Agile Implementation Methodology Introduction & High-Level Overview
17 Slides6.34 MB

Agile Implementation Methodology Introduction & High-Level Overview

Agenda 1. Introduction 2. What is Agile? 3. How does it work? 4. Agile Benefits 5. Agile Prerequisites SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 2
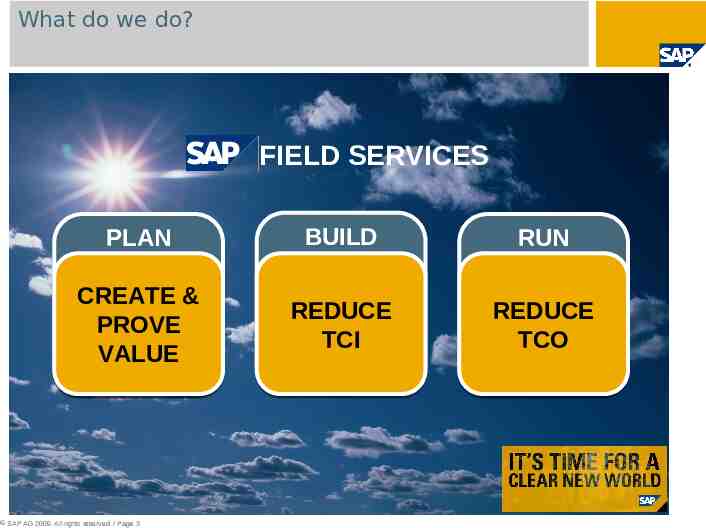
What do we do? FIELD SERVICES PLAN BUILD RUN CREATE & PROVE VALUE REDUCE TCI REDUCE TCO SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 3
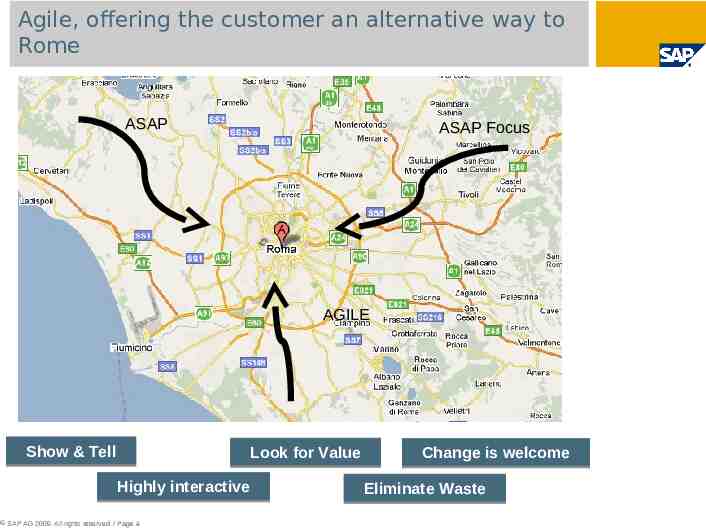
Agile, offering the customer an alternative way to Rome ASAP ASAP Focus AGILE Show & Tell Look for Value Highly interactive SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 4 Change is welcome Eliminate Waste
Agenda 1. Introduction 2. What is Agile? 3. How does it work? 4. Agile Benefits 5. Agile Prerequisites SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 5
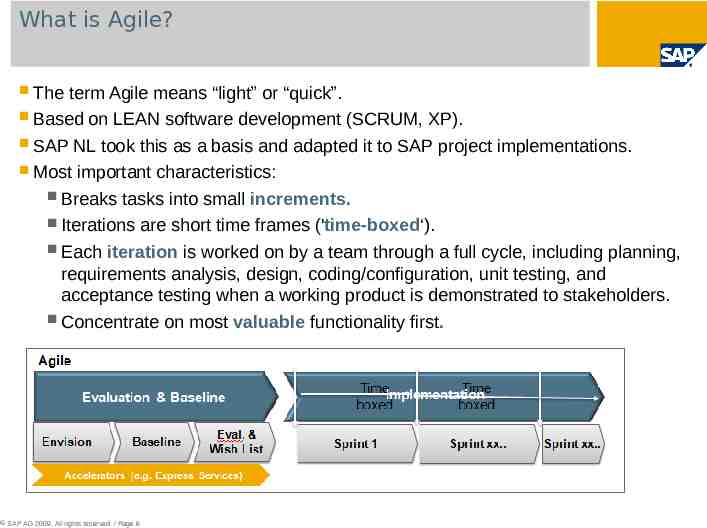
What is Agile? The term Agile means “light” or “quick”. Based on LEAN software development (SCRUM, XP). SAP NL took this as a basis and adapted it to SAP project implementations. Most important characteristics: Breaks tasks into small increments. Iterations are short time frames ('time-boxed‘). Each iteration is worked on by a team through a full cycle, including planning, requirements analysis, design, coding/configuration, unit testing, and acceptance testing when a working product is demonstrated to stakeholders. Concentrate on most valuable functionality first. SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 6

Agenda 1. Introduction 2. What is Agile? 3. How does it work? 4. Agile Benefits 5. Agile Prerequisites SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 7
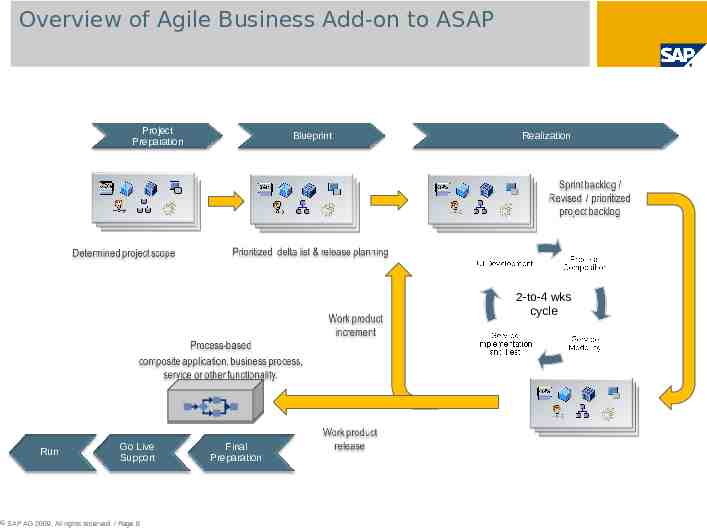
Overview of Agile Business Add-on to ASAP Project Preparation Blueprint Realization 2-to-4 wks cycle Run Go Live Support SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 8 Final Preparation
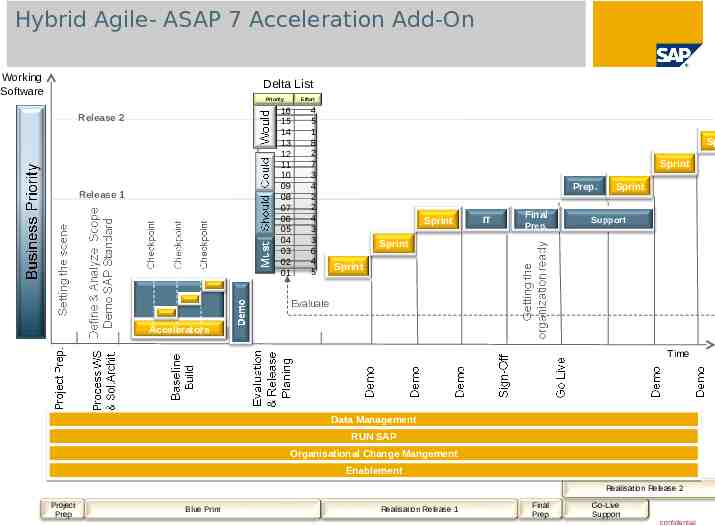
Hybrid Agile- ASAP 7 Acceleration Add-On Working Software Delta List Priority Effort 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 Release 2 Release 1 4 5 1 8 2 7 3 4 2 2 4 3 3 6 4 5 Sp Sprint Prep. Sprint IT Final Prep. Sprint Support Sprint Sprint Evaluate Accelerators Time Data Management RUN SAP Organisational Change Mangement Enablement Realisation Release 2 Project Prep Blue Print Realisation Release 1 Final Prep Go-Live Support confidential
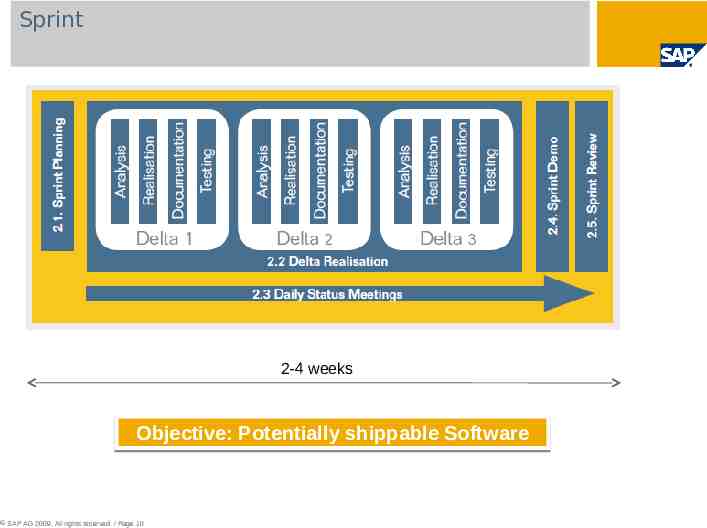
Sprint 2-4 weeks Objective: Potentially shippable Software SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 10
Agenda 1. Introduction 2. What is Agile? 3. How does it work? 4. Agile Benefits 5. Agile Prerequisites SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 11
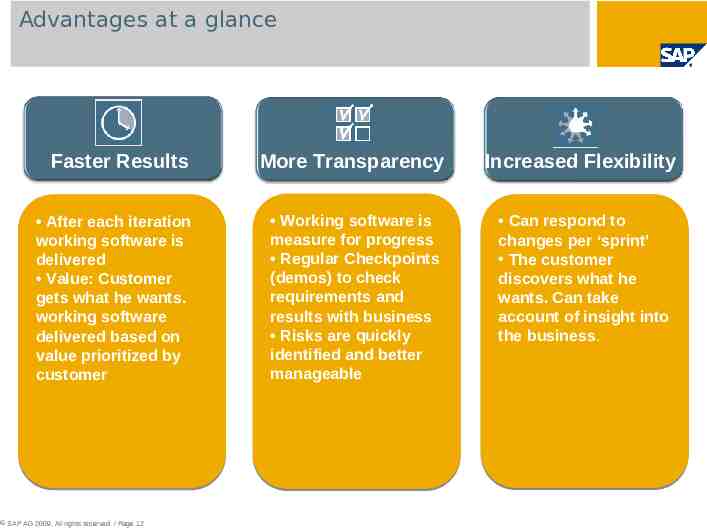
Advantages at a glance Faster Results More Transparency Increased Flexibility After each iteration working software is delivered Value: Customer gets what he wants. working software delivered based on value prioritized by customer Working software is measure for progress Regular Checkpoints (demos) to check requirements and results with business Risks are quickly identified and better manageable Can respond to changes per ‘sprint’ The customer discovers what he wants. Can take account of insight into the business. SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 12

Agenda 1. Introduction 2. What is Agile? 3. How does it work? 4. Agile Benefits 5. Agile Prerequisites SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 13

Agile Prerequisites Before starting with an Agile project Prepare your Organization & align stakeholders Understanding the rules of Agile (Change is normal, adapt, scope, speed, business driven projects) Align stakeholders what to expect from Agile project approach (chances, risks) Assign proper resources (quantitative & qualitative) to the project and have them focus on the project. Identify capable business process owners (product owners) one of the most critical success factors Fast decision making necessary, you need to empower the key people but they also need to know when it’s time to involve the Steering Committee. Be available on a daily basis and mandatory participation in Daily Scrum meeting, Sprint meeting, demo, lessons learned etc. Know your objectives and the business priorities Know the To Be (not As-is) processes in scope Know what you want to achieve and what brings value for your organization. SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 14
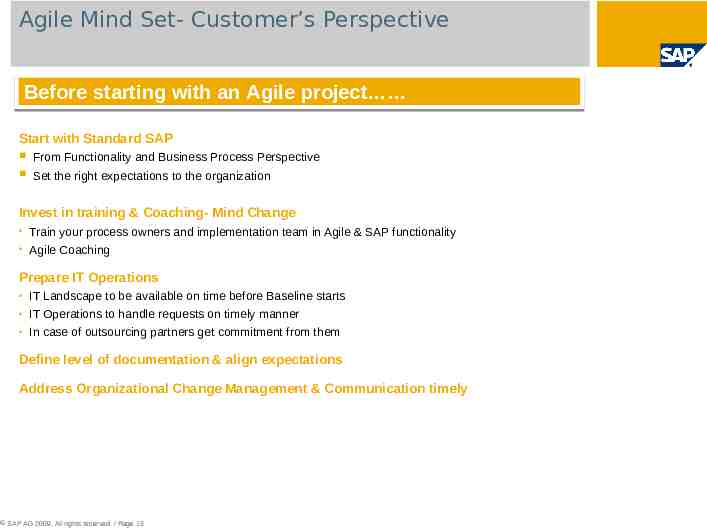
Agile Mind Set- Customer’s Perspective Before starting with an Agile project Start with Standard SAP From Functionality and Business Process Perspective Set the right expectations to the organization Invest in training & Coaching- Mind Change Train your process owners and implementation team in Agile & SAP functionality Agile Coaching Prepare IT Operations IT Landscape to be available on time before Baseline starts IT Operations to handle requests on timely manner In case of outsourcing partners get commitment from them Define level of documentation & align expectations Address Organizational Change Management & Communication timely SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 15

Discussing Agile “There are different levels of Agility” Good Practices of Agile Leverage pre-configured and Best Practice Processes as a baseline to add value in short iterations. Integration of pre-configured content and value prototyping services Identify bite size pieces: work with a manageable scope of processes and controllable dependencies Gain buy in and build confidence through early review cycles: receive early and frequent confirmation that their requirements can be met Succeed through incremental improvements and growing functionality Allow for flexibility - Ability to respond to change through manageable portions Manage deadlines – Time is fixed- scope will be adapted Conditions that Challenge Agile Lack of business contributions and commitment or slow decision-making. Physically separated project team members. Separation reduces the efficiency of an Agile communication process. Limited possibilities to slice & dice: Implementation projects with complex system landscapes and interdependent applications that share data structures and processes, which cannot be replaced separately makes management of dependencies more challenging. Initiatives that require long term planning and approval processes due to organizational strategic commitments or the nature of the industry (e.g. regulated industries) Acceleration techniques need to be tailored to the customer’s situation, culture, and risk profile SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 16

Copyright 2009 SAP AG All Rights Reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be changed without prior notice. Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other software vendors. Microsoft, Windows, Excel, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, System i, System i5, System p, System p5, System x, System z, System z10, System z9, z10, z9, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, eServer, z/VM, z/OS, i5/OS, S/390, OS/390, OS/400, AS/400, S/390 Parallel Enterprise Server, PowerVM, Power Architecture, POWER6 , POWER6, POWER5 , POWER5, POWER, OpenPower, PowerPC, BatchPipes, BladeCenter, System Storage, GPFS, HACMP, RETAIN, DB2 Connect, RACF, Redbooks, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, Intelligent Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli and Informix are trademarks or registered trademarks of IBM Corporation. Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries. Adobe, the Adobe logo, Acrobat, PostScript, and Reader are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation. UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group. Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc. HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C , World Wide Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Java is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. JavaScript is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under license for technology invented and implemented by Netscape. SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP Business ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries. Business Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal Decisions, Web Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Business Objects S.A. in the United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an SAP company. All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications may vary. These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warrant. SAP AG 2009. All rights reserved. / Page 17






