Strategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic Choice
38 Slides959.93 KB

Strategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic Choice Chapter 8

Learning Objectives Identify a variety of functional strategies that can be used to achieve organizational goals and objectives Understand what activities and functions are appropriate to outsource in order to gain or strengthen competitive advantage Recognize strategies to avoid and understand why they are dangerous Construct corporate scenarios to evaluate strategic options Develop policies to implement corporate, business and functional strategies Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-2

Functional Strategy Functional strategy the approach a functional area takes to achieve corporate and business unit objectives and strategies by maximizing resource productivity Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-3

Marketing Strategy Marketing strategy deals with pricing, selling and distributing a product Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-4

Marketing Strategy Market development strategy a company or business unit can (1) capture a larger share of an existing market for current products through market saturation and market penetration or (2) develop new uses and/or markets for current products. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-5

Marketing Strategy Product development strategy a company or unit can (1) develop new products for existing markets or (2) develop new products for new markets. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-6

Marketing Strategy Brand extension using a successful brand name to market other products Push strategy trade promotions to gain or hold shelf space in retail outlets Pull strategy advertising to “pull” products through the distribution channels Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-7

Marketing Strategy Skim pricing offers the opportunity to “skim the cream” from the top of the demand curve with a high price while the product is novel and competitors are few Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-8

Marketing Strategy Penetration pricing attempts to hasten market development and offers the pioneer the opportunity to use the experience curve to gain market share with low price and then dominate the industry Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-9

Financial Strategy Financial Strategy examines the financial implications of corporateand business-level strategic options and identifies the best financial course of action The management of dividends and stock price is an important part of a corporation’s financial strategy. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-10

Financial Strategy Leveraged buyout company is acquired in a transaction financed largely by debt usually obtained from a third party Reverse stock split investor’s shares are split in half for the same total amount of money Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-11

Research and Development Strategy Research and Development Strategy deals with product and process innovation and improvement also deals with the appropriate mix of different types of R&D and question of how new technology should be accessed Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-12

Research and Development Strategy Technological leader pioneering an innovation Technological follower imitating the products of competitors Open innovation firm uses alliances and connections with corporate, government, academic labs and consumers to develop new products and processes Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-13

Operations Strategy Operations Strategy determines how and where a product or service is to be manufactured, the level of vertical integration in the production process, the deployment of physical resources and relationships with suppliers Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-14

Purchasing Strategy Purchasing Strategy deals with obtaining raw materials, parts and supplies needed to perform the operations function multiple, sole and parallel sourcing Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-15

Purchasing Strategy Multiple sourcing the purchasing company orders a particular part from several vendors Sole sourcing relies on only one supplier for a particular part Parallel sourcing two suppliers are the sole suppliers of two different parts, but they are also backup suppliers for each other’s parts Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-16

Logistics Strategy Logistics Strategy deals with the flow of products into and out of the manufacturing process Trends include: Centralization Outsourcing Internet Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-17

HRM Strategy HRM strategy addresses the issue of whether a company or business unit should hire a large number of lowskilled employees who receive low pay, perform repetitive jobs and will most likely quit after a short time (the fast-food restaurant strategy) or hire skilled employees who receive relatively high pay and are cross-trained to participate in selfmanaging work teams Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-18

Information Technology Follow-the-sun management project team members living in one country can pass their work to team members in another country in which the work day is just beginning. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-19

The Sourcing Decision: Location of Functions Outsourcing purchasing from someone else a product or service that had been previously provided internally the reverse of vertical integration Offshoring the outsourcing of an activity or a function to a wholly owned company or an independent provider in another country. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-20

Disadvantages of Outsourcing Customer complaints Locked in to long-term contracts Lack of ability to learn new skills and develop new core competencies Lack of cost savings Poor product quality Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-21

Errors in Outsourcing to Avoid Outsourcing the wrong activities Selecting the wrong vendor Writing a poor contracts Overlooking personnel issues Lack of control Overlooking hidden costs Lack of an exit strategy Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-22
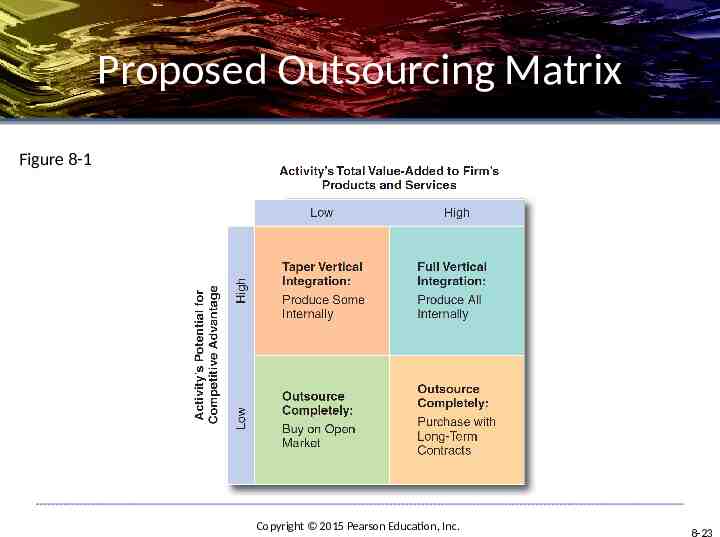
Proposed Outsourcing Matrix Figure 8-1 Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-23

Strategies to Avoid Follow the leader Hit another home run Do everything Arms race Losing hand Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-24

Strategic Choice: Selecting the Best Strategy Corporate scenarios pro forma (estimated future) balance sheets and income statements that forecast the effect each alternative strategy and its various programs will likely have on division and corporate return on investment Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-25

Corporate Scenario Steps 1. Use industry scenarios to develop 2. 3. assumptions about the task environment Develop common-size financial statements for prior years Construct detailed pro forma financial statements for each strategic alternative Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-26
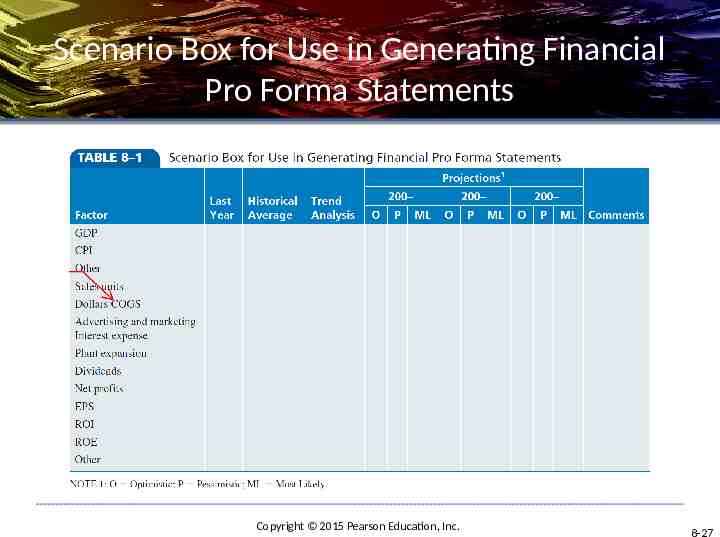
Scenario Box for Use in Generating Financial Pro Forma Statements Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-27

Management’s Attitude Toward Risk Risk composed not only of the probability that the strategy will be effective but also of the amount of assets the corporation must allocate to that strategy and the length of time the assets will be unavailable for other uses Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-28

Management’s Attitude Toward Risk Real-options approach when the future is highly uncertain, it pays to have a broad range of options open Net present value calculates the value of a project by predicting its payouts, adjusting them for risk and subtracting the amount invested Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-29

Stakeholder Priority Matrix Figure 8-2 Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-30

Questions to Assess Stakeholder Concerns 1. 2. 3. 4. How will this decision affect each stakeholder? How much of what stakeholders want are they likely to get under the alternative? What are the stakeholders likely to do if they don’t get what they want? What is the probability that they will do it? Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-31

Pressures from Stakeholders Political strategy plan to bring stakeholders into agreement with a corporation’s actions constituency building, political action committee contributions, advocacy advertising, lobbying and coalition building Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-32

Pressures from the Corporate Culture If there is little fit, management must decide if it should: Take a chance on ignoring the culture. Manage around the culture and change the implementation plan. Try to change the culture to fit the strategy. Change the strategy to fit the culture. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-33

Process of Strategic Choice Strategic choice the evaluation of alternative strategies and selection of the best alternative Failure almost always stems from the actions of the decision maker, not from bad luck or situational limitations. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-34

Avoiding the Consensus Trap Devil’s advocate assigned to identify potential pitfalls and problems with a proposed alternative strategy in a formal presentation may be an individual or a group Dialectical inquiry requires that two proposals using different assumptions be generated for each alternative strategy under consideration Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-35

Process of Strategic Choice Criteria for evaluating alternatives includes: Mutual exclusivity Success Completeness Internal Consistency Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-36

Developing Policies When crafted correctly, an effective policy accomplishes three things: It forces trade-offs between competing resource demands. It tests the strategic soundness of a particular action. It sets clear boundaries within which employees must operate, while granting them the freedom to experiment within those constraints. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-37

Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 8-38






