WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT Industrial Logistics (BPT 3123) Industrial
14 Slides879.12 KB

WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT Industrial Logistics (BPT 3123) Industrial Technology Management Programme Faculty of Technology

Chapter Outline Introduction Need for Warehousing Management Primary Functions of Warehouse Types of Warehouse Warehousing Strategies Warehousing Functions

Lesson Outcomes Understand warehouse management concept or approach Explain the role and major activities of warehouses and distribution centers

Introduction Nowadays, warehouse are more properly viewed as places where products may be stored and assortments of products created in accordance with customer requirements Distribution Center term are being used to emphasize the difference between the storage activity and the strategic role of warehouses For an ideal logistics system – storage is held to a minimum and inventory moves continuously throughout the supply chain on its destination to fill customer needs

Warehousing Management Primary purpose of a warehousing management is to control the movement and storage of materials within an operation and process the associated transactions. Warehousing is viewed as a place to store inventory as well as a facility for switching the inventory. Need for warehousing management: a. Reduce inventory b. Reduce labor cost c. Increase storage capacity d. Increase customer service e. Increase inventory accuracy

Warehouse Management Primary Functions of Warehousing 1. Trans-Shipment Point – A facility where products are received, sorted, sequenced and selected into loads consistent with the customers’ needs 2. Stockpiling – The storage of inventories in warehouses to protect against seasonality either in supply or demand 3. Production Support – A warehouse dedicated to storing parts and components needed to support a plant’s operations

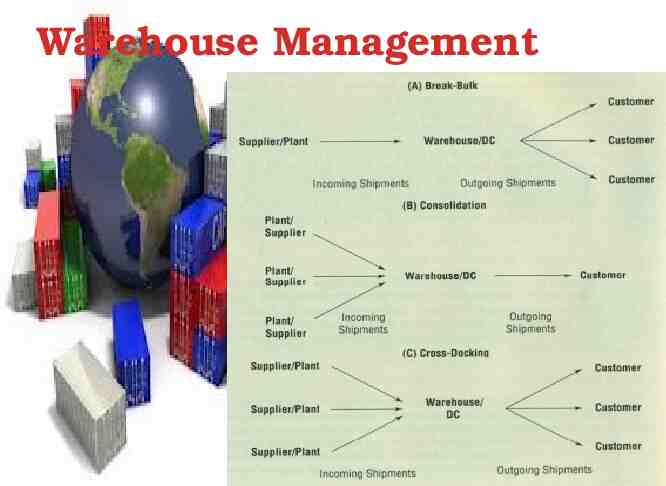
Warehouse Management 4. Break-Bulk – Splitting a large shipment into individual orders and arranging for local delivery to customers 5. Warehouse Consolidation – Combining shipments from a number of sources into one larger shipment going to a single location 6. Cross-Docking – Combines break-bulk warehouse activities and consolidation
Warehouse Management

Warehouse Management 7. Reverse Logistics Support – The logistics needed to send products or packaging materials back to disassembly, reclamation or disposal sites – Returned products can be remanufactured or updated for resale 8. Value-Added Services – Any work that creates greater value for customers – Services may change the physical features or configuration of products so they are presented to customers in a unique or customized manner

Warehouse Management Warehouse Functions 1. Receiving and Unloading – Inbound shipments must be received and unloaded from the transportation vehicles – Part of this activity may also involve checking the shipment for the correct quantities and for potential damage to products 2. In-Storage Handling – Once unloaded the goods must be moved to the desired destination within the facility, whether this is an actual storage location or a shipping area in the case of a cross-dock facility

Warehouse Management 3. Storage – Products are held, even if for only a few minutes in a storage area 4. Order-Picking – The products are removed from storage assembled into appropriate quantities assortments to fill customer orders and and 5. Staging – The assembled orders are moved to an area in the warehouse in readiness for loading into a transportation vehicle bound for customer locations 6. Shipping – Involves verifying that the assembled orders are correct and the actual loading of the transportation vehicles

Warehouse Management Types of Warehouse 1. Private Warehouse – Facility that is owned and operated by the firm that own the products 2. Public Warehouse – A firm that offers warehouse services to the public for a fee based on the amount of spaced used and the number of shipments into or out of the facility 3. Contract Warehouse – Companies offer to build, own and operate warehouse facilities for the benefit of clients who do not want to undertake those responsibilities themselves

Warehouse Strategies A private or contract facility may be used to cover basic year round requirements Public facilities are used to handle peak seasons Public and contract warehouse have demonstrated more responsiveness as they offer location flexibility Public and contract warehousing increases the potential for industry synergy Public and contract warehouses are able to design operations and facilities to meet higher volumes of multiple clients Public warehousing facility can provide complete logistical support .

Summary Warehouse are more properly viewed as places where products may be stored and assortments of products created in accordance with customer requirements Warehouses perform several functions over and above storage. It also provide benefits through consolidation, break-bulk, cross-docking and assortment activities






