Introduction to ITIL and IT Service Management
31 Slides2.07 MB

Introduction to ITIL and IT Service Management

Functions, Roles & Processes Introduction to IT Service Management

What is Functions? Functions are unit of organisations (e.g. a team department or group of people) specialised to perform certain type of work and responsible for specific outcomes – The Service Desk is an example of a Function They are self-contained with capabilities and resources necessary for their performance and outcomes They have their own body of knowledge, which accumulates from experience

What is Process? A set of coordinated activities combining and implementing resources and capabilities in order to produce an outcome which directly or indirectly creates to customer or stakeholder Processes are strategic assets when they create competitive advantage and market differentiation

Process Structure Norms Measure Input Data, information & knowledge Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 Desired outcome
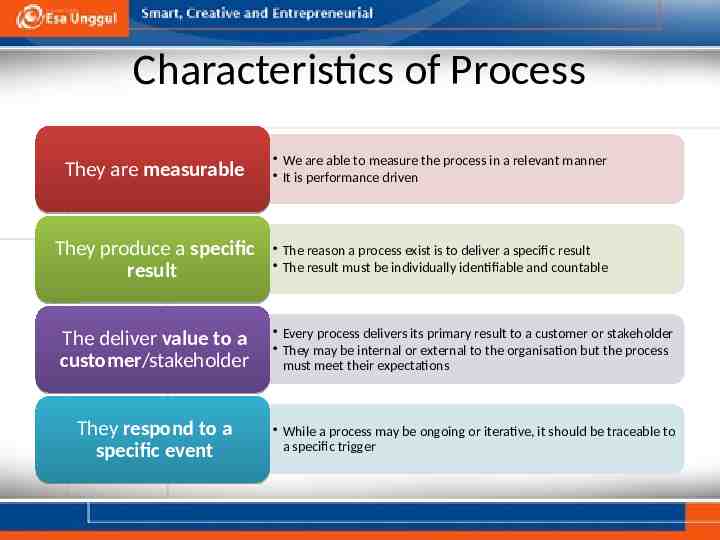
Characteristics of Process They are measurable We are able to measure the process in a relevant manner It is performance driven They produce a specific result The reason a process exist is to deliver a specific result The result must be individually identifiable and countable The deliver value to a customer/stakeholder Every process delivers its primary result to a customer or stakeholder They may be internal or external to the organisation but the process must meet their expectations They respond to a specific event While a process may be ongoing or iterative, it should be traceable to a specific trigger

What is a Role? “A set of responsibilities, activities and authorities granted to someone” One person or team may have multiple roles – For example, the roles of Configuration Manager and Change Manager may be carried out by a single person Roles are described within processes

Units of Organisation Structure Team Group Department Division People who work A number of people A formal organisation A number of together to achieve a who perform similar structure which exists departments that have common objective, but activities but may work to perform a spesific been grouped together, not necessarily in the in different set of defined activities often by geography or same organisation departments, divisions on an ongoing basis product line structure or organisations A department is made Team carry out roles up of teams Teams are part of departments

Process Owner, Service Owner & the RACI Model Introduction to IT Service Management

Process Owner Responsible to ensure that process is performed according to agreed & documented process and meets the aims of the process definition. Document & publish process Define KPI’s Review KPI’s Process design Improving the process Review enhancements Service Improvement Program (CSI) Address process issues Training and roles Review and audit Ensure staff resources

Service Owner Responsible to the Customer for initiation, transition & ongoing maintenance & support of a particular service – Prime contact – Ensure that delivery & support meet requirements – Identify Service Improvement opportunities – Liaise with Process Owners – Facilitate effective monitoring & performance – Accountable to IT Director

Process & Service Owners - RACI One way to help define the appropriate roles is to use the RACI model RACI – Responsible – Those responsible to do the task – Accountable – Those who are accountable of the task – Consulted – Those who are consulted – Informed – Those informed on progress

Sample of RACI Model Service Level Manager C Problem Manager Security Manager Procurement Manager Activity 1 Director Service Management AR I I C Activity 2 A R C C C Activity 3 I A R I C Activity 4 I A R I Activity 5 I I C I A

Key Advantages of ITIL Independent (and in Public Domain) Comprehensive and Modular Links IT to the Business Universally applicable Business based approach to IT Common Vocabulary and it works (at least in can if done well)

Key ITIL/ITSM Objectives To align IT services with the current and future needs of the business and its Customers To continually improve the quality of the IT services delivered To reduce the long-term cost of service provision In addition, the ITIL framework helps improve the availability, reliability, stability and security of mission critical IT services by providing demonstrable performance indicators to measure and justify the cost of service quality.

The Service Lifecycle IT Service Management as a Practice

The Service Lifecycle Is the axis around which the lifecycle rotates Provides guidance on how to design, develop and implement service management not only as an organisational capability, but as a strategic asset SS It implement strategy Strategic objectives are ultimately realized through service operations, therefore making it a critical capability SD, ST & SO It occurs throughout the entire lifecycle Helps place and priorities improvement programmes and projects based on strategic objectives CSI

Service Lifecycle Governance Processes Continual Service Improvement Process Service Strategy Processes Service Lifecycle Operational Processes Service Design Processes Demand Management Service Transition Processes Service Operation Processes Strategy Generation Service Portfolio Management Service Measurement Financial Management Service Catalogue Management Service Level Management Capacity Management Availability Management Service Continuity Management Information Security Management Supplier Management Service Reporting Transition Planning & Support Change Management Service Asset & Configuration Management Release & Deployment Management Service Validation & Testing Evaluation Knowledge Management Service Improvement Event Management Incident Management Request Fulfillment Problem Management Access Management Operation Management

Service Lifecycle Decision Levels Service Strategy Service Design Tactical Service Transition Operational Service Operation Improvement Service Improvement Continual Continual Service Strategic

Summary For every stage within the Service Lifecycle we see an input/feedback into all other stages Service Strategy Strategies Policies Standards Output Service Design Plan to create and Modify Services and Service Management processes Feedback – lesson learnt for improvement Service Transition Manage transition of a New or changed Service or Service Management process into production Output Service Operation Day-to-day operations of Services and Service Management processes Output Continual Service Improvement Activities embedded within the Service Lifecycle

Cultural Aspects & Excellence in Service Management

Cultural Aspects & Excellence Customers & consumers Process improvement Management commitment What is culture? What is service culture? What is customer service?

Customers & Consumer (User) A customer is a recipient of a service - someone who deals with trader & habitually purchases from them A user, in ITIL terms, is the person using the service on daily basis The way in which service is delivered is dependent on the people delivering the service

What do customers want from IT? (Back to Basic) Services are available WHEN THEY NEED THEM Value for money Services are Business Aligned Their expectations are better managed To be kept informed Confidence in IT’s ability to deliver A single point of contact & communication

What do IT Manager’s want? To deliver a professional, stable & consistently improved service to the business To demonstrate accountability and value for money To build a flexible & scalable service department they & their team are proud of

Process Improvement Service Management implementation is a process improvement The objective of process improvement is to improve the service A Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is an ongoing initiatives

Management Commitment Motivating & leading by example Authority given to required decision makers Sponsor & ITSM “champion” assigned Training Big picture & long term strategic solution Realistic implementation timetable Appropriate tools to support the process Under Project Management

“A customer is the most important visitor on our premises. He is not dependent on us. We are dependent on him. He is not an interruption of our work. He is the purpose of it. He is not an outsider to our business. He is part of it. We are not doing him a favour by serving him. He is doing us a favour by giving us the opportunity to do so.” Mahatma Gandhi

Service Culture A culture is value and beliefs of organization A service culture means orientation towards helping people “people don’t care how much you know until they know how much you care”

Customer Service Customer service is. – providing the right quality of services to meet the customer’s requirement – help customers make best use of these services – being receptive to customer’s needs and problems and provide them with effective support at all time Tools: Customer profiling
Testing Your Knowledge






