Lesson 2. Leadership From Within Visual 2.1 Leadership and
25 Slides1.96 MB

Lesson 2. Leadership From Within Visual 2.1 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Lesson 2 Objectives Describe how self-knowledge and understanding contribute to effective leadership. Use self-assessment, self-reflection, and authentic feedback to increase your self-knowledge. Identify factors that underlie your thought process and affect your ability to lead. Differentiate between inquiry and advocacy and identify strategies for balancing the two. Identify personal goals for improving your inner capacity for leadership. Visual 2.2 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Where Leadership Begins In his book, Leading from the Inside Out: Becoming a Leader for Life, Kevin Cashman said: Visual 2.3 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Paradigms That Guide Thinking Paradigms are mental models that provide a structure for our thoughts and guide our thinking. They help us make sense of all of the information that we encounter by telling us what to pay attention to, how to arrange what we pay attention to, how to draw conclusions, and how to interpret things. Visual 2.4 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Three Work Paradigms The Hired Hand The Broker The Leader Visual 2.5 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Activity: Which Paradigm? Instructions: Read the descriptions in your Student Manual of how different people approach their leadership roles. Decide which leadership paradigm each one represents: The Hired Hand The Broker The Leader Visual 2.6 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Three Lenses of Leadership Telescopic lens Mid-distance lens Microscopic lens Visual 2.7 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Self-Knowledge Visual 2.8 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Benefits of Increased Self-Knowledge Understand others. Understand and manage their reactions to others. Appreciate others’ points of view. Leverage their strengths. Strengthen or compensate for their weaknesses. Earn trust. Be aware of how they impact others, both positively and negatively. Have more self-confidence. Visual 2.9 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)
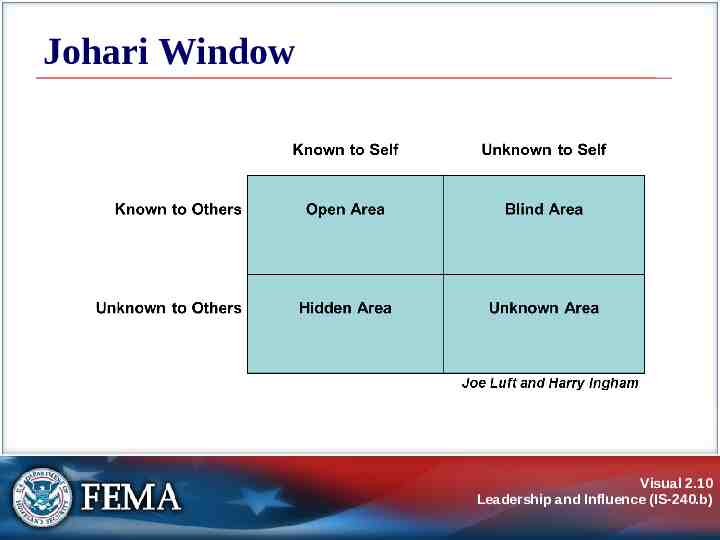
Johari Window Visual 2.10 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)
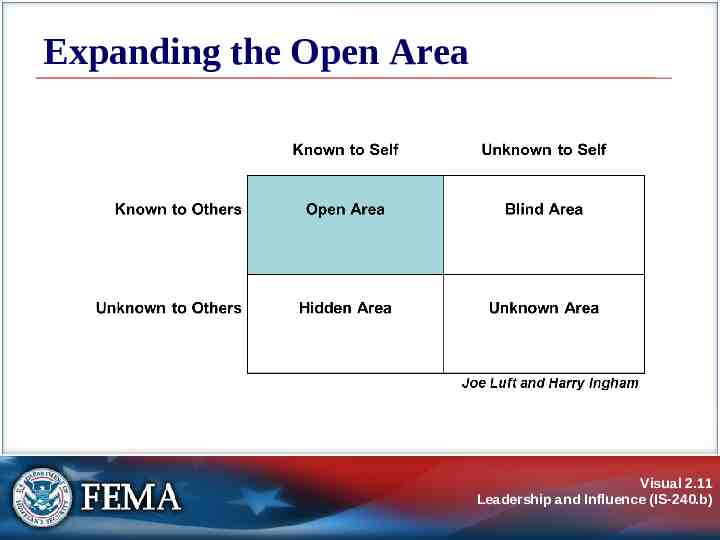
Expanding the Open Area Visual 2.11 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Ways To Increase Self-Knowledge Self-assessment Self-reflection Soliciting authentic feedback Visual 2.12 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Self-Assessment We tend to be an outward-oriented society. That tendency leads us to think that both our problems and their solutions are outside of us. Our culture doesn’t put a high priority on self-assessment. Visual 2.13 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Self-Reflection Visual 2.14 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Activity: Self-Reflection Instructions: Return to the Leadership Behaviors SelfAssessment you completed in Lesson 1, and compare your time spent on telescopic behaviors to your time spent on mid-distance/microscopic behaviors. Next, reflect on the questions in your Student Manual. Finally, given your reflections on these questions, reconsider the personal goals you identified at the end of Lesson 1. Visual 2.15 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Authentic Feedback Visual 2.16 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Tips for Encouraging Authentic Feedback Before you ask for feedback, be clear in your own mind why you’re asking. Ask for feedback only when you are open to hearing it. Listen to what they have to say. Take notes. Avoid being defensive. Restate what the speaker has told you. Ask followup questions to gain clarity. Thank them. Visual 2.17 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Understanding How You Think Sometimes it’s difficult to differentiate between what a person actually says and how we interpret what they said. In other words, our own beliefs affect what and how we hear. Visual 2.18 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Ladder of Inference I take ACTI ONS based on my beliefs. I adopt BELIEFS about the world. I draw CONCLUSIONS. I make ASSUMPTIONS based on the meanings I added. I add MEANINGS (cultural and personal). I select DATA from what I observe. All the information in the world. Visual 2.19 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Creating a Leadership Environment Listen carefully to what people actually say. Try not to interpret at first. Listen for conclusions and beliefs yours and theirs. Listen for directly observable data. Suspend your certainties and conclusions. What must be the Ladder of Inference in their minds? Visual 2.20 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Inquiry vs. Advocacy Inquiry. Inquiry involves talking with other people and learning from them. At this stage, you are not judging, arguing, or trying to present your own viewpoint you are just learning. Advocacy. Advocacy involves “selling” an idea or position or directing attention to certain facts you think are relevant. This is when you begin to evaluate ideas, narrow the field, and work toward consensus. Visual 2.21 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Balancing Inquiry and Advocacy The key—both within yourself and in working with a team—is to balance inquiry and advocacy. You need both. Visual 2.22 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Activity: Your Inner Leader Instructions: Think about a specific group that you are responsible for leading. In the Johari Window in your Student Manual, fill in the following information: Open Area: Things about you that are known both to you and to the group. Hidden Area: Things about you that you know but the group doesn’t know. Try to list at least five things in each area. Visual 2.23 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Activity: Your Inner Leader Instructions: (Continued) Identify at least one item in your Hidden Area that, if brought into the Open Area, could improve your effectiveness as a leader. What would be a good way to make this trait known to the group? What are some strategies you can use to learn about what lies in your Blind Area? Review the personal goals that you recorded in Lesson 1. Add at least one new goal, based on what you have learned in this lesson. Visual 2.24 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)

Summary and Transition In this lesson, you learned about the: Importance of self-knowledge. Paradigms that guide thinking. Johari Window. Ladder of Inference. In Lesson 3, you will learn about the leader’s role in facilitating change. Visual 2.25 Leadership and Influence (IS-240.b)






