Social Media: It has changed how the world works from the media to
24 Slides6.07 MB

Social Media: It has changed how the world works from the media to learning to recruitment Have you made the change? Jonathan Burns 2014 Kentucky NAEP Fall Meeting September 28-30, 2014

About Jonathan 5 years at University of Kentucky University Budget Office – Budget Director Associate College of Pharmacy – Director of Non-Grant Accounting, Payroll Sponsored Projects Administration – Accounting Supervisor Senior 6 years in the banking/finance industry Best Buy computer sales/tech bench during undergrad Bachelor of Business Administration / Management from UK Master of Business Administration from MSU Researched social media in business Emphasis in health care

Presentation Agenda What is Social Media? 1 2 Types and Uses of Social Media Pro’s and Con’s of Social Media 3 Laws of Social Media 4 5 Suggestions for Organizations and Social Med 6 Questions?

Activity Who can name what social media brand these icons represent?

What is Social Media? A few statistics: Facebook has approximately 1 billion monthly users (Oaks) Twitter manages a quarter billion monthly users (Oaks) Up to 114 billion minutes per month are spent on social media (Oaks) Just in the United States alone (Oaks) The 55-64 age bracket is the most rapidly increasing demographic on Twitter (Digital Imperia) Two new users join LinkedIn every second (Richards) YouTube is more popular than TV among US adults of age 18-34 (Digital Imperia) Nearly 12 years of continuous footage is loaded on to YouTube daily (Richards) If social media sites were countries: China, Facebook, Google , Twitter, India, US (Richards)

What is Social Media? Definitions: Dictionary.com – “websites and other online means of communication that are used by large groups of people to share information and to develop social and professional contacts.” It “gives you the ability to check perception. You’re not speaking at people anymore – you are speaking with them.” (Parker) Many see public relations (PR) and social media as the same. This is not the case: “PR is about positioning, and social media is about becoming, being, and improving.” (Parker) “A social media site is a platform that allows user-generated content to emerge through interactions and collaborations in a virtual community.” (Smith and Harwood)
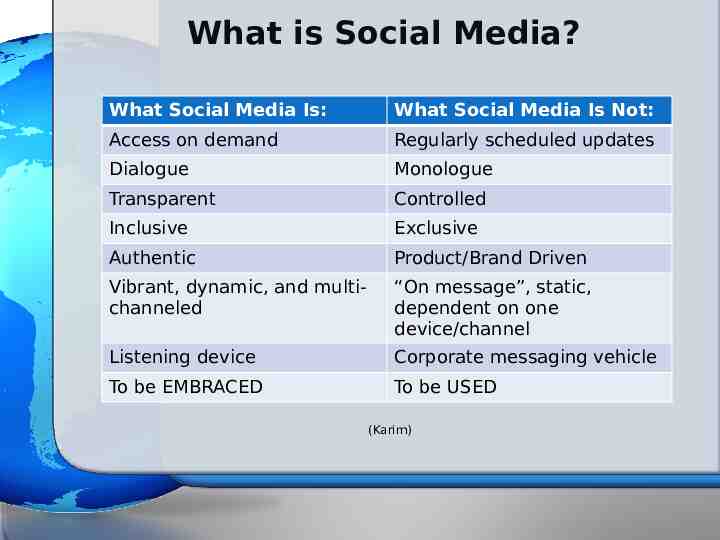
What is Social Media? What Social Media Is: What Social Media Is Not: Access on demand Regularly scheduled updates Dialogue Monologue Transparent Controlled Inclusive Exclusive Authentic Product/Brand Driven Vibrant, dynamic, and multichanneled “On message”, static, dependent on one device/channel Listening device Corporate messaging vehicle To be EMBRACED To be USED (Karim)
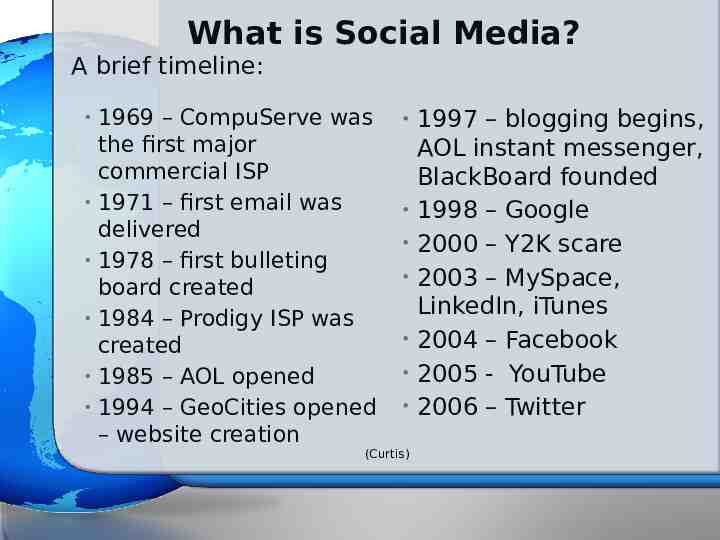
What is Social Media? A brief timeline: 1969 – CompuServe was the first major commercial ISP 1971 – first email was delivered 1978 – first bulleting board created 1984 – Prodigy ISP was created 1985 – AOL opened 1994 – GeoCities opened – website creation (Curtis) 1997 – blogging begins, AOL instant messenger, BlackBoard founded 1998 – Google 2000 – Y2K scare 2003 – MySpace, LinkedIn, iTunes 2004 – Facebook 2005 - YouTube 2006 – Twitter

Types and Uses of Social Media The world before social media: (Dunn)

Types and Uses of Social Media Social Networks – Facebook, Google , LinkedIn Microblogging – Twitter, Tumblr Allows users to share their favorite content with others (McIntosh) Media Sharing – YouTube, Instagram, Flickr Author can write (blog) about any interest. Others can read, search, comment (McIntosh) Social Bookmarking – Reddit, Pinterest, Digg Focus on short updates that are pushed out to anyone subscribed to receive updates (Grahl) Blogs – Blogger, WordPress Allow the user to connect with other people of similar interests and/or backgrounds (Grahl) Allows users to upload and share media (video, pictures, etc.) (Grahl) Wikis – Wikipedia Content created as a result of multiple users working on the same content (McIntosh)
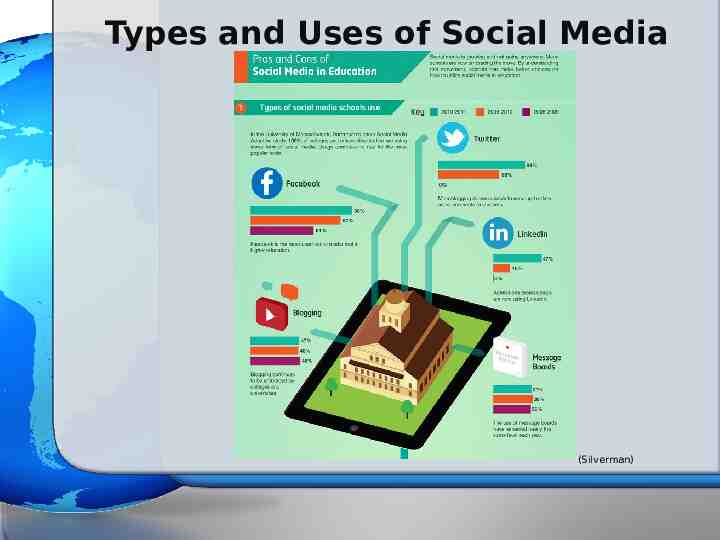
Types and Uses of Social Media (Silverman)
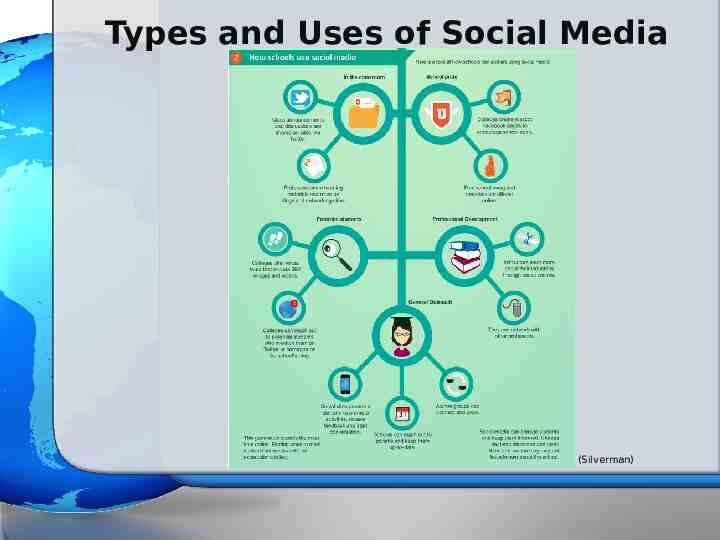
Types and Uses of Social Media (Silverman)

Types and Uses of Social Media (Silverman)

Pro’s and Con’s of Social Media The use of social media can both benefit and hurt an organization Most organizations focus on what not to do. Rather, the focus should be on getting involved (Karim) Employees are often an organization’s most valuable assets. By enabling employees to use social media, the organization can take advantage of that key asset (Karim) “Companies resist social media engagement for the same reason people resist authentic, loving relationships – a fear of intimacy.” (Karim) Communication will improve both inside and outside the organization There is, however, the ability for social media to negatively affect the organization

Laws of Social Media When things are going good, there are positive results. What about when they aren’t? Only one organization has consistently spoken out about social media in the workplace, the NLRB The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) has taken the lead among government agencies in addressing employer social media policies and discipline against employees for social media use (Mayer Brown) The NLRB has looked at many cases and ruled fairly consistent on them Their rulings aim to protect concerted activity (Mayer Brown) The National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) states that it “guarantees employees not only the right to form, join, or assist labor organizations, but also the right to engage in other concerted activities for the purpose of collective bargaining or other mutual aid protection.” (Mayer Brown)

Laws of Social Media Case Studies: 1. American Medical Response of Connecticut – had a social media policy that barred employees from depicting the company “in any way” on Facebook or other social media sites (Greenhouse) 2. This policy was challenged. What was the outcome? The NLRB ruled that the policy was too restrictive and “overly broad” and it improperly limited the employees’ rights to discuss working conditions among themselves (Greenhouse) Wal-Mart – employee was fired for complaining about work on Facebook (Walker) Employee challenged the disciplinary action. What was the outcome? The NLRB sided with Wal-Mart and upheld the disciplinary action (Walker)

Laws of Social Media Case Studies: (cont’d) What was the difference in the two cases? Concerted Activity The NLRB says that social media should be available to be used for concerted activity and will be protected for that reason (Walker) In other words, if an employee is discussing with other employees about work conditions, etc., they should be protected. If just complaining about work and not working with others for a change, they should not be protected (Walker)

Suggestions for Organizations and Social Media Some sources suggest not doing anything and just let it run its course Other sources suggest to completely block all employees from using social media I suggest that there should be a policy in place that allows employees to act freely on social media, but not enough to greatly hurt an organization “The reality is that your employees will participate in social media, and it’s very difficult to control what they say.” (Seiple) “Happy employees equal positive PR.” (Seiple) “Customers are already talking about you and your products in the virtual arena. The question is whether you are contributing to the conversation.” (Munro and Ciobo)

Suggestions for Organizations and Social Media Understand how social media fits into and can enhance your overall organizational strategy (Karim) Learn what the tools are and how to use them and then develop a specific strategy (Karim) Expect mistakes and failures, they help you grow (Karim) Emphasize what employees can do rather than the ‘thou shalt nots’ (Parker) It is recommended that employees sign their understanding of the social media policy (Parker) Reach is key. Every employee has their own social reach; empowering employees can extend the reach of the organization (Seiple)

Suggestions for Organizations and Social Media (Parekh)

Suggestions for Organizations and Social Media Three reasons why procurement professionals should embrace social media: 1. 2. 3. It is free. Procurement people can reach out and collaborate with millions of people, and connect with the “right” people (Ashcroft) It is who you know, not what you know. Twitter has search mechanisms that makes it easy to locate people who may help you, and trust, with procurement challenges (Ashcroft) Everything happens in real time. Stories, news, research and ideas are shared and built up, which is ideal for procurement people (Ashcroft)

Questions Jonathan Burns @JBurnsMBA (Twitter) www.linkedin.com/pub/jonathan-burns-mba/34/259/56a/
References Ashcroft, Stephen. “Three Reasons Why Procurement Professionals Should Embrace Social Media.” 25 November 2013. Web. 26 August 2014. http://www.supplymanagement.com/blog/2013/11/three-reasons-why-procurement-professionals-should-embracesocial-media Curtis, Anthony. “The Brief History of Social Media.” 2013. Web. 26 August 2014. http://www2.uncp.edu/home/acurtis/NewMedia/SocialMedia/SocialMediaHistory.html Digital Imperia. “5 Social Media Statistics to Make You Astounded.” 23 November 2013. Web. 15 September 2014. http://www.digitalimperia.com/social-media/5-social-media-statistics-to-make-you-astounded.html Dunn, Jeff. “How the World Worked Before Social Media.” 21 May 2014. Web. 26 August 2014. http://www.edudemic.com/before-social-media/ Grahl, Tim. “The 6 Types of Social Media.” 2014. Web. 26 August 2014. http://outthinkgroup.com/tips/the-6-types-of-socialmedia Greenhouse, Steven. "Company Accused of Firing Over Facebook Post." The New York Times Breaking News, World News & Multimedia. 08 Nov. 2010. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/09/business/09facebook.html. Karim, Muhammad. "Personal Branding and Enhancing Employee Relations with Social Media." 2010. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://www.slideshare.net/mkarim/personal-branding-and-enhancing-employee-relations-with-social-media. Mayer Brown. "National Labor Relations Board Focusing On Employee Use of Social Media." 29 Sept. 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://www.mayerbrown.com/publications/article.asp?id 11621. McIntosh, Kevin. "Different Types of Social Media." 14 Apr. 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://kevinmcintosh.com/social-media-marketing/different-types-of-social-media/. Munro, Peter and Ciobo, Marco. “Social Media: Are You Part of This Conversation?” 2012. Web. 26 August 2014. http://www.atkearney.com/paper/-/asset publisher/dVxv4Hz2h8bS/content/social -media-are-you-part-of-thisconversation/10192
References Oaks, Jessica. “How Social Media has Changed Us.” 20 December 2013. Web. 26 August 2014. http://www.socialnomics.net/2013/12/20/how-social-media-has-changed-us/ Parekh, Rajul. “3 Tips for Businesses Building Their Social Media Presence.” 30 December 2013. Web. 17 September 2014. http://blog.getcourse.com/3-tips-for-businesses-building-their-social-media-presence Parker, Rachel. "Social Media for Recruiting and Employee Relations." 11 May 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://www.slideshare.net/resonancesocial/social-media-for-recruiting-and-employee-relations-7943292. Richards, Madeleine. “12 Astounding Social Media Stats.” 26 June 2014. Web. 15 September 2014. http://blog.marginmedia.com.au/Our-Blog/bid/102003/12-astounding-social-media-stats Seiple, Pamela. How to Leverage Social Media for Public Relations Success: Using Social Media to Generate Media Coverage and Improve Brand Sentiment. http://www.hubspot.com/Portals/53/docs/hubspot social media pr ebook.pdf. Silverman, Matt. “How Higher Education Uses Social Media.” 03 February 2012. Web. 26 August 2014. http://mashable.com/2012/02/03/higher-education-social-media/ Smith, Stuart and Harwood, Peter. "Social Media and Its Impact on Employers and Trade Unions." Sept. 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. Social media and its impact on employers and trade unions. Walker, Lindsay. "Can We Fire Employees for Social Media Comments? 03 Aug. 2011. Web. 14 Nov. 2011. http://i-sight.com/employee-relations/employees-fired-for-social-media-comments/.






