Role of a Professional in Governance: Focus on Quality B through
54 Slides3.57 MB

Role of a Professional in Governance: Focus on Quality B through STRATEGIC PLANNING

What is Quality? Conformity to Standards? Working within tolerance? Excellence in work? Innovation at work? Adherence to rules ?

Quality is a service or the product which satisfies needs of the stakeholders and sometimes exceeds his expectations

LESSON 1 INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION TO TO STRATEGIC STRATEGIC PLANNING PLANNING Slide # 4

INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION TO TO STRATEGIC STRATEGIC PLANNING PLANNING Objectives: On completion of this lesson the learner will be able to Slide # 5 1. Define Strategic Planning 2. Distinguish between Long Range Planning and Strategic Planning 3. List the reasons for carrying out Strategic Planning 4. List the alternatives of Strategic Planning 5. State when Strategic Planning should be done 6. Identify who should do Strategic Planning

1. What is SP? DEFINITION DEFINITION OF OF STRATEGIC STRATEGIC PLANNING PLANNING Strategic Planning is a future orientated process wherein an organisation specifies what it wishes to become and how it proposes to get there. Slide # 6

Where are we now? Parameter % Graduated % Employed Revenue Generated Industry Partnerships Awards Received Slide # 7 Now

Where do we want to be in the Future? Parameter % Graduated % Employed Revenue Generated Industry Partnerships Awards Received Slide # 8 Future

How do we get there? Where we are STRATEGIES now Parameter % Graduated % Employed Revenue Generated Industry Partnerships Awards Received Slide # 9 Now Where we want to be in the Future Future

DEFINITION DEFINITION OF OF STRATEGY STRATEGY Strategy is a way of using the organisation’s internal resources to respond to its external environment in order to be successful. How do you measure success? Achievement of goals / objectives / targets within the specified time Slide # 10

INDICATORS OF INSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENT Inputs: Quantum of inputs (funds etc) received Diversity of stakeholders and their commitment Processes: Curriculum Development Industry Institute Partnership Teaching – Learning Evaluation of Students’ performance Modernisation and Maintenance of Facilities Student Services Slide # 11 Contd

Extension Services Campus Environment Management Information System Human Resource Management Financial Management Products: Slide # 12 Passouts and their track record of Job placement Publications of the institute, its staff and students Research and Development Projects completed Patents obtained / Awards received

STAKEHOLDER Any person, group, organisation that can place a claim on the institute’s attention / resources / output. OR is affected by the output. Who are the Stakeholders of your Polytechnic / Engineering College? Slide # 13

STAKEHOLDERS DTE Principal Professors / H. of Depts. Teachers & Support Staff Students (& their Families) Employers & Community at large What are their wants and needs? Slide # 14

External Environment Organisation’s Internal Environment Slide # 15

CHANGES IN THE EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT 1. Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation of Indian economy. 2. Impact of developments in Information and Communication technologies. 3. Concern for quality and relevance of educational programmes. 4. Decreasing funding support from Government for technical education. 5. Increasing number of commercial / private training organisations. 6. Increasing importance assigned to: Environment (Preservation of nature – Pollution Control) Development of women Development of poor Slide # 16

WHY STRATEGIC PLANNING? 1. To proactively anticipate change (external forces / trends), measure the impact and respond effectively with new systems and revised product offerings. 2. To follow a Bottom-Up Model and ensure the participation of all Stakeholders in the planning process. 3. To enable an organisation to optimally utilize its resources and maximize performance. 4. To continually adapt to reality. Slide # 17

TWO MODELS OF PLANNING Top – Down Model Bottom – Up Model Slide # 18

POWER AND IMPORTANCE Importance Essential to the daily functioning of the organisation Power Ability to cause change Slide # 19

TOP – DOWN MODEL DTE Power decreases and Importance increases Principal Professors / H. of Depts Teachers & Support Staff Students Employers & Community Slide # 20 Internal Focus

BOTTOM – UP MODEL D.T.E Principal Professors & H. of Depts. Teachers & Supporting Staff Students External Focus Slide # 21 Employers and Community

Aligning the People in the organisation Slide # 22

A MISALIGNED ORGANISATION WITHOUT A STRATEGIC PLAN Environment organisation Slide # 23

AN ORGANISATION WITH A STRATEGIC PLAN BUT DOES NOT HAVE ITS MEMBERS ALIGNED WITH THE PLAN Environment Slide # 24

AN STRATEGIC AN ORGANISATION ORGANISATION WITH WITH A A STRATEGIC PLAN PLAN AND AND ITS ITS MEMBERS MEMBERS ALIGNED ALIGNED WITH WITH THE THE PLAN PLAN Environment Slide # 25

LESSON 2 STEPS STEPS IN IN STRATEGIC STRATEGIC PLANNING PLANNING Slide # 26

STEPS STEPS IN IN STRATEGIC STRATEGIC PLANNING PLANNING Objectives: On completion of this lesson the learner will be able to Slide # 27 1. List the eight steps involved in the strategic planning process. 2. Describe the activities to be performed in each of the eight steps.

1. Initiate Strategic Planning Process 8. Clarify Vision 2. Clarify Mandate and Mission 7. Develop Work plan and Action plans 3. Conduct SWOT analysis 6. Formulate Projects 4. Identify Thrust areas 5. Formulate Goals Figure 1: A Model of the Strategic Planning Cycle Slide # 28

STEPS IN THE STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS Key Key Stakeholders Stakeholders 1. 1. Initiate Initiate SP SP Process Process 2. 2. Clarify Clarify Mandate Mandate and and Mission Mission 3. 3. SWOT SWOT Analysis Analysis 4. 4. Thrust Thrust Areas Areas (( Prioritised) Prioritised) Thrust Thrust Areas Areas 5. 5. Formulate Formulate Goals Goals 6. 6. Formulate Formulate Projects Projects 7. 7. Work Work Plan Plan // Action Action Plan Plan S. S.Plan Plan Slide # 29

STEPS IN THE STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS Key Key Stakeholders Stakeholders 1. 1. Initiate Initiate SP SP Process Process 2. 2. Clarify Clarify Mandate Mandate and and Mission Mission 3. 3. SWOT SWOT Analysis Analysis 4. 4. Thrust Thrust Areas Areas (( Prioritised) Prioritised) Thrust Thrust Areas Areas 5. 5. Formulate Formulate Goals Goals 6. 6. Formulate Formulate Projects Projects 7. 7. Work Work Plan Plan // Action Action Plan Plan S. S.Plan Plan Slide # 30

STEP 2. CLARIFY ORGANISATIONAL MANDATE Definition: A description of what an organisation must do and is permitted to do by the legitimate higher authority Mandate Slide # 31

STEP 2. DEVELOP A MISSION STATEMENT Mission Statement highlights what the organisation wishes to do and become, within and beyond its Mandate. Mandate Mission Slide # 32

DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANDATE AND MISSION ASPECT COMPARED MANDATE MISSION Source Given by the authorities Developed by the people who established the who work in the organisation (specified organisation. from outside) Focus What the organisation must do? Slide # 33 What the organisation wishes to do within and beyond its mandate

Mission Mission Elements Elements Refers to what the organisation wishes to do and become, within and beyond its mandate. 1. Organisational Purpose Why it exists External Focus 2. Stakeholders Identify stakeholder expectations 3. Goals What the organisation aspires to become within a specified period 4. Core Values Beliefs about what is desirable and makes us distinctive and unique Slide # 34

VALUES VALUES Values are basic convictions about what is right or wrong, good or bad, desirable or undesirable. Core values Most important values of the institute Examples: Slide # 35 Equity Quality Innovation Staff development Environment development

Global Factors / Trends / Forces GENERAL ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political Shifting Student/Employer Needs, Competitors, Collaborators External Environment Technical Institution Suppliers Plannin g Systems Processes Leadership Performance People Internal Environment RESOURCES Capital Technological Human Property Products Industry Links -- Advisory Committee Board of Governors -- MOE Competition Slide # 36 Products S T U D E N T S E M P LO Y ER S

STEP 3. SWOT ANALYSIS Assessment of Internal & External Environment In Ex S W O T Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Slide # 37
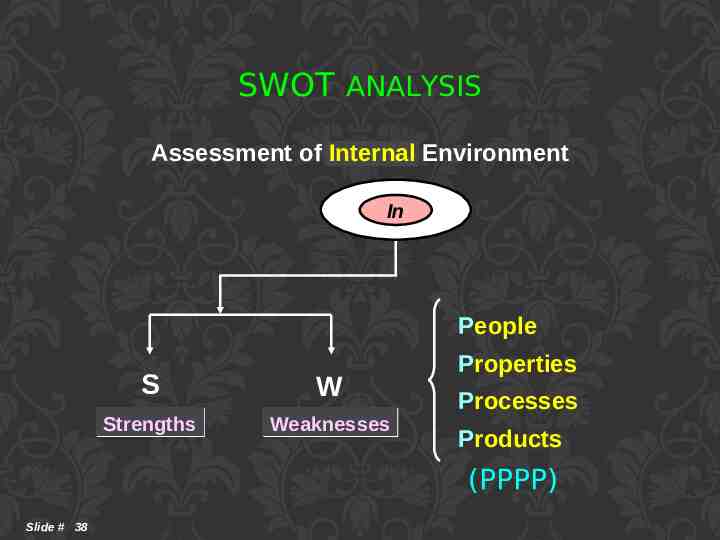
SWOT ANALYSIS Assessment of Internal Environment In People S W Strengths Weaknesses Properties Processes Products (PPPP) Slide # 38

SWOT ANALYSIS Strengths Weaknesses What makes us special? What are our soft spots? What resources (inputs) strategies (processes) and performances (outputs) do we handle well? What resources (inputs) strategies (processes) and performances (outputs) do we not handle well? What are strengths? What are our weaknesses? our internal (PPPP) Slide # 39 internal
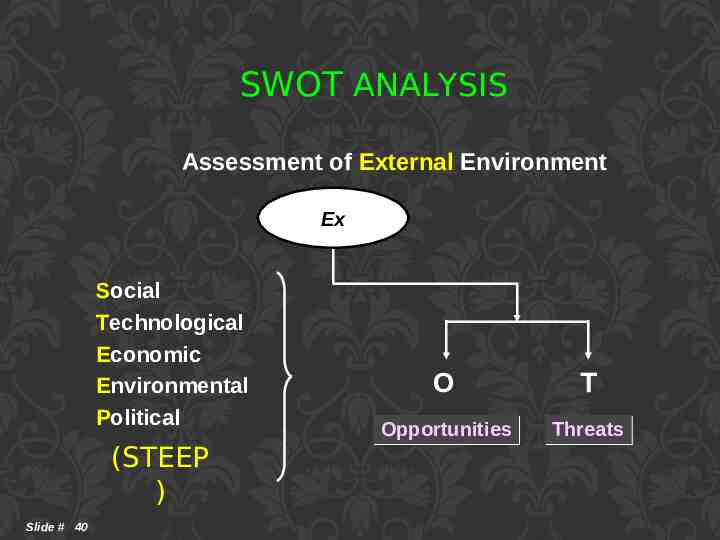
SWOT ANALYSIS Assessment of External Environment Ex Social Technological Economic Environmental Political (STEEP ) Slide # 40 O T Opportunities Threats

SWOT ANALYSIS Opportunities Threats What trends and events can help us? What trends and events can hinder us? What are the positive social, technological, economic, environmental and political forces influencing us? What are the negative social , technological, economic, environmental and political forces influencing us? What are our major external opportunities? What are our major external threats? (STEEP) Slide # 41

ASSESSING THE EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT 1. Identifying the shifts in the needs of Customers and potential Clients and 2. Identification of Competitors and Collaborators (CCCC) Slide # 42

INFORMATION SOURCES FOR SWOT What is the source of strategic intelligence? 1. Identify information Sources for Assessing Internal Environment 2. Identify information Sources for Assessing External Environment Slide # 43

TOOLS FOR COLLECTING SWOT INFORMATION 1. QUESTIONNAIRES 2. INTERVIEW SCHEDULES 3. OBSERVATION SCHEDULES 4. FOCUS GROUP MEETINGS The information collected has to be analyzed for planning Slide # 44

What makes the planning process Strategic? Those actions that enable you to continually adapt, innovate, resolve issues and overcome barriers Slide # 45
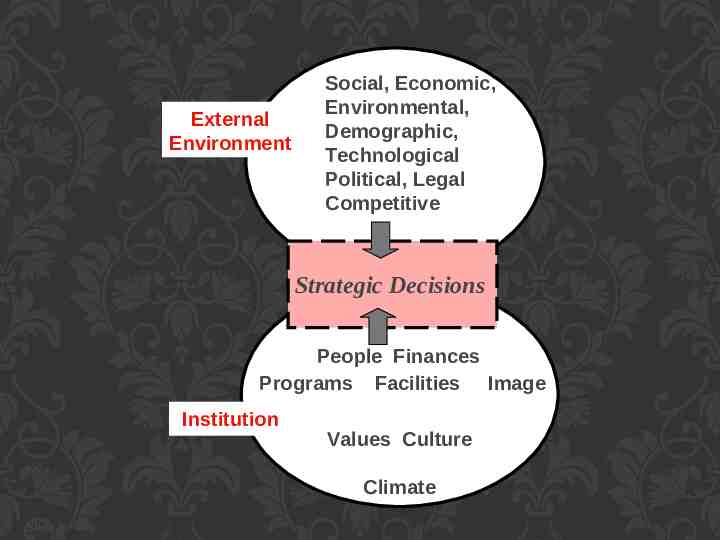
External Environment Social, Economic, Environmental, Demographic, Technological Political, Legal Competitive Strategic Decisions People Finances Programs Facilities Image Institution Values Culture Climate Slide # 46

CREATING DIFFERENTIAL ADVANTAGE Opportunities, Threats Core Values External Environment Thrust areas & Projects Strategic Decisions Internal Institution Strengths and Weaknesses Slide # 47

STEPS IN THE STRATEGIC PLANNING PROCESS Key Key Stakeholders Stakeholders 1. 1. Initiate Initiate SP SP Process Process 2. 2. Clarify Clarify Mandate Mandate and and Mission Mission 3. 3. SWOT SWOT Analysis Analysis 4. 4. Thrust Thrust Areas Areas (( Prioritised) Prioritised) Thrust Thrust Areas Areas 5. 5. Formulate Formulate Goals Goals 6. 6. Formulate Formulate Projects Projects 7. 7. Work Work Plan Plan // Action Action Plan Plan S. S.Plan Plan Slide # 48

STEP 4. IDENTIFY THRUST AREAS A Thrust Area is an important functional area of the organisation requiring CHANGE. It will be related to an important OUTPUT of the organisation Thrust Areas Examples: Slide # 49 Operational Micro-Level Activity

EXAMPLES OF THRUST AREAS 1. Facilities (Infrastructure) development 2. Curriculum Development 3. Student Services 4. Staff development 5. Management Information System 6. Industry Institute Partnerships 7. Continuing Education Programmes 8. Environment Development 9. Women in Development Slide # 50

DEFINITION OF STRATEGY Strategy is an approach or plan for achieving a goal especially over a long period of time. Slide # 51

STEP 8. ESTABLISH A VISION FOR THE ORGANISATION A A Vision Vision Statement: Statement: Slide # 52 Indicates the desired future state of the organisation Sets the direction for the organisation from a long term perspective

When to develop the Vision Statement? Can be developed after we complete the process of Strategic Planning Slide # 53

Thank You! [email protected] 9923040795






