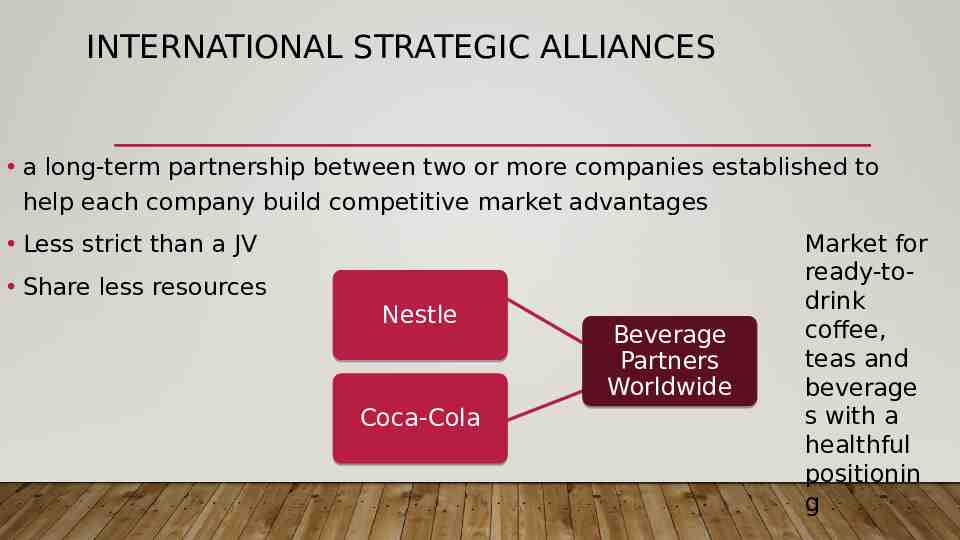
INTERNATIONAL STRATEGIC ALLIANCES a long-term partnership between two or more companies established to help each company build competitive market advantages Less strict than a JV Share less resources Nestle Coca-Cola Beverage Partners Worldwide Market for ready-todrink coffee, teas and beverage s with a healthful positionin g

FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT The buying of permanent property and businesses in foreign nations Foreign subsidiary Foreign Direct Investmen t
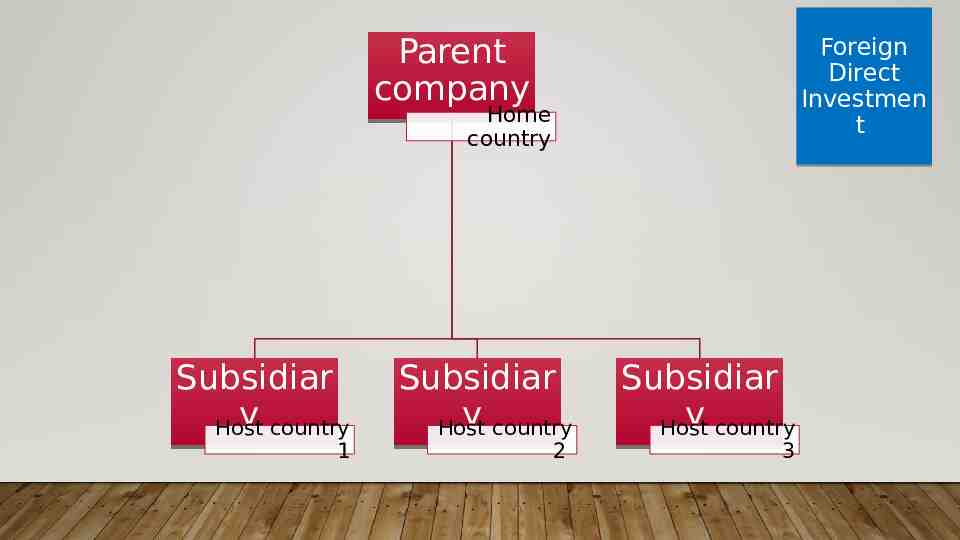
Parent company Foreign Direct Investmen t Home country Subsidiar y country Host 1 Subsidiar y country Host 2 Subsidiar y country Host 3

FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT Foreign Direct Investmen t Multinational corporation Manufactures and markets many products in many countries (MUST have physical facilities) Multinational stock ownership and management Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) investment funds controlled by governments holding investment stakes in foreign companies https://www.swfinstitute.org/sovereign-wealth-fund-rankings/

3-4 Evaluate the forces that affect trading in global markets.

SOCIOCULTURAL Values Langua ge Attitude s Culture Beliefs Religion Social structur es

Never assume what works in one country will work in another. McDonald’s local menu: https://www.businessinsider.com/mcdonalds-int ernational-menu-items-2015-7#mcdonalds-cro atias-tzatziki-wrap-11

AD SLOGAN MISTAKES

PARKER PENS Marketing: The Quink pen "won't leak and embarrass you. "Spanish mistranslation: The Quink pen won't embarazar you - make you pregnant.

ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL Exchange rate the value of one nation’s currency relative to the currencies of other countries. 1: 5 1: 6

ECONOMIC AND FINANCIAL Exchange rate Floating: Fixed: the value of one nation’s currency relative to the currencies of other countries. foreign exchange market determines price of currency government determines values Devaluation How do fluctuations in exchange rates affect factors of production? Import and export balance?

LEGAL AND REGULATORY FORCES Antitrust rules Taxes Labor relations Product liability Patents Child labor Copyrights Trade practices Prison labor

LEGAL AND REGULATORY FORCES Corruption Organization for Economic Cooperation and Developememt (OECD) Corruption Perception Index: https://www.transparency.org/news/feature/corrupti on perceptions index 2017

PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL FORCES Weak transportation and distribution systems Unclean water Sewer systems Internet use and availability Home electrical systems

3-5 Debate the advantages and disadvantages of trade protectionism.

TRADE PROTECTIONISM Government regulations to limit the import of goods and services Argue that it protects domestic jobs Wary of foreign competition Tariff: A tax on imports Protective Revenue

TRADE PROTECTIONISM Quotas: Limits on the number of imported goods in certain categories Embargo

TRADE PROTECTIONISM Nontariff barriers: Less formal barriers to free trade Automobile engine and emission standards Product testing requirements Customs procedures Domestic production requirements

WTO (WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION) 1948 GATT General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade Goal to lower trade barriers 1994: WTO 159 members Goal to mediate trade disputes and oversee business practices https://www.wto.org/index.htm

Free Trade Area No tariffs or quotas for goods entering from one country to another NAFTA (USMCA) Customs Union Free trade Common External Tariff Common market No internal tariffs / common external tariffs No quotas Free movement of goods, services, capital, people

COMMON MARKETS (SINGLE MARKET) European Union (EU) Mercosur The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Economic Community Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)

COMMON MARKETS (SINGLE MARKET) EU members and Euro users: https://europa.eu/european-union/about-eu/countri es en#countries-using-the-euro Growth of common markets hurt global trade?






