Awareness During Anesthesia Do You Remember…? 112/08/07 Liu,
23 Slides1.15 MB

Awareness During Anesthesia Do You Remember ? 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 1

References Awareness during anesthesia Awareness with recall during general anesthesia – Incidence and risk factors Anethesiology 2000; 92: 597-602 BIS Monitoring to Prevent Awareness during Gene ral Anesthesia Anesth Analg 86: 1084-1089, 1998 Awareness during anesthesia Anesthesiology Clinics of North America Volume 20 Number 3 Septembe r 2002 Anethesiology 2001; 94:520-2 Awareness detected by auditory evoked potential monitoring 112/08/07 BJA 91 (2): 209-2 (2003) Liu, Chih-Min 2

Before talking about it Did you ever forget anything ? Patients are concerned that they would not be asleep during their surgery ( more then 50%) For anesthesiologists, awareness under anesthesia ranks second only to death as a “dreaded” complication 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 3

Definitions Consciousness ‘The state of being conscious; awareness of one’s own existence, sensation, thoughts, surroundings, etc’ Awareness ‘Having knowledge, conscious, cognizant’ 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 4

Incidence of awareness during anesthesia General surgery 1960: 1.2% 2000: 0.11% to 0.16% Cardiac surgery 1977: 5.8% 1998: 0.3% Other types of surgery Major trauma High from 11% up to 4 3% Obstetric surgery (C/S) 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 1968: 11.8% 1991: 0.9% 5

Patient perceptions of awareness Most common Sounds and conversation – 89% to 100% Sensation of paralysis - 85% Anxiety and panic Helplessness and powerlessness Pain - 39% Least common 112/08/07 Visual perceptions Intubation or tube Feeling the operation without pain Liu, Chih-Min 6

After-effects of Awareness During General Anesthesia Mental after-effects Muscle relaxation Pain Fear of dying Medico-legal after-effects 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 7

Mental after-effects 37% of patients were responded with Disbelief Ignorance Anger 14% of patients were told 112/08/07 “just a bad dream” “all in your imagination” “were med or hallucinating” “had a seventh sense” Liu, Chih-Min 8

Then there were Sleep disturbances fear when falling asleep Repetitive nightmares 52.4% Anxiety and panic attacks 55% Depression Flashbacks Avoidance of medical care Preoccupation of death Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) 14.3% to 22% From months (20m) to years (17y)! 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 9

Medico-legal after-effects Very large compensations USD 1,000 to 600,000 Risk factors No volatile agents used Female Obstetric or gynecology procedure Opioid only Muscle relaxant 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 10

Causes of Awareness Light anesthesia Nitrous/opioid/relaxant anesthesia Myocardial depression Hypovolemia Cesarean section Difficult intubation Premature discontinuation of anesthetic 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 11

Causes of Awareness Machine malfunction or misuse of tec hnique Failure to check equipment Vaporizer and circuit leaks Intravenous infusion errors Accidental administration of muscle rela xant to awake patient 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 12

Causes of Awareness Increased anesthetic requirements Variability in anesthetic requirements fo r intravenous agents Increased anesthetic requirement becau se of chronic alcohol, opioid, and cocain e abuse 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 13
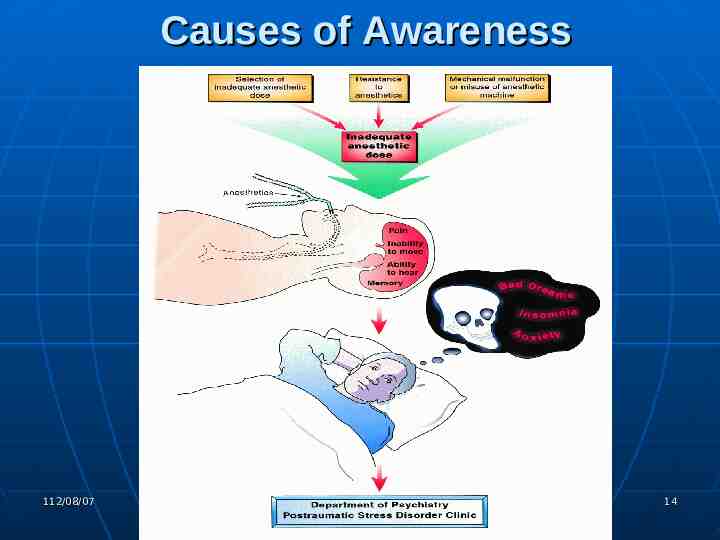
Causes of Awareness 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 14

Prevention of awareness 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Administer amnestic premedicants. Maintain vigilance regarding equipment and monitori ng. Minimize use of complete neuromuscular blockade. Supplement nitrous/opiate anesthesia with a potent volatile anesthetic. Maintain 0.8–1.0 MAC of a potent volatile anesthetic by itself. Administer adequate dose of induction agent. Obtain informed consent for high-risk patients. Mask auditory input. Provide education. Monitor for awareness. 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 15

Methods of detecting awareness Postoperative interview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Structured Best Questions asked during interviews What is the last thing you remember before going to sleep for the operation? What is the first thing you remember after waking after the operation? Do you remember anything in between? Did you have any dreams? What is the most unpleasant thing you remember from your operation and anesthesia? 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 16

Methods of Monitoring Consciousness During General Anesthesia Clinical signs Sympathetic activities: HR, BP, sweating , pupillary dilatation, lacrimation Unreliable Isolated forearm technique EEG BIS AEP 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 17

Awareness detected by auditory evoked potential monitoring BJA 91 (2): 209-2 (2003) Case report Accidental interruption of drug delivery is a common cause of awareness during general anesthesia A rapid change of AEP was noted when infusion of anesthetics was stopped 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 18
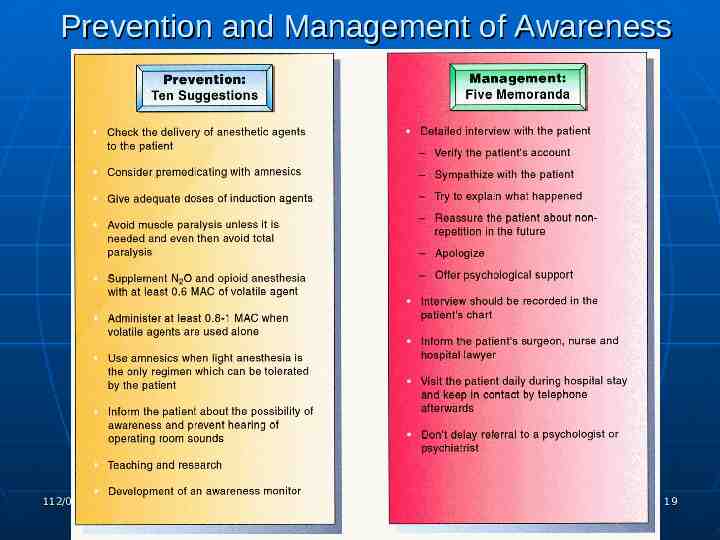
Prevention and Management of Awareness 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 19

Conclusions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Incidence in general anesthesia: 0.10.2% Incidence in cardiac surgery: 0.3% Lower dose of anesthetics are associated with higher incidence of intra-op awareness; insufficient concentration Standard physiologic monitoring is not reliable, such as AEP or BIS; however, clinical signs are much more unreliable Psychiatric after-effect of awareness range from no effect to PTSD 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 20

Conclusions 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. There is no evidence that any kind of premedication would affect the incidence of awareness If prolonged laryngoscopy is required, one should no t forget to add the induction agents or inhalation ag ent In critical hemodynamic situation, BZD instead of ge neral anesthetics may be acceptable NMBs should be used as sparingly as possible If the patient has a history of awareness under anest hesia, it would be wise to use monitor If the patient has suffered from awareness, psychiatr ic consultation and follow-up is recommended. 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 21

Discussion Structured post-operative interviews Best method however Large number of patients Very sick patients: difficult to interview Feedback information to the anesthesiologists Education Incidence from 4% to 1.5% in one study Changes in drugs dosage Increase in volatile agents, I.V. anesthetic agents Decrease in muscle relaxant BZD? Have effect on memory but are not likely to be anesthetic 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 22

Thanks for your attention! 112/08/07 Liu, Chih-Min 23






