Richard Whitley Director Steve Sisolak Governor State of
59 Slides639.80 KB

Richard Whitley Director Steve Sisolak Governor State of Nevada Department of Health and Human Services Regional Center Services to Individuals with Autism Aging and Disability Services Division Jessica Adams, Deputy Administrator 04/09/2023 Helping people. It’s who we are and what we do.

Agenda 1. Overview of Developmental Services Regional Centers & Eligibility 2. Number of Persons with Autism Spectrum Disorder Served 3. Available Services, including Vocational Supports 4. Requirements of Direct Support Staff 5. Impact of COVID-19 on Regional Center Services 2

Nevada Developmental Services Nevada Developmental Services (DS) provides services to individuals who reside in the state of Nevada who have an intellectual disability or developmental disability and who meet federal qualification guidelines for services DS provides services to eligible individuals throughout the lifespan – from birth until death Services provided through one of 3 Regional Centers 3

Nevada Regional Centers Sierra Regional Center (SRC)– covering Washoe County Rural Regional Center (RRC)– covering all of rural Nevada, with office locations in: Carson City Elko Fallon Fernley Gardnerville Winnemucca Mesquite Pahrump Desert Regional Center (DRC)– covering Clark County, except rural areas 4

Intake Inquiry Methods Walk –In Phone Fax PR/Application Events Mail Web Inquires 5

Intake Process The Intake specialist assists the applicant to gather information to determine if the individual meets eligibility requirements. Individuals apply at a regional center based on the area in which they live. Once the information is gathered, it is reviewed by an Eligibility Committee. If needed, psychological testing and assessment can be done by the Regional Center to inform eligibility. 6

Supporting Documentation Intellectual Disability Requires a diagnosis by a licensed psychologist OR a finding by a certified school psychologist Is supported by test results including intellectual assessment scores and assessment of adaptive behavior Developmental Disability Autism Spectrum Disorders: diagnosed by a licensed psychologist, neurologist, pediatrician, psychiatrist, or educational assessments completed by a certified school psychologist Neurological Disorders (seizure disorders, cerebral palsy, TBI): diagnosed by a neurologist or other qualified physician and substantiated by medical records (e.g., EEG, neuroimaging) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and other Neurodevelopmental Disorders: are substantiated by medical records (e.g., neurological evaluation, neuroimaging) from a neurologist or geneticist Genetic/Chromosome Disorders: diagnosed by a physician based on results of genetic/chromosome testing 7

Eligibility A person may qualify for Developmental Services from the state of Nevada if she or he is a legal resident of Nevada and has a confirmed diagnosis of: Intellectual Disability Developmental Delay (under 6 years of age) Developmental Disability 8

Intellectual Disability Intellectual Disability is characterized by significant limitations in both: Intellectual functioning Adaptive skills This is considered to be a lifelong condition originating before the age of 18 years. Requires a diagnosis by a licensed psychologist OR a certified school psychologist. Intellectual Disability is supported by test results including intellectual assessment scores and assessment of adaptive behavior. Significant limitations in intellectual functioning refers to impairments in general mental capacity, such as learning, reasoning and problem solving. 9

Developmental Delay A child under the age of 6 years old may qualify for services if the child has a diagnosis of Developmental Delay and demonstrates substantial functional limitations in at least two of the five areas. “Capacity for Independent Living” is not evaluated for children under 6 years of age Children who initially qualify for Regional Center Services under “Developmental Delay” are reassessed at age 6 to determine that they meet criteria for either an Intellectual Disability or a Developmental Disability. 10

Developmental Disability Examples of types of Developmental Disabilities: Autism Spectrum Disorder Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) / Fetal Drug Affect (FDA) Epilepsy Down Syndrome Prader-Willi Syndrome Fragile X Cerebral Palsy Traumatic Brain Injury Genetic/neurological conditions Must occur before 22 years of age. Substantial functional limitations must occur in three or more of the following areas of major life activity 11

Substantial Functional Limitations Determination of substantial functional limitations is based on the result of an assessment of adaptive behavior Areas of Major Life Activity: Self-care Understanding and use of language Learning Mobility Self-direction Capacity for independent living 12

Self-Care “Self-care” refers to the demonstration of ageappropriate skills in areas such as toileting, eating, dressing, personal hygiene and grooming. 13

Understanding and Use of Language “Understanding and use of language” includes the demonstration of age-appropriate skills in comprehending and expressing information including written communication - Speaking/sign language - facial expression, body movement, - touch or gestures. 14

Learning “Learning” refers to age-appropriate functional academic skills related to learning at school that also have direct application in one’s life. 15

Mobility “Mobility” includes the demonstration of ageappropriate skills to ambulate and orient within the home and community. Related skills include orienting and moving about in the home and nearby neighborhood in order to complete activities of daily living, and the ability to travel in unfamiliar places or use public transportation. 16

Self-Direction “Self-direction” refers to the age-appropriate ability to set realistic goals or make plans independently of others and accomplish such goals in a timely manner. Related skills include orientation to home and place and to other persons, persistence, maintaining attention and concentration, initiating and completing activities, and maintaining behavior/emotional stability. 17

Capacity for Independent Living For an adult, these skills include the ability to tell time, use money, initiate and maintain relationships, hold a job and engage in leisure and recreation activities. Areas of competence include clothing care, housekeeping, property maintenance, food preparation and cooking, planning and budgeting for shopping, home safety and daily scheduling. 18

Notification of Eligibility & Appeals All applicants are notified via letter of the eligibility decision Those who are found to not qualify can appeal the decision: ADSD Appeals Appeal through Nevada Medicaid Those who do appeal receive: Statewide Eligibility Review Committee Fair Hearing through Nevada Medicaid Linkage and Referral Can re-apply if more diagnosis supporting documentation is found/received 19
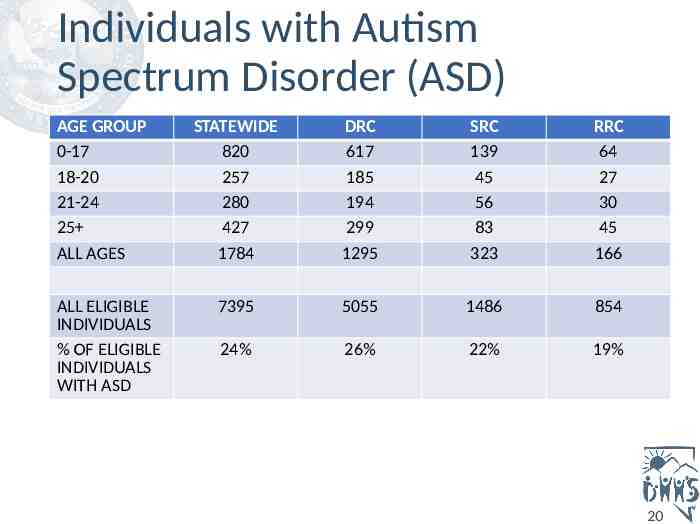
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) AGE GROUP 0-17 18-20 21-24 25 ALL AGES ALL ELIGIBLE INDIVIDUALS % OF ELIGIBLE INDIVIDUALS WITH ASD STATEWIDE 820 257 280 427 1784 DRC 617 185 194 299 1295 SRC 139 45 56 83 323 RRC 64 27 30 45 166 7395 5055 1486 854 24% 26% 22% 19% 20
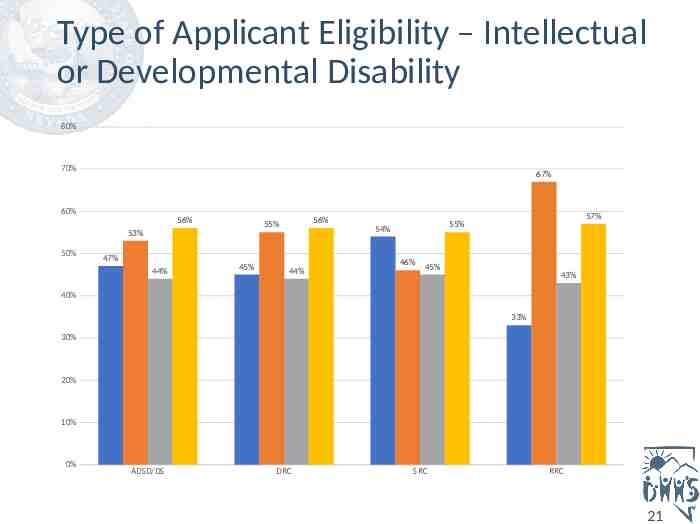
Type of Applicant Eligibility – Intellectual or Developmental Disability 80% 70% 67% 60% 56% 53% 50% 47% 44% 56% 55% 45% 44% 57% 55% 54% 46% 45% 43% 40% 33% 30% 20% 10% 0% ADSD/DS DRC SRC RRC 21
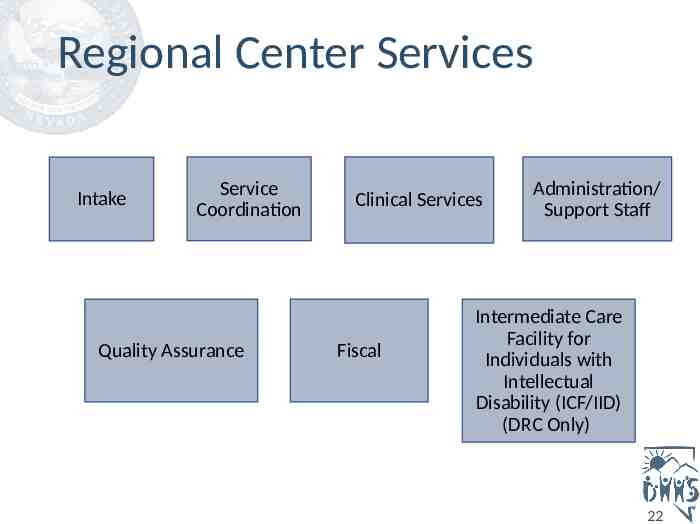
Regional Center Services Intake Service Coordination Quality Assurance Clinical Services Fiscal Administration/ Support Staff Intermediate Care Facility for Individuals with Intellectual Disability (ICF/IID) (DRC Only) 22

Service Coordination All opened cases are assigned a Service Coordinator, as required by Nevada Revised Statutes (NRS) 435. The primary role of the Service Coordinator is to assist individuals in developing and carrying out a Person Centered Plan (PCP). 23

Person Centered Plan (PCP) This plan describes the individual, their current financial, living, and medical status, and, most importantly, describes the individual’s goals. This plan is reviewed every 3 months and re-written annually or more often if circumstances change. The PCP also describes services that the individual will need to be successful, such as supervision, training, medical and other types of ongoing supports. These services can be provided by natural community supports, by family and friends, or can be provided by a contracted provider of the Regional Center. 24

Person Centered Planning Process The individual’s wants, needs, and priorities are the center of the plan and the individual is in control of their life and their choices. The Service Coordinator often acts as a mediator between team member who may disagree and must balance individual choice, dignity of risk, and true harm or self harm due to a potential inability to recognize harm. 25
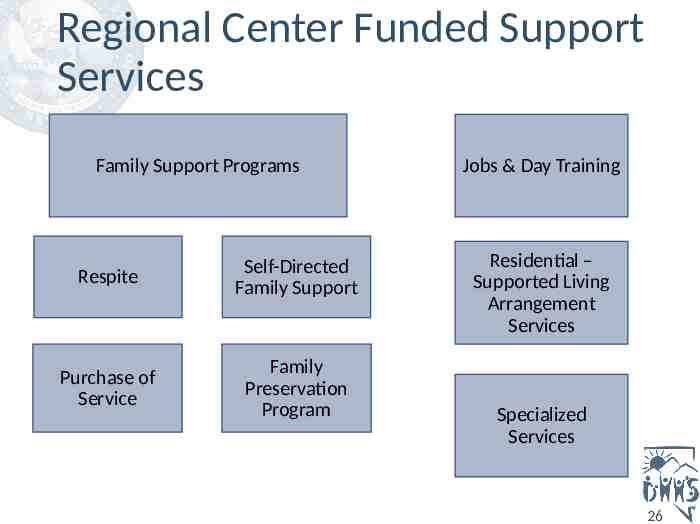
Regional Center Funded Support Services Family Support Programs Respite Self-Directed Family Support Purchase of Service Family Preservation Program Jobs & Day Training Residential – Supported Living Arrangement Services Specialized Services 26

Family Support Services Only for individuals living in their family home Respite Currently 125/month, family chooses their own provider(s) Purchase of Service Potential once per year funding up to 250 to assist families with emergencies or to purchase service items not covered by insurance Self-Directed Family Support Current allotment of 450/month to purchase specialized services chosen by the family Family Preservation Program Only for individuals with severe or profound ID Current allotment of 374/month paid to family 27

Contracted Provider Services Services include: Jobs & Day Training Residential Services – Supported Living Arrangements Specialized Services Non-Medical Transportation Behavioral Consultation, Training & Intervention Nursing Counseling Nutritional Counseling Primarily funded through the Home & Community Based Services 1915(c) Waiver for Individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities 28

Jobs & Day Training (JDT) Services There are 4 distinct types of vocational or JDT services: Day Habilitation Prevocational Services Supported Employment Individual Small Group Career Planning 29

Day Habilitation Regularly scheduled activities in a non-residential setting that assist with the acquisition, retention or improvement in self-help, socialization and adaptive skills including performing activities of daily living and community living. Services focus on enabling the participant to attain or maintain his or her maximum potential. Services are not vocational in nature (for the primary purpose of producing goods or performing services). May be used for meaningful retirement activities in the community. 30

Prevocational Services Provides for leaning and work experience, including volunteer work, where an individual can develop general, non-job or task-specific strengths and skills that contribute to employability in paid employment within integrated community settings. Services are intended to develop and teach general skills that will optimally lead to integrated community employment at or above minimum wage. Individuals may be paid at special minimum wages (less than minimum wage) while receiving prevocational services if the provider has been certified by the U.S. Department of Labor to pay special minimum wages. 31

Individual Supported Employment Provided to individuals that need intensive, ongoing supports to obtain (job development) and maintain (job coaching) a job in a competitive integrated community work setting for which the individual is compensated at or above minimum wage. Customized Employment is one way to provide Individual Supported Employment in which the provider focuses on the strengths of the individual and works with potential employers to customize a job that will benefit both the employer and the employee. Outcome is for individuals to have sustained employment, paid at or above minimum wage, in an integrated community setting. 32

Small Group Supported Employment Small Group Supported Employment provides services and training to two (2) to eight (8) individuals who are working in a regular business, industry or other community setting. These supports must be provided in a manner that promotes integration in the workplace and interaction between participants and people without disabilities within those workplaces. Outcome is for individuals to have sustained employment, paid at or above minimum wage, in an integrated community setting. 33

Career Planning Person-centered, comprehensive employment planning and support services that provide individuals with assistance to obtain, maintain or advance in competitive employment of self-employment. This service is time-limited (216 hours provided within a 6-month time period each year) and will result in a plan that will guide supported employment services for achieving competitive, integrated employment with pay at or above minimum wage. Examples of services include experiential learning opportunities, job exploration, job shadowing, informational interviewing, assessment of interests, and benefits counseling. 34

Residential or Supported Living Arrangement (SLA) Services Goal is for the individual to live as independently as possible in the community Occur on a spectrum of service based on the individual’s need Happen in multiple environments Family home Individual’s home/apartment Shared Living home Intensive Supported Living (ISLA) home – 24-hour supports 35

Residential Support Services Direct services and protective oversight provided to the individual to assist in the acquisition, improvement, retention and maintenance of the skills necessary for the individual to successfully, safely and responsibly reside in their home and community. Services are individually planned and are provided on a continuum of service delivery ranging from intermittent (up to 40 hours a week) to twenty-four (24) hour supported living arrangements. In 24-hour living arrangements, overnight staff can be either awake or asleep depending on the needs of the individuals living in the home. 36

Residential Support Services Examples Examples of direct services include: Health & Fitness Medical Support ADL’s (Personal Care) IADL’s (Home Management) Socialization Money Management Recreation Safety Skills Dietary Support Supervision 37

Residential Support Management Ensures the health and welfare of individuals receiving residential support services by assuring those services are planned, scheduled, implemented and monitored as preferred and needed. Residential support managers perform various tasks including: assisting with the development of goals; development of habilitation plans; assisting with applying for and obtaining community resources and benefits; assisting with locating housing; problem solving and crisis management; support with budgeting, bill paying, and keeping appointments; following up on health and welfare concerns; and training residential support staff. 38

Room & Board Monies For individuals living outside of their family home, Developmental Services can provide a monthly amount for room & board to supplement the individual’s income Any income received by the individual (SSI, RSDI, SSDI, employment income, food stamps, etc.) is used in full before any state dollars are authorized Paid to the SLA provider Standardized amounts for food & personal needs Limits for max rent & utilities One-time cost monies also available to assist with various needs (e.g. deposits, furniture, damages to the home, etc.) 39

Specialized Services These services include: Non-Medical Transportation Behavioral Consultation, Training & Intervention Nursing Counseling Nutritional Counseling 40

Non-Medical Transportation Can be performed by either an SLA or JDT provider or used to purchase public transportation passes. Transportation services that enable individuals to gain access to community services, activities and resources, such as grocery shopping, banking and social events. Limited to a maximum of 100 per month. 41

Behavioral Consultation, Training & Intervention Behaviorally-based assessment and intervention for individuals, as well as support, training and consultation to family members, caregivers, paid residential support staff, or jobs and day training staff. May include services such as Functional Behavioral Assessment, development of behavior support plans, training to the team on behavioral support plans and data collection processes and monitoring of the behavior support plan implementation. Limited to 5200.00 per year. 42

Nursing Medical Management (Community Support Services) – RN or LPN Development of health services support plans; professional observation and assessment; training of staff; monitoring/assessment of condition; referrals to medical providers; hospital discharge planning; etc. Nursing Assessment – RN only Assessment of current health status, needs, preferences and abilities which also includes recommendations for medical and mental health care. Direct Services – RN or LPN Provision of routine medical and health care services that are integral to meeting the daily needs of individuals. Skilled nursing services such as medication administration, wound care, nasogastric or gastronomy tube feedings, ostomy care, tracheotomy aspiration care, catheter care, etc. May be delivered in an individual’s home, day program or other community settings. 43

Counseling Provides assessment/evaluation, consultation, therapeutic interventions, support and guidance for individuals and/or family members, caregivers and team members, that is not covered by Medicaid State Plan. Can be provided in an Individual or a Group setting. Limited to 1500.00 per year. 44

Nutritional Counseling Initial assessment and re-assessment of an individual’s nutritional needs, including the development of an individual’s nutritional plan, and training and education of the individual and staff. Performed by a registered Dietician. Limited to 1300.00 per year. Service does not include the cost of meals or food items. 45

Qualified Providers Both Nevada Revised Statutes (NRS) 435 & Federal HCBS Waiver regulations require providers to be approved & certified by the Regional Center Each Regional Center Quality Assurance (QA) department certifies or qualifies every provider Jobs and Day Training and Supported Living Arrangement providers are certified for 1-3 years Specialized service providers (e.g. behavioral intervention, nursing, etc.) are verified to hold required experience, education and/or professional licensure each year Ensures quality standards of care across the state Minimizes risk of abuse, neglect & exploitation 46

Provider Certification GENERAL ADMINISTRATIVE ITEMS EMPLOYEE FILES KNOWLEDGE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS TRACKING AND TRENDING OF DATA & SAFEGUARDS DOCUMENTATION OF SERVICES & SUPPORTS FINANCIAL ACCOUNTABILITY 47

Provider Staff Requirements 18 years of age High diploma or equivalent Three positive reference checks prior to hire Completed FBI & State fingerprint criminal clearance check with no convictions of disqualifying offenses per NAC 435 Not on the “Office of Inspector General List of Excluded Individuals and Entities” or the Nevada Medicaid Exclusion List 48

Provider Staff Requirements cont. Current, appropriate licensure & credentials if needed (nurses, behaviorists, nutritionists, etc.) Current CPR & First Aid Certification Medication Administration Certification, as applicable Crisis Prevention/Intervention Certification, as applicable 49

Provider Staff Orientation Training Orientation Training Requirements Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities Prevention, Recognition & Reporting of Mistreatment of Individuals Receiving Services Mental Health as a Co-Occurring Disorder in Individuals with ID/DD Incident Reporting Personal Rights/Responsibilities, Dignity and Respect, and Due Process of Restrictions Disaster and Emergency Preparedness Medical Supports and Identifying & Managing Medical Emergencies Medication Supports 50

Provider Staff Orientation Training (continued) Orientation Training Requirements continued: Standard Precautions and Infection Control PCP Planning, Person Centered Goals, Plan Implementation and Reporting on Progress HIPAA and Confidentiality Handling Conflict and Complaints/Grievance Procedures Positive Behavior Approaches and Supports Ethics, Boundaries and Professional Behavior Documentation and Billing Requirements “Hands On” job orientation specific to the needs of the individuals the staff will be supporting 51

Provider Staff Annual Training Annual Training Requirements: Prevention, Recognition & Reporting of Mistreatment of Individuals Receiving Services Mental Health as a Co-Occurring Disorder in Individuals with ID/DD Incident Reporting Personal Rights/Responsibilities, Dignity and Respect, and Due Process of Restrictions Disaster and Emergency Preparedness Medical Supports and Identifying & Managing Medical Emergencies Medication Supports 52

Provider Staff Annual Training (continued) Annual Training Requirements continued: Standard Precautions and Infection Control HIPAA and Confidentiality Positive Behavior Approaches and Supports Ethics, Boundaries and Professional Behavior 53

Impact of COVID-19 Developmental Services implemented various changes and flexibilities in mid-March to assure health & safety of individuals served & staff: Face-to-face visits by Service Coordinators or other Regional Center staff are limited with contact completed via electronic or telephonic means when possible. Majority of congregate JDT work sites were closed from March 18, 2020 – mid-June 2020. Some still remain closed. Those that are open must follow 5 pages of guidelines that were issued on June 11, 2020. Due to site closures, JDT providers have been allowed to provide services in a person’s home. 54

Impact of COVID-19 (continued) Continued changes & flexibilities: Some JDT services have been provided remotely (e.g. activities over Zoom) Many individuals in supported employment were at least temporarily laid off due to business closures Residential SLA services were adjusted as needed Increased hours provided in 24-hour environments Some individuals and families choose to temporarily stop intermittent SLA services Provided increased room & board funding where needed to ensure sufficient supplies of cleaning products, food, PPE or other emergency supplies 55

Current Status of COVID-19 Impact Intake services have continued throughout the pandemic Face-to-face visits with precautions in place were beginning to increase, although optional visits are now paused again due to “Stay At Home 2.0” announced on November 10, 2020 Congregate JDT site remain open under various guidelines including staff mask usage, social distancing of workspace, temperature checks, increased cleaning, limited capacity, etc. Some individuals have returned to competitive employment who had previously been laid off In-home or virtual JDT services continue as requested 56

QUESTIONS? 57

Contact Information Jessica Adams Deputy Administrator [email protected] (775) 684-5894 58
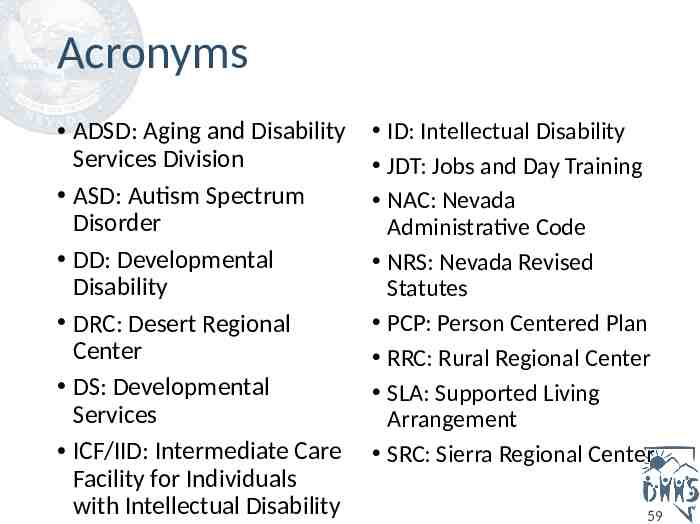
Acronyms ADSD: Aging and Disability Services Division ASD: Autism Spectrum Disorder DD: Developmental Disability DRC: Desert Regional Center DS: Developmental Services ICF/IID: Intermediate Care Facility for Individuals with Intellectual Disability ID: Intellectual Disability JDT: Jobs and Day Training NAC: Nevada Administrative Code NRS: Nevada Revised Statutes PCP: Person Centered Plan RRC: Rural Regional Center SLA: Supported Living Arrangement SRC: Sierra Regional Center 59






