Position-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
21 Slides369.00 KB

Position-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs

Questions for Consideration What is a position-time graph? What is a velocity-time graph? How do features on one graph translate into features on the other?

Distance-Time Graphs Show an object’s position as a function of time. x-axis: time y-axis: distance

Distance-Time Graphs Imagine a ball rolling along a table, illuminated by a strobe light every second. 0s 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 7s 8s You can plot the ball’s position as a function of time. 9 s 10 s

Distance-Time Graphs 10 9 Distance(cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 time (s)

Distance-Time Graphs What Straight line, upward 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 slope 2 What kind of motion created this graph? Constant 10 position (cm) are the characteristics of this graph? speed 1 time (s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10

Distance-Time Graphs Each type of motion has a characteristic shape on a D-T graph. Constant speed Zero speed (at rest) Accelerating (speeding up) Decelerating (slowing down)

Distance-Time Graphs time (s) Constant speed in positive direction. pos. (m) speed is represented by a straight segment on the D-T graph. pos. (m) Constant time (s) Constant speed in negative direction.
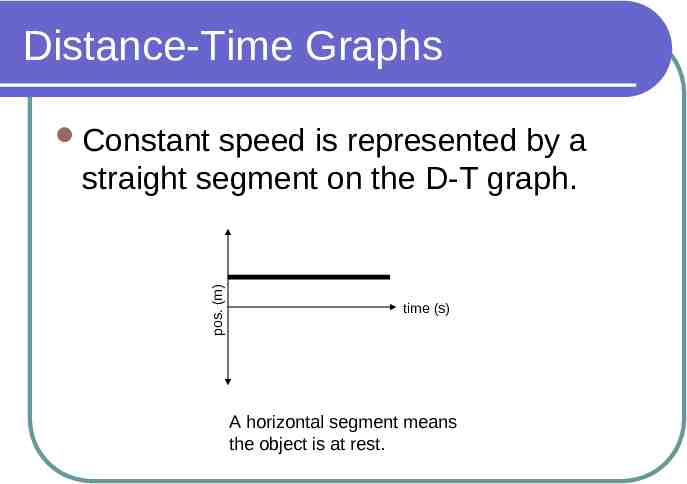
Distance-Time Graphs speed is represented by a straight segment on the D-T graph. pos. (m) Constant time (s) A horizontal segment means the object is at rest.

Distance-Time Graphs time (s) Speeding up in positive direction. pos. (m) segments on the D-T graph mean the object’s speed is changing. pos. (m) Curved time (s) Speeding up in negative direction.

Distance-Time Graphs time (s) Traveling in positive direction, but slowing down. pos. (m) segments on the D-T graph mean the object’s speed is changing. pos. (m) Curved time (s) Traveling in negative direction, but slowing down.

Distance-Time Graphs The slope of a D-T graph is equal to the object’s velocity in that segment. slope 50 position (m) change in y 40 30 slope change in x (30 m – 10 m) 20 10 slope 10 20 time (s) 30 (30 s – 0 s) (20 m) (30 s) 40 slope 0.67 m/s

Distance-Time Graphs The following D-T graph corresponds to an object moving back and forth along a straight path. Can you describe its movement based on the graph? N position (m) S time (s)

Velocity-Time Graphs A velocity-time (V-T) graph shows an object’s velocity as a function of time. A horizontal line constant velocity. A straight sloped line constant acceleration. Acceleration Positive Not slope positive acceleration. necessarily speeding up! Negative Not change in velocity over time. slope negative acceleration. necessarily slowing down!
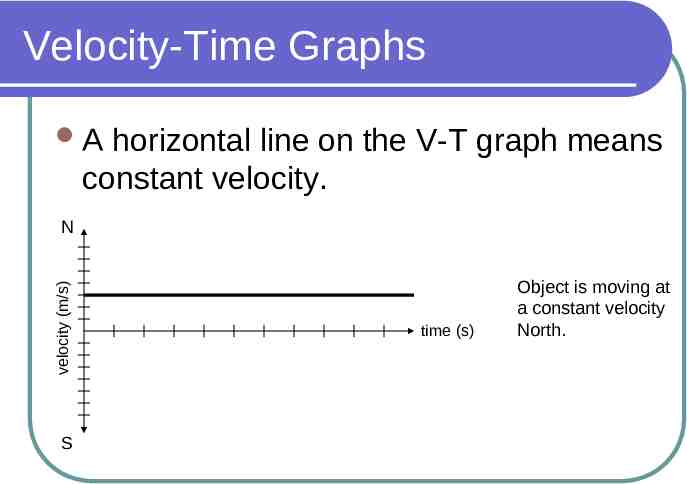
Velocity-Time Graphs A horizontal line on the V-T graph means constant velocity. velocity (m/s) N S time (s) Object is moving at a constant velocity North.

Velocity-Time Graphs A horizontal line on the V-T graph means constant velocity. velocity (m/s) N S time (s) Object is moving at a constant velocity South.

Velocity-Time Graphs If an object isn’t moving, its velocity is zero. velocity (m/s) N S Object is at rest time (s)

Velocity-Time Graphs If the V-T line has a positive slope, the object is undergoing acceleration in positive direction. If v is positive also, object is speeding up. If v is negative, object is slowing down.

Velocity-Time Graphs V-T graph has positive slope. velocity (m/s) S time (s) Positive velocity and positive acceleration: object is speeding up! velocity (m/s) N N S time (s) Negative velocity and positive acceleration: object is slowing down.

Velocity-Time Graphs If the V-T line has a negative slope, the object is undergoing acceleration in the negative direction. If v is positive, the object is slowing down. If v is negative also, the object is speeding up.

Velocity-Time Graphs V-T graph has negative slope. velocity (m/s) S time (s) Positive velocity and negative acceleration: object is slowing down, velocity (m/s) N N S time (s) Negative velocity and negative acceleration: object is speeding up! (in negative direction)






