Human Body Systems
37 Slides2.32 MB

Human Body Systems

Nervous System Functions Controls all body’s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body

Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord

What it helps you do Move Sense things from the environment And much more!

Interactions with other systems: All systems – helps keep the systems functioning

Integumentary (Skin) System Function 1st line of defense against disease Helps maintain body temperature Keeps fluids inside Main Parts Skin Sweat glands Hair nails

What it helps you do Helps you maintain fluids (don’t dehydrate) Helps you know your environment by feeling things around you Protect organs Remove waste

Interactions with other systems Works with the excretory and the immune system to help remove cellular waste and protect us from disease.

Skeletal System Support and protect body parts. Helps maintain homeostasis Makes red blood cells (red bone marrow)

Skeletal System: Parts & Function Main parts: Bones Cartilage Connective Tissue Function: Helps support your body parts Helps support your body during movement Helps protect your major organs: Skull protects the brain Sternum and ribs protects the heart and lungs Vertebra protect the spinal cord

Skeletal System Interactions Works with the muscular system to help you move.

Muscular System Function Helps you move. Moves materials through the body Main parts Muscles Tendons Ligaments Muscles in organs

Three types of muscles found in the body: Cardiac – found in the ( muscle) - attaches to the bones ( muscle) Smooth – lines and vessels. ( muscle)

Muscular Systems help you Helps you move Helps you move materials through the body Maintain homeostasis Skeletal muscles work in pairs: one contracts and the other returns to its original length.

Interactions with other systems Works with the skeletal system to help you move by your muscles pulling on your bones. Works with the nervous system and controls the types of movements: voluntary (under your control – ex: talking) and involuntary (NOT under your control – ex: heartbeat)

Three types of muscles found in the body: Cardiac – found in the heart ( muscle) Skeletal- attaches to the bones ( muscle) Smooth – lines organs and vessels. ( muscle)

Circulatory (Cardiovascular) System Function Carries blood and nutrients to the cells of the body Carries waste away from the cells, such as carbon dioxide. Main Parts Heart Blood (made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells & platelets) Veins Arteries

What it helps you do Arteries help carry oxygenated blood away from the heart Veins carry un-oxygenated blood toward the heart Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins. Gas exchange takes place here.

Interactions with other systems: Works with the respiratory system to help you transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Works with the excretory to help remove waste from the body. Works with the digestive system to transport nutrients. Works with the muscular system to help circulate nutrients.

Respiratory System Function Puts oxygen into the body & removes Carbon dioxide Main parts Lungs Nasal passages Throat Nose

What it helps you do Breathe Sustain life

Interactions with other systems: Circulatory – transports vital materials to the cells

Digestive System Function Takes food & breaks it down into nutrients the body needs

Digestive System Main parts: Mouth Stomach Liver Pancreas Small intestines Large intestines Rectum

What it helps you do It provides nutrients to your body’s cells

Interactions with other systems: Circulatory – helps transport nutrients to the body’s cells

Excretory System Functions Removes wastes from blood Removes harmful substances from blood Regulates body fluids

Excretory System Main Parts Kidneys Urinary bladder

What it helps you do Maintain homeostasis Removes waste

What system does it interact with: Circulatory – to help remove waste from the blood

Immune System Functions Fights off disease
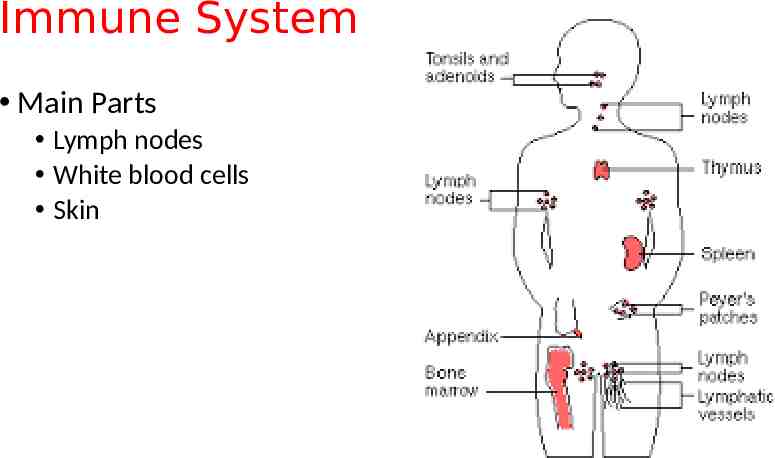
Immune System Main Parts Lymph nodes White blood cells Skin

What it helps you do Maintain a healthy body

Interactions with other systems: Circulatory, integumentary, lymphatic – helps fight diseases

Reproductive System Functions Produce offspring Males- make sperm Females- make eggs

Reproductive System Main Parts Male Penis Testes Female Uterus Ovary Vagina

What it helps you do Continuation of the species






