Teaching Test Taking Strategies J M E SS E R B S N, R N
68 Slides1.58 MB

Teaching Test Taking Strategies J M E SS E R B S N, R N

Objectives Recognize value of basic study tips for student and faculty Develop understanding of basic test taking strategies Gain knowledge to assist students in decreasing test taking anxiety Determine specific strategies that can be utilized to assist students in successful study/test taking performance Recognize how strategies can assist in developing the QSEN knowledge, skills, and attitudes of nursing practice

What are Test Taking Strategies? Skills and approaches, unrelated to the traits a test is intended to measure, which: May increase test the takers' scores May include the effects of coaching or experience in taking tests

Why Utilize Test Taking Strategies? Increase pass rate Faculty satisfaction Accreditation and compliance Institutional financial stability Student retention

Why Utilize Test Taking Strategies? Student performance Student engagement Preparation for board exams Produces students who are prepared to perform the QSEN competencies of knowledge, skills, and attitudes (KSA’s)

How do test taking strategies relate to the KSA’s? Students use strategies and critical thinking to problem solve during review in the areas of: Patient-centered care Teamwork and collaboration Evidence-based practice Quality improvement Safety Informatics

Research and Development Adobe Connect Review Sessions Practicum for MSN completion Test preparation assistance for current and previous students Foster student engagement to facilitate increased success
Adobe Connect Review Sessions
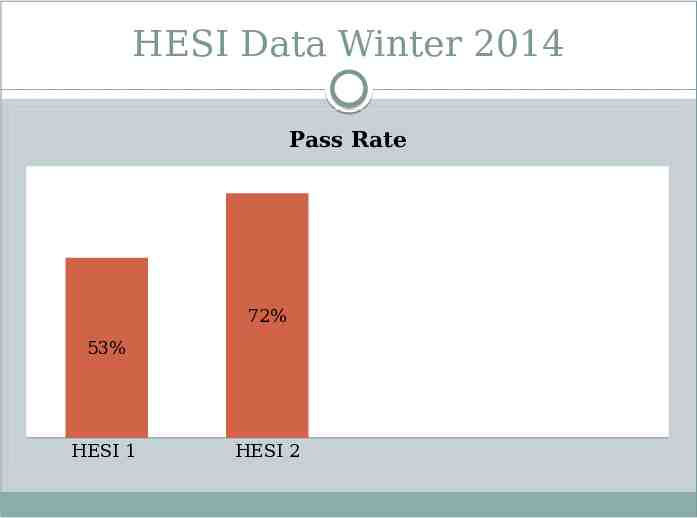
HESI Data Winter 2014 Pass Rate 72% 53% HESI 1 HESI 2
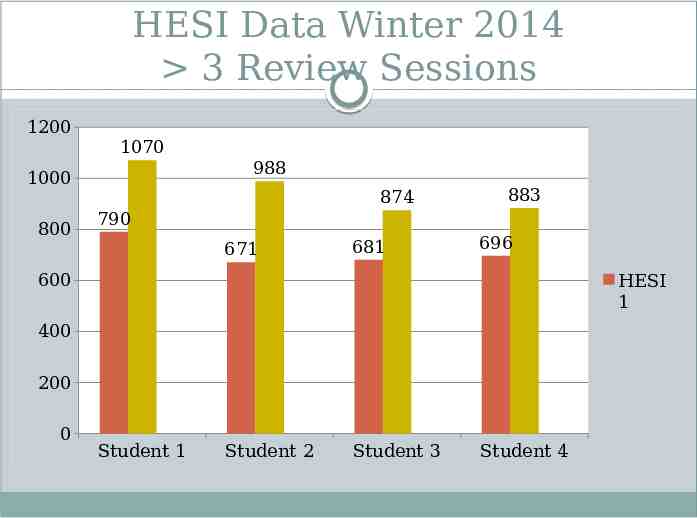
HESI Data Winter 2014 3 Review Sessions 1200 1070 1000 800 988 874 883 790 671 681 696 600 HESI 1 400 200 0 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Student 4
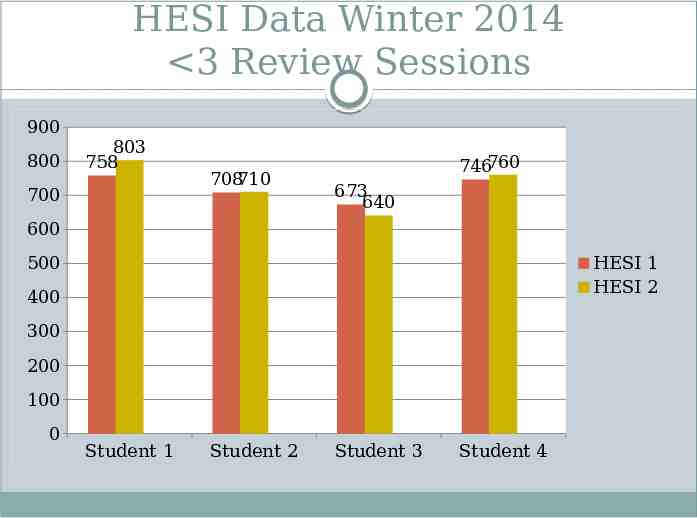
HESI Data Winter 2014 3 Review Sessions 900 800 803 758 700 708710 746760 673 640 600 HESI 1 HESI 2 500 400 300 200 100 0 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Student 4
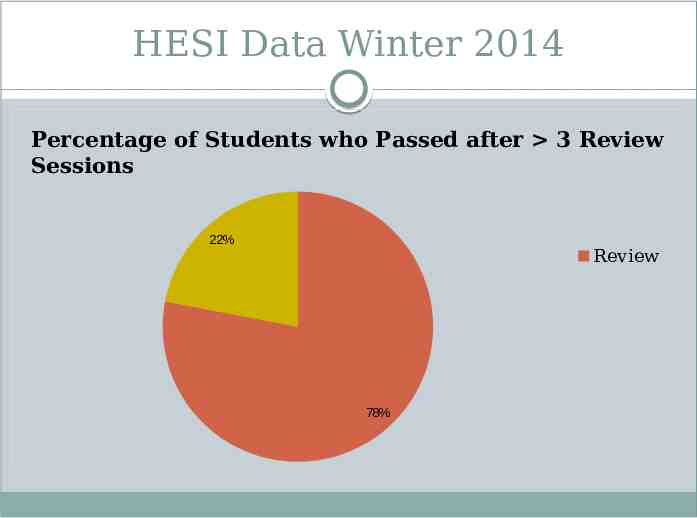
HESI Data Winter 2014 Percentage of Students who Passed after 3 Review Sessions 22% Review 78%

These strategies were effective for my students Imagine the possibilities

Where Can We Use These Strategies? Utilized in various testing environments On campus Online setting Board examinations

When Do We Start? Integration of test taking strategies Introduce early in the curriculum College 100 course Discuss strategies prior to first exam

Study Tips Class attendance Assigned material Organized and clear lecture notes Questions to increase understanding Meet with professors

Study Tips Tutoring services Remediation programs Advisory assistance Study groups

Study Tips Learn the technical vocabulary Index cards Organize information Review systematically Review early

Study Tips Divide material into logical sections Concentrate on one at a time Take frequent study breaks Practice answering questions Examine previous tests

Study Tips Ascertain location, date, time of test Determine the test format (multiple choice, essay, matching) What to bring? Pencils/calculator Get plenty of sleep

Study Tips Get up early enough to avoid rushing Eat a healthy breakfast Snacks Avoid Caffeine Get to the test site early/do not continue to study

Anxiety Reduction Relaxation response: any technique or procedure that helps you become relaxed Effect of negative self-talk Short-term and long-term relaxation response Emotional (somatic) test anxiety Deep breathing techniques

The Tensing and Differential Method 1.Put feet flat on the floor. 2.Grab underneath the chair with hands 3.Push down with feet and pull up on chair at the same time for about five seconds 4.Relax for five to ten seconds 5.Repeat the procedure two or three times 6.Relax all muscles except the ones that are actually used to take the test

The Palming Method 1.Close and cover eyes using palms of hands 2.Think of some real or imaginary relaxing scene 3.Visualize this relaxing scene for one to two minutes 4.Open eyes and repeat 5. Add sounds or smells to enhance the scene

The Parts of a Question The case (sometimes called scenario) – the description of the client and what is happening to him/her The stem – the part of the question that asks the question The correct response Distracters – incorrect but feasible choices

POW Put the question into your own words Rewording the question to gain understanding Increases comprehension What is the question really asking?
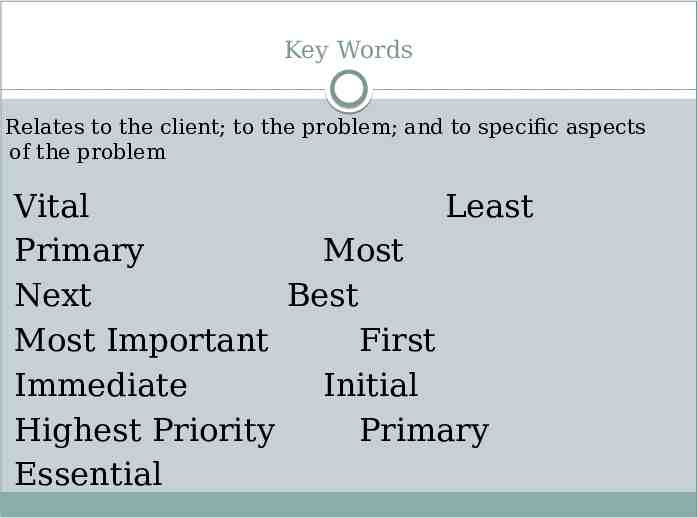
Key Words Relates to the client; to the problem; and to specific aspects of the problem Vital Least Primary Most Next Best Most Important First Immediate Initial Highest Priority Primary Essential

What is the Time Frame? Words like early or late in relation to symptoms are very important Preoperative Postoperative Care on the day of surgery

Eliminating Answer Choices Take out the two answers that you know are not correct Anxiety decreases with a 50% chance of picking the right response Strategy for use in multiple choice questions

Predicting Answers Do not pick the answer that jumps out at you Make sure to carefully consider each answer choice Eliminate the wrong answers to derive the correct answer

When doing a physical assessment of a 17-year old primigravida who is at 30 weeks of gestation, a nurse should expect which finding is related to mild preeclampsia? 1. 2. 3. 4. Epigastric discomfort Trace proteinuria Dyspnea Blood pressure of 150/100 mm hg

See it jump out from choice 4? This is the wrong answer All choices are related to preeclampsia The question is asking about mild preeclampsia Choices 1,3, and 4 relate to severe preeclampsia Trace proteinuria is the correct response
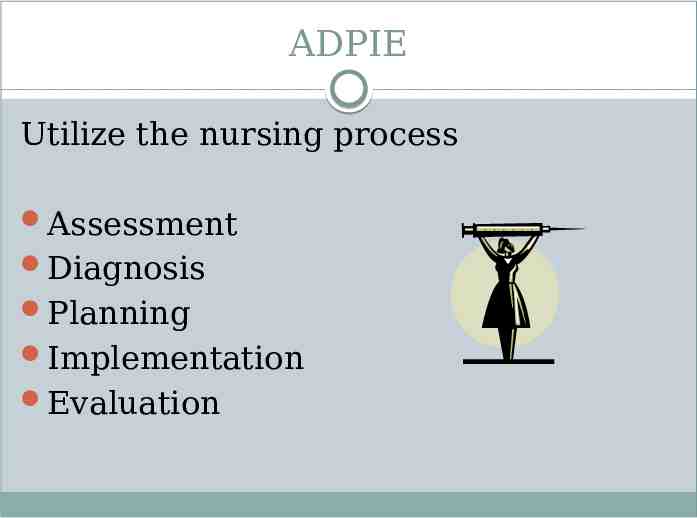
ADPIE Utilize the nursing process Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation

Assess Always assess before you act Question regarding care that includes both assessments and implementations “Is there enough information given to take action?” If there is not, you must assess first

The night after an exploratory laparotomy, a patient who has a nasogastric tube attached to low suction reports nausea. A nurse should take which of the following actions first? 1. Administer the prescribed antiemetic to the patient 2. Determine the patency of the patient’s nasogastric tube 3. Instruct the patient to take deep breaths 4. Assess the patient for pain

Determine the patency of the patient’s nasogastric tube

Assessment versus Implementation Eliminate the implementations first unless you are certain the question gives you enough information to take action If the question does give you enough information to act, you must assess eliminate the answer choices involving unnecessary assessment

A nurse enters a client's room and finds that the wastebasket is on fire. The nurse immediately assists the client out of the room. The next nursing action would be to: 1. Call for help 2. Extinguish the fire 3. Activate the fire alarm 4. Confine the fire by closing the room door

Activate the fire alarm The order of priority in the event of a fire is to rescue the clients who are in immediate danger The next step is to activate the fire alarm The fire is then confined by closing all doors Finally, the fire is extinguished

Prioritization Most, first, best, initial in a question You must establish priorities You are picking the answer with the highest priority

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Selfactua lizati on purs ue inner talen t creat ivity fulfill ment Selfestee m achie veme nt mast ery reco gniti on resp ect Belo ngin g/ Love Love r frien ds fami ly spou se Safe ty secu rity stab ility free dom fro m fear Phy siol ogic al food wat er shel ter war mth

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Dictates priorities in care Needs must be met on the lower levels prior to addressing higher levels Physiological needs always come before psychosocial needs (safety, security)

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Pain is considered a psychosocial need unless: it is extreme (kidney stones) interferes with the ability to render care (changing dressing on a burn patient)

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Safety and security involve emotional needs Example: Mastectomy patient needs to communicate loss When you find questions regarding human needs-use Maslow’s Hierarchy

Think Safety First If there are physiological needs in some choices and psychosocial needs in others you can eliminate the psychosocial answers After that keep Maslow’s second rung, safety in mind

A nurse is performing an admission assessment on a patient scheduled for possible gallbladder surgery. The patient is scheduled the following day for an oral cholecystography. Which of the following would be most important for the nurse to include in the initial assessment? 1. Any allergies the patient might have 2. Specific location of any pain 3. Family history of gallbladder disease 4. Review of any medications the patient has been taking

Any allergies the patient may have All choices are assessments All of these assessments should be included in the initial interview The potential for an allergic reaction is specific to safety

PHAN Priority-Hierarchy-ABC’s-Nursing process(ADPIE) Follow the pathway when answering priority questions
ABC’s Airway Breathing Circulation Should be used after Maslow for priority questions Must be relevant to the question, not all responses are the airway

ABC’s Airway breathing and circulation are essential to life Although Maslow lists excretion as a physiological need, it will not be important if the patient cannot breathe!

A patient who is one day postoperative after gall bladder surgery reports pain at the surgical site. Before giving a narcotic analgesic medication to the patient, it is essential for a nurse to take which of the following actions? 1. Measure the drainage from the patient’s T-tube 2. Record the patient’s report on the chart 3. Take the patient’s pulse rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure 4. Determine if the patient has voided

Take the patient’s pulse rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure

Select All That Apply Select all that apply questions on the NCLEX are increasing in numbers Treat each answer as a true or false response

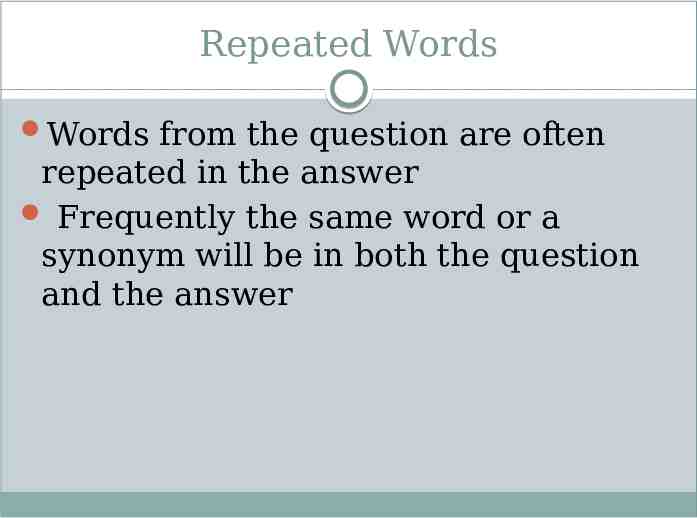
Repeated Words Words from the question are often repeated in the answer Frequently the same word or a synonym will be in both the question and the answer
Opposites When two answers are opposite such as high blood pressure and low blood pressure or increase the drip rate and stop the IV, or turn on the right side and turn on the left side, the answer is usually one of the two

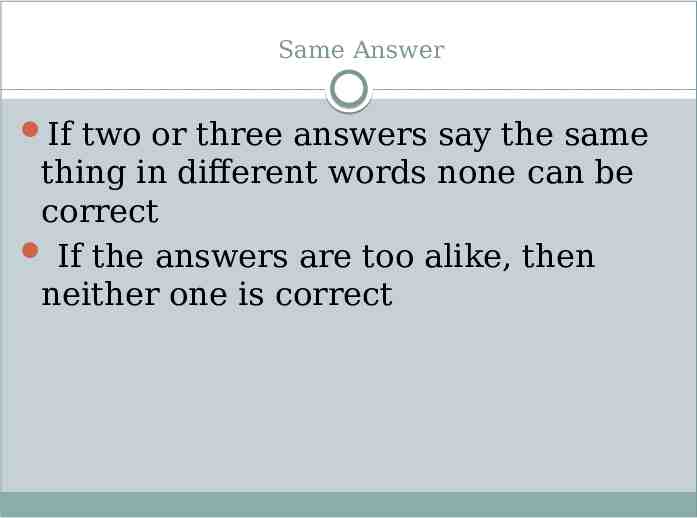
Same Answer If two or three answers say the same thing in different words none can be correct If the answers are too alike, then neither one is correct
Umbrella Answer One answer includes the others There may be more than one correct answer One answer is better than all the others because it includes them Also known as global option or comprehensive option

A nurse from the emergency room receives s telephone call from the emergency medical services and is told that several victims who survived a plane crash and are suffering from cold exposure will be transported to the hospital. The initial nursing action of the emergency nurse is which of the following? 1. Supply the trauma room with bottles of sterile water and normal saline. 2. Call the laundry department and ask the department to send as many warm blankets as possible to the emergency room. 3. Call the nursing supervisor to activate the agency disaster plan. 4. Call the intensive care unit to request that nurses be sent to the emergency room.

Call the nursing supervisor to activate the disaster plan

Odd Answer Wins The answer that is different from the others is apt to be the correct answer It may be the longest or the shortest or simply very different in content or style

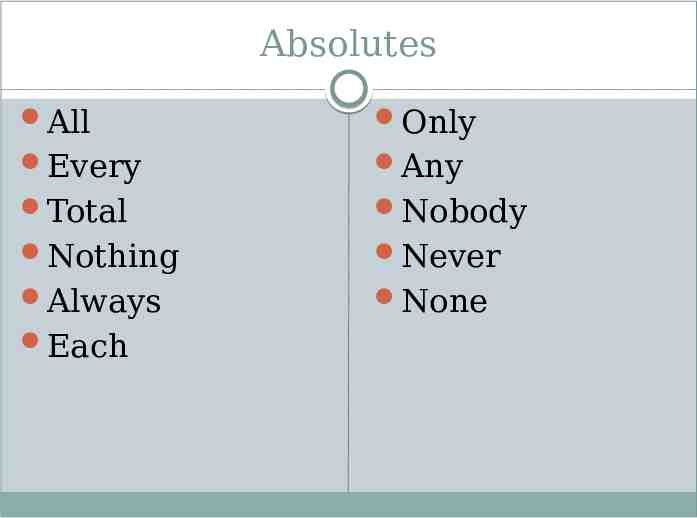
Absolutes Answers containing universal or absolute words are very apt to be incorrect Very little in life or nursing is always correct or incorrect Answers stated in absolute terms should be looked at with great caution

Absolutes All Only Every Any Total Nobody Nothing Never Always None Each
Test Item Check List DID THE STUDENT CAREFULLY Read the stem? Read all of the options? Read the stem again? Look for key words? Eliminate obviously incorrect options?

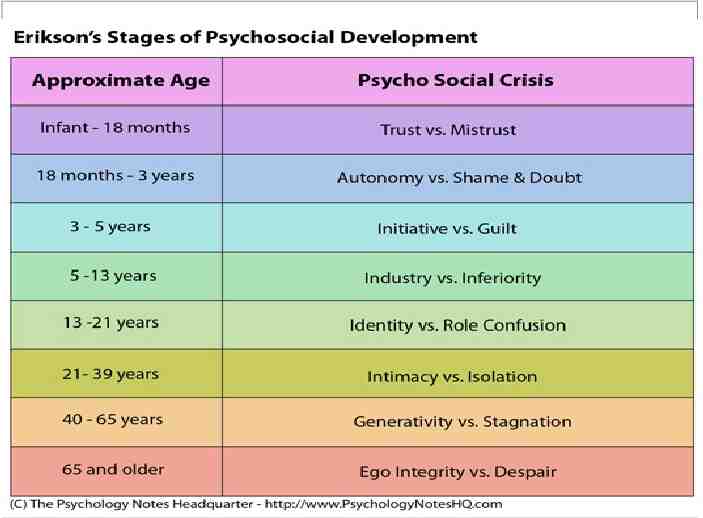
Key Strategies POW Key Words ADPIE Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs PHAN Erikson’s Stages of Development ABC’s Elimination

Summary Preparation of study techniques Anxiety reduction strategies Follow up with remediation plans Consistent feedback to student Preparation for examination by teaching effective test taking strategies

Questions? Comments?
References NCLEX Reviewers. (2014). Test taking tips and strategy to help you pass the NCLEX. Retrieved from NCLEX Reviewers: http://nclexreviewers.com nclex.blogspot.com. (2014). Questions that require prioritizing. Retrieved from NCLEX Test Taking Strategies: http://testtakingstrategies-nclex.blogspot.com North Shore Community College. (2014). Preparing for tests, taking tests, and test taking anxiety. Retrieved from Test Taking Strategies: http://www.northshore.edu PMCI Careers. (2014). NCLEX Review and Preparation. Retrieved from Professional medical Careers Institute Vocational Nursing Program: http://www.pmcicareers.com QSEN. (2014). Competencies. Retrieved from QSEN Institute: http://www.qsen.org/competencies/ Reference.md. (2014). Definition of test taking skills. Retrieved from Encyclopedia of Medical Concepts: http://www.reference.md/files/D058/mD058013.html