SQA
25 Slides340.00 KB

SQA

What is "Quality"? "Quality of Design" and "Quality of Conformance" -- Roger Pressman User Satisfaction compliant product good quality delivery within budget and schedule -- Robert Glass

Standard Definition Software Quality - Conformance to: 1. 2. 3. explicitly stated functional and performance requirements, explicitly documented development standards, and implicit characteristics that are expected of all professionally developed software.

SQA Components 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pre-Project Components Development and Maintenance Activities Error Reduction Infrastructure SQ Management Components SQA System Assessment Human Components Software Quality Assurance by Galin

1. Pre-Project Components Contract Review Development and Quality Plans Development schedules manpower requirements tools Quality Plans Plans measurable quality goals success criteria for each project phase scheduled V&V activities

Obvious Question Q: Why should the software geeks worry about the contract? A: Because the software team must do the work and assure the product's quality. loosely defined requirements unrealistic budgets unrealistic schedules A: Contract review is required by ISO 9001

IEEE 730 - Standard for SQA Plans Plan Sections 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Purpose Reference Documents Management Documentation Standards, Practices, and Conventions Reviews and Audits Software Configuration Management Problem Reporting and Corrective Action Tools Techniques and Methodologies Code Control Media Control Supplier Control Records Collection, Maintenance, and Retention

2. Life Cycle Components Software Testing Reviews varying levels of formality specs, designs, code modules, documents, etc Maintenance corrective adaptive functional

Formal Technical Reviews FTRs are the primary quality control activity. Justification to err is human other people are better at finding our faults than we are good way for other people to learn details about another part of the project

FTR Guidelines 3 to 5 people includes the producer, review leader, recorder no more than two hours preparation small portions only narrow focus increases likelihood of find an error meeting duration less than two hours outcome: accept, accept pending changes, reject report is signed and saved

FTR Guidelines Review the Product, not the person! Set an agenda and keep it. Limit debate and rebuttal. Find errors, don't try to solve them. Take written notes. Limit number of participants and have advance preparation. Allocate resources and schedule time for FTRs. Conduct training for reviewers. Review your earlier reviews.

3. Error Prevention and Improvement Infrastructure Next Slide work procedures see link to NASA templates and checklists staff training preventive actions configuration control Last Class document control

Example types of Work Instructions audit process for subcontractors design documentation templates C programming instructions coordination and cooperation with the customer follow-up of beta site reporting monthly progress reporting Galin: page 316

4. Management Components Project Progress schedules, budgets, risk analysis, Quality Metrics Quality Costs

Statistical SQA 1. Info about defects are collected and categorized. 2. Defects are traced to their root cause. 3. Isolate the vital 20% 4. Move to correct problems that caused defects. SSQA is similar to "Six Sigma" Pareto Principle: 80% of defects can be traced to 20% of causes.

5. SQA Assessment Quality Management Standards SEI CMM ISO 9001 Details o'plenty Next Week

SEI CMM Levels 1. Initial 2. Repeatable 3. process in documented and standardized Managed 5. tracks costs, has a schedule similar projects can repeat earlier successes Defined 4. ad hoc, perhaps chaotic detailed process and product measurements Optimizing continuous process improvement

ISO Standards for Quality ISO 9000 : Quality Management and Quality Assurance Standards - Guidelines for selection and use ISO 9001 : Quality Systems - Model for quality assurance in design/development, installation, and servicing ISO 9000-3 : Guidelines to applying 9001 to software

ISO 9000 ISO 9000 seeks to set criteria which achieve a goal and is not prescriptive as to methods. The requirements come in Sections 4 to 8. Section 4 is entitled General Requirements Section 5 is entitled Management Responsibility Section 6 is entitled Resource Management Section 7 is entitled Product Realization Section 8 is entitled Measurement, analysis and improvement In each of these areas, ISO 9001: 2000 seeks to set out key requirements, which if met will ensure quality. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO 9000

Other Quality-Related Standards ANSI/IEEE 730 - Standard for Software Quality Assurance Plans ANSI/IEEE 983 - Software Quality Assurance Planning ANSI/IEEE 1028 - Standard for Software Reviews and Audits ANSI/IEEE 1012 - Standard for Software Verification and Validation

6. Human Components Management SQA Unit SQA committees and forums

The SQA Group Participates in the development of the project's software process description. Reviews software engineering activities to verify compliance with the defined process. Audits designated software work products to verify compliance with those defined as part of the software process. Ensures that deviations in software work and work products are documented and handled according to a documented procedure. Records any noncompliance and reports to senior management. Coordinates and controls change. Helps collect and analyze metrics.
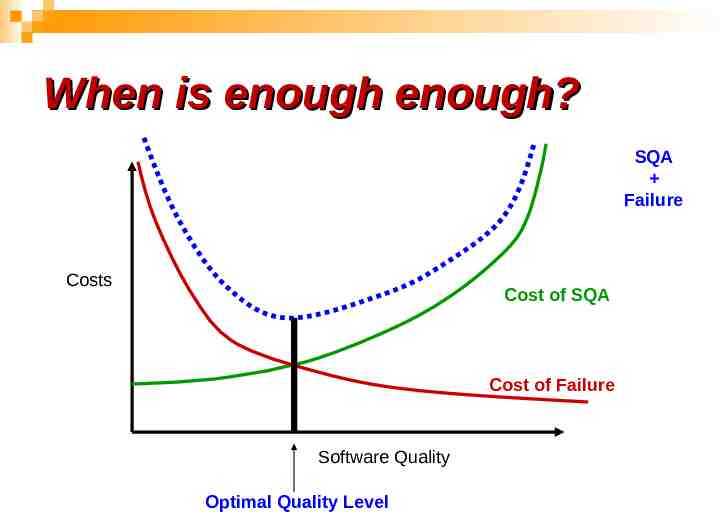
When is enough enough? SQA Failure Costs Cost of SQA Cost of Failure Software Quality Optimal Quality Level

Summary "Quality" includes explicit and implied properties as well as the development process. FTRs are a key part of SQA. An SQA Group is highly recommended. QA must be part of the plan and schedule. SSQA is a commonly used formal approach to quality assurance and process improvement.

Next Time SEI CMM ISO 9001






