Campus Networking Best Practices Session 3: Layer 0 Campus
25 Slides3.45 MB

Campus Networking Best Practices Session 3: Layer 0 Campus Network Structured Cabling Dale Smith University of Oregon & NSRC [email protected]

We all have some ugly wiring
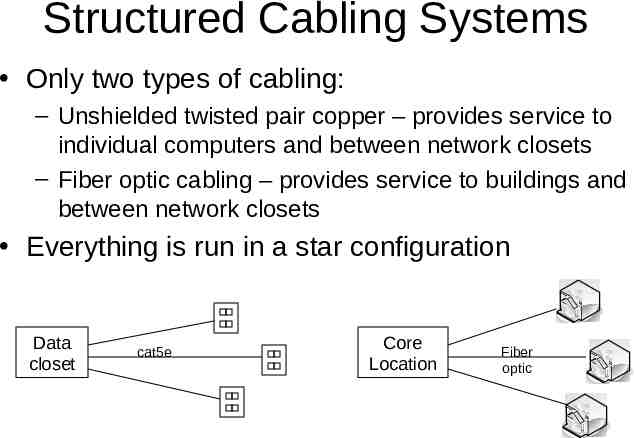
Structured Cabling Systems Only two types of cabling: – Unshielded twisted pair copper – provides service to individual computers and between network closets – Fiber optic cabling – provides service to buildings and between network closets Everything is run in a star configuration Data closet cat5e Core Location Fiber optic

Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Run in star configuration from Network Closet location to individual outlets in offices or labs. Run at least two cables to every outlet – I recommend four if you can afford it. Run at least six cables between network closets if the distance is less than 90 meters Question: what type of cable to run? Cat5, cat5e, Cat6, ?
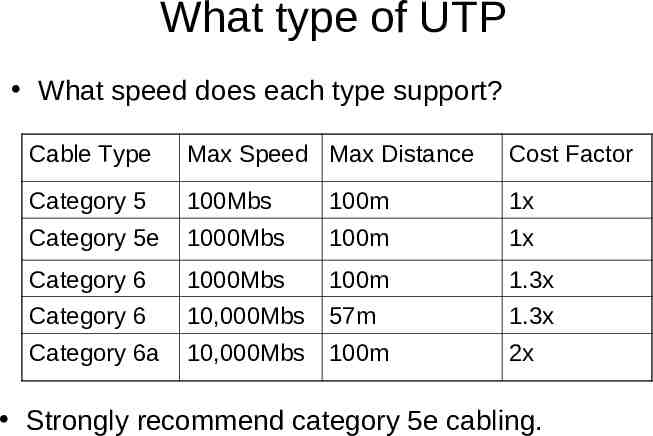
What type of UTP What speed does each type support? Cable Type Max Speed Max Distance Cost Factor Category 5 100Mbs 100m 1x Category 5e 1000Mbs 100m 1x Category 6 1000Mbs 100m 1.3x Category 6 10,000Mbs 57m 1.3x Category 6a 10,000Mbs 100m 2x Strongly recommend category 5e cabling.

Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable Labeling is a key to reduce work later

Fiber Optic Cabling Two basic types of fiber – Multi Mode limited to 2km @ 100Mbs – Single Mode 70km @ virtually unlimited Multiple types of multi mode – 62.5 micron core – 50 micron core Multiple types of single mode – Optimized for 1310 and 1550 nm operation – Optimized for WDM operation
Physics of Fiber

What type of Fiber? Multi mode Fiber – 62.5 micron 100baseFX for 2km, optical interface cost 250 USD 1000baseSX for 275m, optical interface cost 250 USD 1000baseLX for 500m, optical interface cost 750 USD 10GbaseSR for 33m, optical interface cost 2000 USD 10GbaseLRM for 220m, optical interface cost 1500 USD (not widely avail) – 50 micron laser optimized 100baseFX for 2km, optical interface cost 250 USD 1000baseSX for 550m, optical interface cost 250 USD 1000baseLX for 500m, optical interface cost 750 USD 10GbaseSR for 300m, optical interface cost 2000 USD 10GbaseLRM for 220m, optical interface cost 1500 USD (not widely avail) Single mode Fiber – – – – – – 100baseFX not supported 1000baseSX not supported 1000baseLX for 5km (most vendors support 10km), cost 750 USD 1000baseLH (not a standard) 70 km with 1550nm lasers, cost 3000 USD 10GbaseLR for 10km, optical interface cost 3000 USD 10GbaseER for 30-40km, optical interface cost 8500 USD

Going Fast on Fiber Multi mode Fiber – 62.5 micron 1Gbs to 500m 10Gbs to 220m – 50 micron laser optimized 1Gbs to 500m 10Gbs to 300m Single mode Fiber – 1Gbs to 70km – 10Gbs to 70km
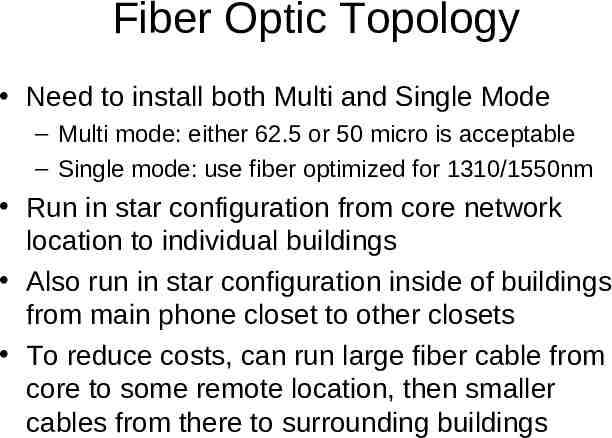
Fiber Optic Topology Need to install both Multi and Single Mode – Multi mode: either 62.5 or 50 micro is acceptable – Single mode: use fiber optimized for 1310/1550nm Run in star configuration from core network location to individual buildings Also run in star configuration inside of buildings from main phone closet to other closets To reduce costs, can run large fiber cable from core to some remote location, then smaller cables from there to surrounding buildings
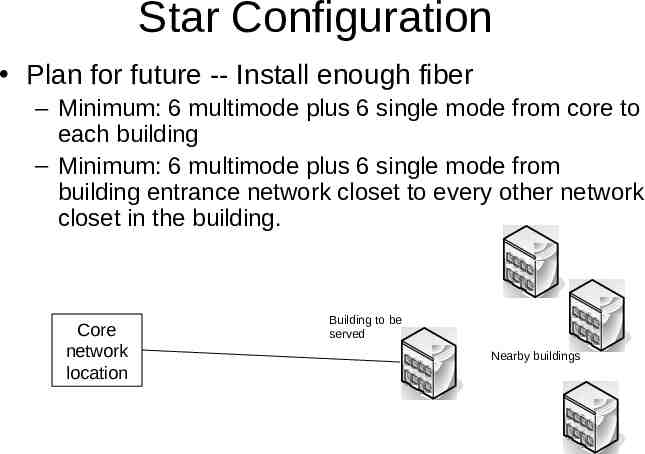
Star Configuration Plan for future -- Install enough fiber – Minimum: 6 multimode plus 6 single mode from core to each building – Minimum: 6 multimode plus 6 single mode from building entrance network closet to every other network closet in the building. Core network location Building to be served Nearby buildings
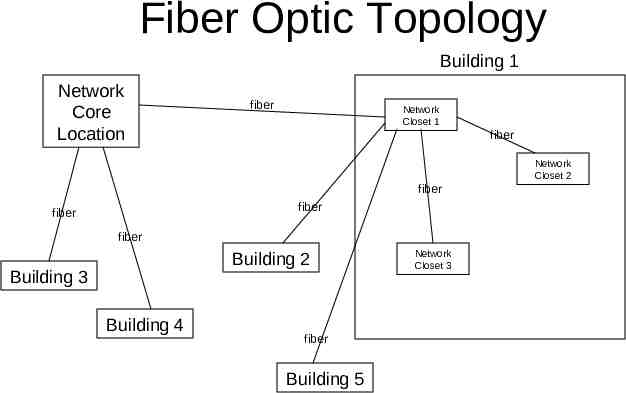
Fiber Optic Topology Building 1 Network Core Location fiber Network Closet 1 fiber Network Closet 2 fiber fiber fiber fiber Building 2 Building 3 Building 4 fiber Building 5 Network Closet 3

Construction Hints Use outdoor cable between buildings – Armored (to protect against rodents) – Loose tube Use indoor cabling inside buildings – tight buffer Standardize on Connectors – Multi mode: ST or SC (epoxy or hot melt) – Single mode: SC or LC (fusion Splice factory UPC pigtail)

Fiber Optic Cable Construction Fiber has bend radius issues
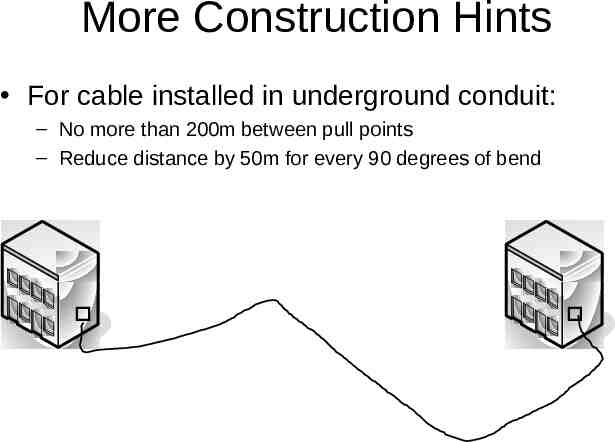
More Construction Hints For cable installed in underground conduit: – No more than 200m between pull points – Reduce distance by 50m for every 90 degrees of bend

Fiber Optic Cable Construction Leave slack loops
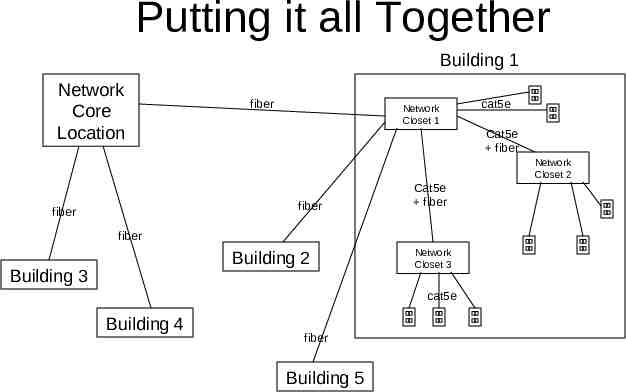
Putting it all Together Building 1 Network Core Location fiber Network Closet 1 cat5e Cat5e fiber Network Closet 2 fiber fiber Cat5e fiber fiber Building 2 Building 3 Network Closet 3 cat5e Building 4 fiber Building 5

How About Going Even Faster? 100 Gigabits? Dispersion becomes your enemy Even single mode fiber has dispersion – Chromatic Dispersion (CD) Even slightly different colors of light travel different speeds – Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) Slight variations from true roundness causes differently polarized light to travel different distances.

The Solution Today is WDM Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) – Provisioning multiple Gigabit or 10 Gigabit using different colors of light – Coarse (CWDM) Fewer waves, low cost 1310nm frequency spectrum Not suitable for amplification – short haul (70km) – Dense (DWDM) more waves More waves, higher cost 1550nm frequency spectrum Suitable for EDFA amplification – long haul (1000s of km)
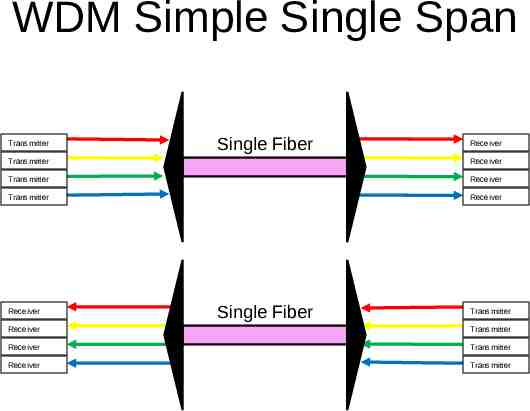
WDM Simple Single Span Transmitter Single Fiber Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Receiver Single Fiber Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter
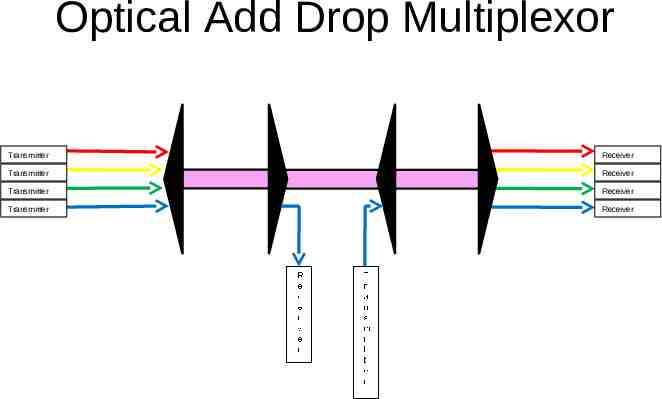
Optical Add Drop Multiplexor Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver Transmitter Receiver
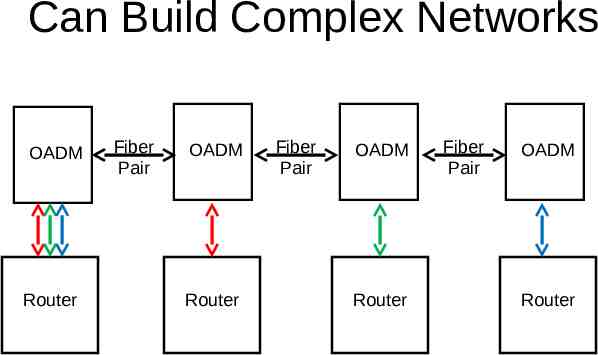
Can Build Complex Networks OADM Router Fiber Pair OADM Router Fiber Pair OADM Router Fiber Pair OADM Router

Layer 0 Summary Install cabling in star configuration – don’t daisy chain Install cat5e or cat6a – cat6 is a waste of money if the runs are over 57m Install both single and multi mode fiber for runs over 300m

Thank You Questions






