Smart Grid & Microgrid R&D Steve Bossart Senior Energy Analyst U.S.
28 Slides1.27 MB

Smart Grid & Microgrid R&D Steve Bossart Senior Energy Analyst U.S. Department of Energy National Energy Technology Laboratory Military Smart Grids & Microgrids Conference May 1-2, 2012

Smart Grid & Microgrid R&D Topics Vision and goals Background Research needs – – – – – – 2 Standards and best practices Technology development Modeling Analysis Evaluation and demonstration Microgrid

Vision and Goals 3

DOE OE Mission Mission of Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability Lead national efforts to modernize the electric grid; Enhance security and reliability of the infrastructure; and Facilitate recovery from disruptions to energy supply Accelerate the deployment and integration of advanced communication, control, and information technologies that are needed to modernize the nation‘s electric delivery network 4

Grid Modernization Goals 5

Background 6

Smart Grid & Microgrid R&D Sources 7

Smart Grid R&D Multi-Year Program Plan 2010-2014 Originally published in 2010 Smart Grid Roundtable Meeting in December, 2009 Multiple stakeholders R&D Groups September 2011 update 8

Criteria for DOE Smart Grid R&D Plan Hindered by lack of standards or conflict with standards Not being addressed by industry or Federal R&D Longer-term, high-risk Transformative, high-payoff Feasible within likely Federal budget Long-term, high-risk R&D in high-impact technologies 9
DOE Planning Process for Microgrid R&D Assembled planning committee with national lab representatives (LBNL, NREL, ORNL, SNL) Formulated microgrid technical performance and cost targets Identified key microgrid components that could benefit from additional R&D Conducted preliminary analysis to determine the baseline and potential research areas 10
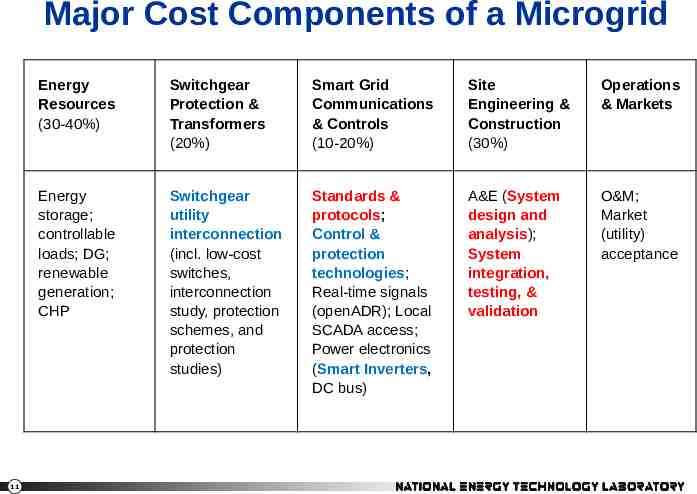
Major Cost Components of a Microgrid 11 Energy Resources (30-40%) Switchgear Protection & Transformers (20%) Smart Grid Communications & Controls (10-20%) Site Engineering & Construction (30%) Operations & Markets Energy storage; controllable loads; DG; renewable generation; CHP Switchgear utility interconnection (incl. low-cost switches, interconnection study, protection schemes, and protection studies) Standards & protocols; Control & protection technologies; Real-time signals (openADR); Local SCADA access; Power electronics (Smart Inverters, DC bus) A&E (System design and analysis); System integration, testing, & validation O&M; Market (utility) acceptance

Development of Microgrid R&D Needs Stakeholder Engagement Convened a Workshop to further define: Baseline performance Areas of research needs End goals (technical/cost targets and their significance) Actionable plan to reach the targets (scope, schedule, participants, milestones) Workshop Details August 30-31, 2011 University of CA, San Diego 73 participants Vendors, electric utilities, national labs, universities, research institutes, end users (including military bases, municipalities, and data centers), and consultants 12

Smart Grid R&D Needs 13

R&D Topics Standards & Best Practices Technology Development Modeling Analysis Evaluation & Demonstrations 14

Standards & Best Practices Developing, maintaining, and harmonizing national and international standards – Interconnection, interoperability, integration, and cyber security Legacy and advanced distribution system protection, operations and automation Defining reliability and ancillary service requirements Define roles of load serving entities, EMS, aggregators, and ISO/RTOs in market Developing best practices to manage PEV charging including “roaming” locations 15

Standards and Best Practices Some Technical Tasks Interoperability and Interconnection – Develop use cases to identify requirements – Develop exploratory and conformance test procedures – Develop schemes for protection, operation, and automation Cyber Security – Identify security requirements for all assets – Develop a security architecture – Develop and validate methods for cyber secure operation Market and Reliability – Describe operating models for power system and market – Develop clearly defined functional roles for entities 16
Technology Development Sensing & measurement – Weather, equipment health, customer devices, Communications and security – Wireless, power line carrier, internet, Advanced components – Power electronics, intelligent loads, V2G, G2V, e-storage. Control methods – Distributed control, DA, mixed AC/DC, adaptive protection Decision and operations support – Visualization, diagnostic & operations, data processing 17

Technology Development “Integration” Integration of DER and DR to reduce peak load and improve efficiency Smart charging PEVs Microgrid Communications and controls Smart inverters for renewables 18 EPRI

Modeling 19
Modeling Modeling, simulation, and visualization Planning, design and operations Behavior, performance, and cost of smart grid assets Impact on generation and T&D operations 20
Modeling Create public library of smart grid software (components, controls) Establish benchmark test cases to validate models and software tools Develop fast computational algorithms and parallel computing capabilities Develop capability to model impact of smart grid on entire grid Develop dynamic response models Continuous update of distribution system Link distributed engineering, work order, outage management, and automated mapping models Integrate communications, markets, and renewable resource models Open standards to describe distribution, smart grid, and consumer assets 21

Analysis 22
Analysis Progress and impact of smart grid investments Support effective cyber security, privacy, and interoperability practices Impact on outage number, duration & extent Impact on power quality and reliability Impact on power system planning Impact of T&D automation on variable renewable integration Potential capacity from DR, DG, and e-storage Consumer studies on acceptance of DR, PEV, storage, energy efficiency, & local generation Evaluate benefits and cost Business case 23

Evaluation and Demonstration 24

Evaluation and Demonstration Gaps in smart grid functionality Gaps in technology performance Protocols in evaluating new components Performance and conformance with emerging standards 25

Microgrid R&D 26
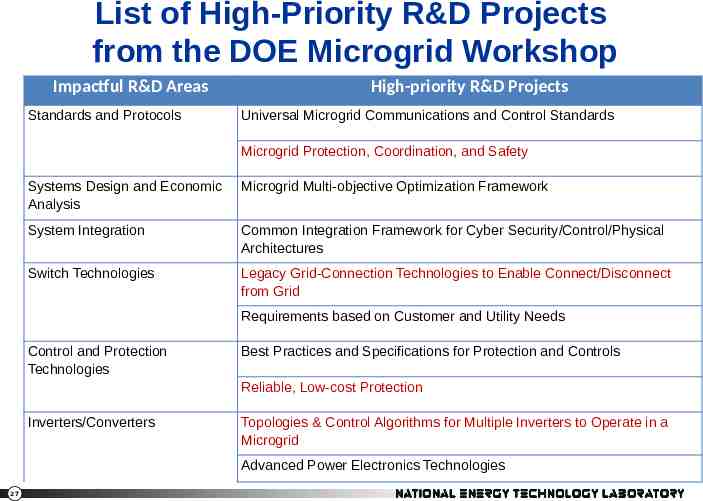
List of High-Priority R&D Projects from the DOE Microgrid Workshop Impactful R&D Areas Standards and Protocols High-priority R&D Projects Universal Microgrid Communications and Control Standards Microgrid Protection, Coordination, and Safety Systems Design and Economic Analysis Microgrid Multi-objective Optimization Framework System Integration Common Integration Framework for Cyber Security/Control/Physical Architectures Switch Technologies Legacy Grid-Connection Technologies to Enable Connect/Disconnect from Grid Requirements based on Customer and Utility Needs Control and Protection Technologies Best Practices and Specifications for Protection and Controls Reliable, Low-cost Protection Inverters/Converters Topologies & Control Algorithms for Multiple Inverters to Operate in a Microgrid Advanced Power Electronics Technologies 27

Contact Information Steve Bossart (304) 285-4643 [email protected] Smart Grid Implementation Strategy www.netl.doe.gov/smartgrid/index.html Federal Smart Grid Website www.smartgrid.gov Smart Grid Clearinghouse www.sgiclearinghouse.org/ 28