SS-08 Electronic Health Records: How will they change the way we
36 Slides2.90 MB

SS-08 Electronic Health Records: How will they change the way we collect data? Speakers: Clarice Brown Michelle Williamson Brian Gugerty Harold Luft 8/7: 1:30-3:00 PM Tuesday Organizers: Monica Wolford Anita Bercovitz

Welcome Clarice Brown Division Director Division of Health Care Statistics NCHS

SS-08 Electronic Health Records: How will they change the way we collect data? Michelle Williamson Brian Gugerty Harold Luft Supporting Standards Development for HIT/EHR Adoption Electronic Health Records “Sourcing” Data for NAMCS

Supporting Standards Development for HIT/EHR Adoption Michelle Williamson, MS, RN Senior Health Informatics Scientist Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Health Statistics Classifications and Public Health Data Standards NCHS Data Users Conference August 7, 2012

Agenda Federal Focus on Health Information Technology (HIT) and Electronic Health Records (EHR) NCHS Participation in HIT/EHR Standards Development

U.S. Plans for Health Information Technology “To lower healthcare cost, cut medical errors, and improve care, we’ll computerize the nation’s health record in five years, saving billions of dollars in health care costs and countless lives.” President Barack Obama First Weekly Address January 24, 2009 Consistent with Bush’s 2014 goal for electronic health records

American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA) President Obama signed ARRA on Feb. 17, 2009 ARRA required HHS to create, vet and publish an initial set of HIT system standards, implementation specifications and testing criteria to promote adoption and “meaningful use” of EHRs ARRA is serving to stimulate adoption of HIT

Standards for HIT/EHR Standards are the essential building blocks for information systems Various types of standards: Message formats and structured documents Core Data Sets Classification Systems and Terminologies Privacy and Security

Standards Development Organizations (SDO) Health Level Seven International (HL7) o o Message Standards (Version 2/Version 3) Document Standards Clinical Document Architecture (CDA)* o Specifies the structure and semantics of "clinical documents" for the purpose of exchange between healthcare providers and patients Continuity of Care Document (CCD) o Implementation guide for sharing Continuity of Care Record (CCR) patient summary data using the HL7 CDA *Source: http://www.hl7.org/implement/standards/product brief.cfm?product id 7

SDOs and Standards Related Organizations Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) X12 o Administrative standards designated under HIPAA to support administrative simplification o Includes the standard transactions for Electronic Data Interchange of health care data for claims, eligibility, enrollment and remittance Many, many more . – NCPDP – NUBC – NUCC – ADA DeCC – – – – CDISC IHE ASTM DICOM

NCHS Focus on Standards It is worthwhile to lay the foundation for standardizing the transmission of survey data as efforts towards developing and implementing EHRs continues

NCHS Standards for Population Health and Healthcare NCHS and its partner organizations have developed, implemented and maintained many of the critical standards used in population health and healthcare: o Standard certificates for vital events o International Classification of Diseases and its clinical modifications o Uniform data sets for hospital and ambulatory care These standards can contribute to and benefit from current deliberations on national standards

NCHS Participates in the HIT Standards Landscape C I H A C C NU C S D PH A D A CH I NUB HA CF ONC NC P X1 2 HI TS P HL DP NC S H V 7

Developing Standards for EHR Birth and Death Data Exchange with Vital Records Systems Birth Registration System (EBRS) Mother's Worksheet Registrar Mother Birth Information Specialist Birth Certificate Birth Event Nurse Physician Electronic Health Record CDC/NCHS State Department of Health
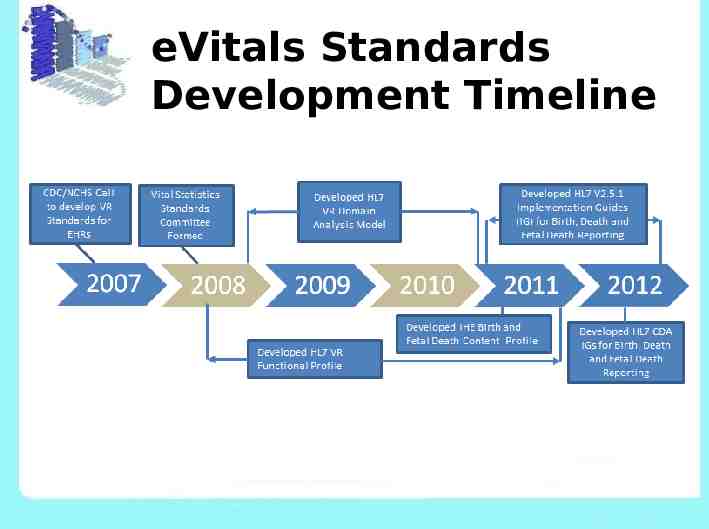
eVitals Standards Development Timeline

Defining Public Health Functional Requirements NCHS has provided support to develop an HL7 Public Health Functional Profile (PHFP) o Identifies functional requirements and conformance criteria for public health-clinical information collection, management and exchanges as they apply to the various public health programs o Based on EHR System Functional Model and Standard, Release 1.1 U.S. Realm o Developed through NCHS collaboration with the Public Health Data Standards Consortium (PHDSC) EHR-PH Task Force

NCHS Engaged in ONC S&I PHRI Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) – Standards and Interoperability (S&I) Framework Public Health Reporting Initiative (PHRI) o Community-led S&I Framework initiative o Focused on harmonizing information exchange standards and creating implementation specifications for PH reporting from healthcare providers to PH agencies to promote HIT adoption and facilitate electronic PH reporting from EHR systems o Includes NCHS User Stories for Division of Vital Statistics and Division of Health Care Statistics

Supporting Maintenance of the ASC X12 Health Care Service Data Reporting Guide (837R) NCHS provided support for development and maintenance of the X12 837R - Health Care Service Data Reporting Guide – Provides a standardized guide for developing and executing the electronic transfer of health care systems data for reporting purposes to local, State, and Federal agencies Evaluate how the ASC X12 837 Health Care Service Data Reporting Technical Report can be expanded to include specific requirements to meet the needs of the surveys
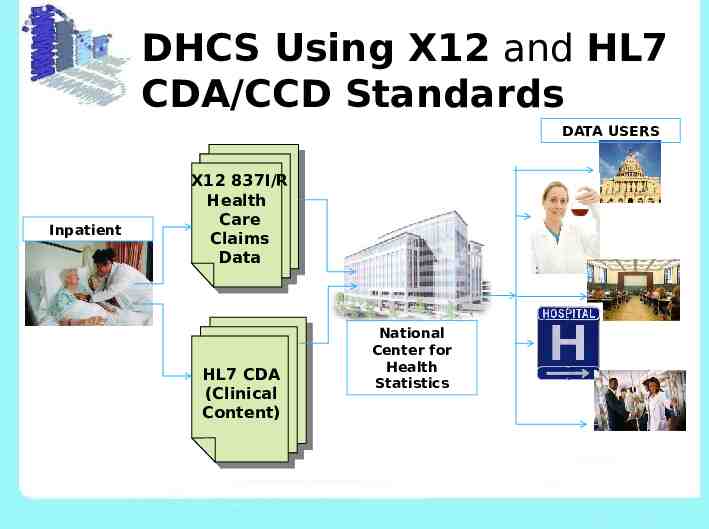
DHCS Using X12 and HL7 CDA/CCD Standards DATA USERS Inpatient X12 837I/R Health Care Claims Data HL7 CDA (Clinical Content) National Center for Health Statistics

SS-08 Electronic Health Records: How will they change the way we collect data? Michelle Williamson Brian Gugerty Harold Luft Supporting Standards Development for HIT/EHR Adoption Electronic Health Records “Sourcing” Data for NAMCS

Electronic Health Records Brian Gugerty, DNS, MS, RN EHR Consultant, GIC Informatics

Division of Healthcare Statistics Core Surveys – National Hospital Care Survey (NHCS) – Hospital Inpatient Discharges – National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS) » ED » OPD » Hospital ASL & Freestanding ASC – National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) – National Study of Long-Term Care Providers (NSLTCP) 1

Promise of Electronic Data More Better Cheaper Faster

Electronic Health Record Drivers ARRA – Meaningful Use Data/ Information for: – Competitive/ Market – Regulatory – Patient Safety – Research – Operations Improvement

Electronic Health Record Drivers Specific driver for Health Information Exchange – Meaningful Use Stage 2 criteria Transition of Care Summary – Eligible Hospitals and Eligible Providers Exchange summary of care for each episode of care 2014
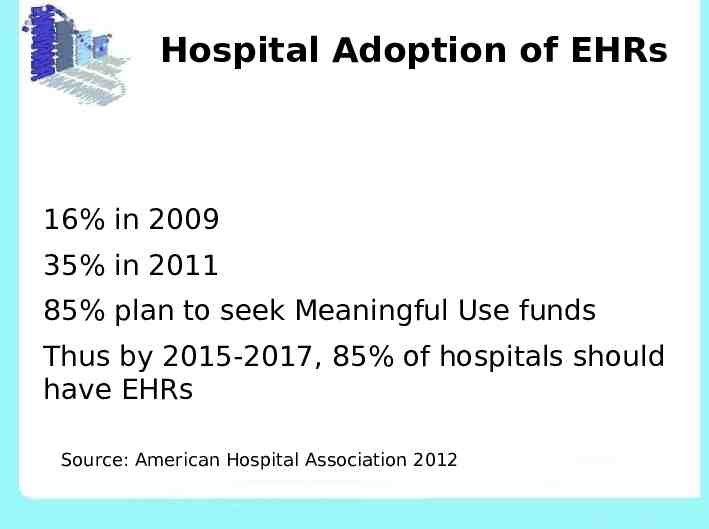
Hospital Adoption of EHRs 16% in 2009 35% in 2011 85% plan to seek Meaningful Use funds Thus by 2015-2017, 85% of hospitals should have EHRs Source: American Hospital Association 2012
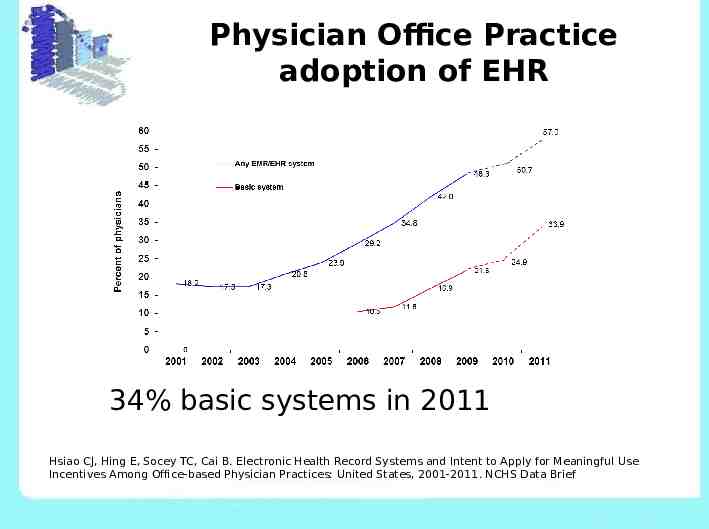
Physician Office Practice adoption of EHR 34% basic systems in 2011 Hsiao CJ, Hing E, Socey TC, Cai B. Electronic Health Record Systems and Intent to Apply for Meaningful Use Incentives Among Office-based Physician Practices: United States, 2001-2011. NCHS Data Brief
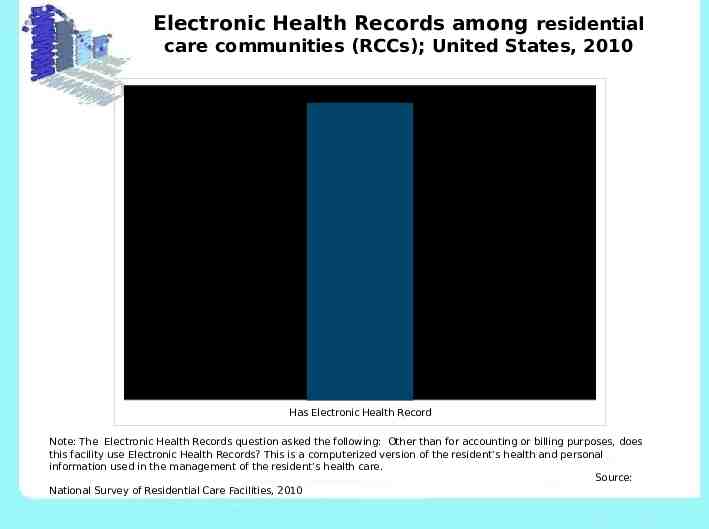
Electronic Health Records among residential care communities (RCCs); United States, 2010 17% Has Electronic Health Record Note: The Electronic Health Records question asked the following: Other than for accounting or billing purposes, does this facility use Electronic Health Records? This is a computerized version of the resident’s health and personal information used in the management of the resident’s health care. Source: National Survey of Residential Care Facilities, 2010
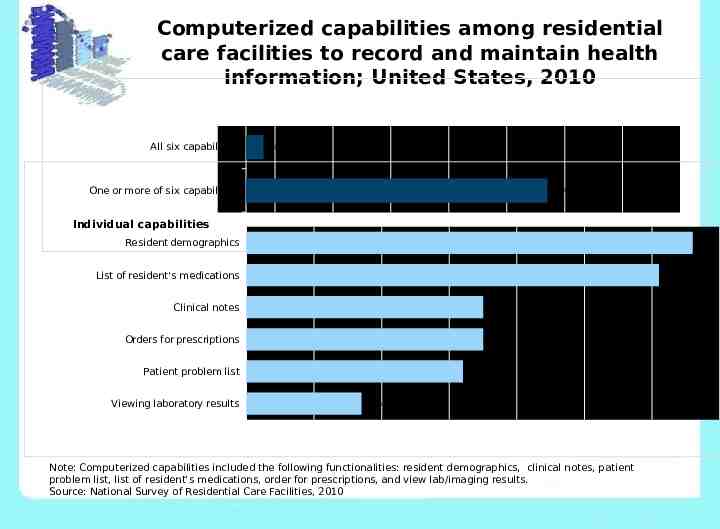
Computerized capabilities among residential care facilities to record and maintain health information; United States, 2010 -5% All six capabilities 5% Series 15% 25%1 35% 45% 55% 65% 75% 3% One or more of six capabilities 52% Individual capabilities Resident demographics 66% List of resident's medications 61% Clinical notes 35% Orders for prescriptions 35% Patient problem list Viewing laboratory results 32% 17% Note: Computerized capabilities included the following functionalities: resident demographics, clinical notes, patient problem list, list of resident’s medications, order for prescriptions, and view lab/imaging results. Source: National Survey of Residential Care Facilities, 2010

EHR Readiness for Research Data Sourcing EHRs not ready to exchange data yet By 2015 – 85% hospitals likely ready to exchange – Likely a similar though somewhat smaller % of medical practices – Not enough data to predict LTC trend

Division of Health Care Statistics Position Gain experience with electronic submission and receipt of standardized administrative & EHR data so that when its truly available we’ll be ready
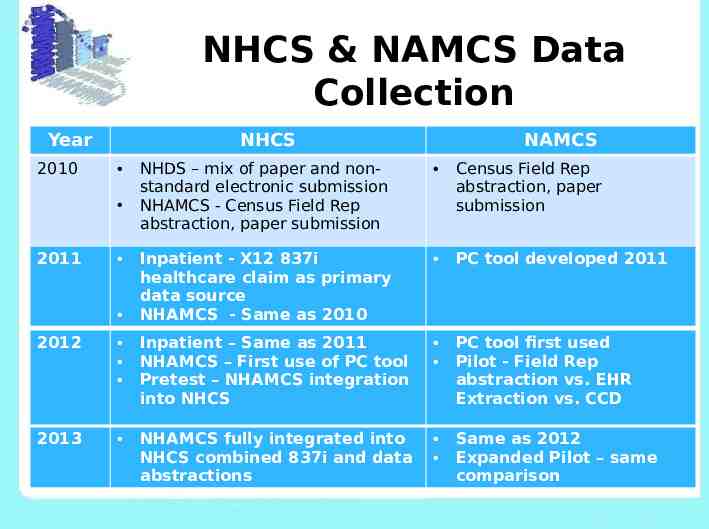
NHCS & NAMCS Data Collection Year 2010 NHCS 2011 NAMCS NHDS – mix of paper and nonstandard electronic submission NHAMCS - Census Field Rep abstraction, paper submission Census Field Rep abstraction, paper submission Inpatient - X12 837i healthcare claim as primary data source NHAMCS - Same as 2010 PC tool developed 2011 2012 Inpatient – Same as 2011 NHAMCS – First use of PC tool Pretest – NHAMCS integration into NHCS PC tool first used Pilot - Field Rep abstraction vs. EHR Extraction vs. CCD 2013 NHAMCS fully integrated into NHCS combined 837i and data abstractions Same as 2012 Expanded Pilot – same comparison
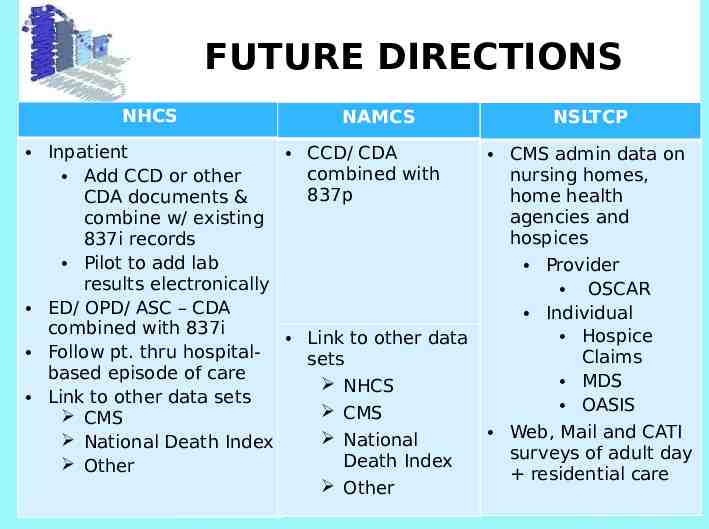
FUTURE DIRECTIONS NHCS NAMCS Inpatient CCD/ CDA combined with Add CCD or other 837p CDA documents & combine w/ existing 837i records Pilot to add lab results electronically ED/ OPD/ ASC – CDA combined with 837i Link to other data Follow pt. thru hospitalsets based episode of care NHCS Link to other data sets CMS CMS National National Death Index Death Index Other Other NSLTCP CMS admin data on nursing homes, home health agencies and hospices Provider OSCAR Individual Hospice Claims MDS OASIS Web, Mail and CATI surveys of adult day residential care

Data collection method and approach to data editing Paper and pencil surveys – Extensive manual and computer assisted editing after collection Computer assisted data collection – Allows for built-in data editing through real time validity and range checks. Electronic data (claims and EHR derived) – Volume of data requires computerized editing with minimal hands-on corrections – Reliant on internal data quality 12
Analytic considerations with electronic data Electronic data (claims and EHR derived) – Data sets, values and formats designed for a purpose other than research -which may create bias Data based on billing information may reflect diagnoses which receive higher reimbursement Data based on billing information may not include variables not relevant for billing – e.g. demographic variables – Greater number of records allows analysis of rare conditions/situations and by multiple variables

SS-08 Electronic Health Records: How will they change the way we collect data? Michelle Williamson Brian Gugerty Harold Luft Supporting Standards Development for HIT/EHR Adoption Electronic Health Records “Sourcing” Data for NAMCS






