CMS IT Governance Process: Intro to the Target Lifecycle
29 Slides669.48 KB

CMS IT Governance Process: Intro to the Target Lifecycle INFORMATION NOT RELEASABLE TO THE PUBLIC UNLESS AUTHORIZED BY LAW: This information has not been publicly disclosed and may be privileged and confidential. It is for internal government use only and must not be disseminated, distributed, or copied to persons not authorized to receive the information. Unauthorized disclosure may result in prosecution to the full extent of the law. 1

Target Life Cycle Governance Process What this course covers: Section I: What is the TLC? Section II: Who is the TLC? Section III: A brief overview of the Four TLC phases 2

TLC Overview – Section I Section I What is the TLC? 3

Governance Framework A framework that: Promotes business flexibility Applies situational governance reviews instead of gate reviews Provides minimal disruption to the system development process Requires self governance by Project Teams Project Team Responsibility 4
Target Life Cycle (TLC) Planning Your Project We’ve moved most of the external oversight up front You must develop your ideas and direction prior to Acquisition Planning We’ve developed a team of IT SMEs to act as your consultants for IT planning Ensures due diligence and sound IT Planning Governance through Enablement 5

Team Responsibility Methodology Based There are an almost overwhelming number of governance laws and guidelines with which project teams must comply. Some areas in CMS have dedicated groups to ensure compliance with their particular scope, such as: Security Accessibility For other areas, project teams should follow processes in their specific methodology to fulfill the IT governance requirements 6

Potential for Audit Many paths to success Artifacts and documentation to support the design and development of the system must be available for Audit purposes, preferably on CMS infrastructure, so Project Teams must maintain and track it Interfacing with other systems, either within or outside of CMS, will require documentation acceptable to both parties A comprehensive set of templates which were developed for CMS’ previous governance framework are perfectly acceptable to use for the TLC Those optional templates are available on the TLC website, CMS.gov/TLC 7

Proactive Governance Proactive governance is the key! We cannot do this without business and system owner cooperation Eliminating formal periodic reviews does not remove the need for the supporting work to be done Every Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) has its own process of planning and documenting systems development Project Managers are now responsible for adherence to the standards of their chosen Project Management Methodology and SDLC that support governance goals 8

TLC Overview – Section II Section II Who is the TLC? 9

GRT Purpose & Goals The Governance Review Team Governance Review Team Advises Project Teams: How to proceed through the IT Governance process What resources are available to help How to properly develop and document their Business Case and Alternatives Analysis How to adhere to required governance oversight The Project Team is responsible for documenting the proposed solutions in their Business Case, for presentation to the Governance Review Board (GRB) 10
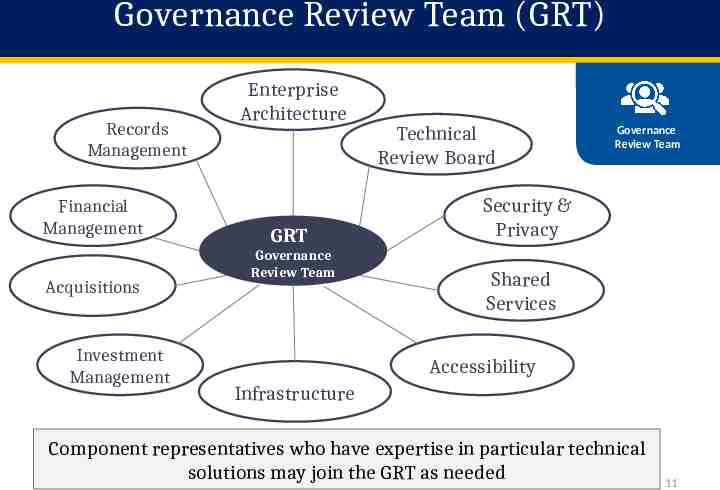
Governance Review Team (GRT) Records Management Financial Management Acquisitions Investment Management Enterprise Architecture GRT Governance Review Team Technical Review Board Governance Review Team Security & Privacy Shared Services Accessibility Infrastructure Component representatives who have expertise in particular technical solutions may join the GRT as needed 11

GRT Purpose & Goals (cont’d.) The GRT: Reviews the business case and alternatives analysis to ensure the application/ functionality is: Not duplicative of another effort Fills a need that cannot otherwise be addressed Aligns with the CMS IT Portfolio goals Governance Review Team Discusses alternative approaches for implementation (if any) of the desired system functionality or new application Makes recommendations to the Governance Review Board (GRB) 12

Governance Review Board (GRB) The Project Team will present the Business Case and Alternatives Analysis to the Governance Review Board (GRB) Governance Review Team This should be a high level presentation of the Business Case and Alternatives, presented by the Business Owner or Manager The GRB may ask technical questions, so there should be technical staff available at the presentation as well The GRB does not approve funding for a project, but is a prerequisite for requesting funding. 13
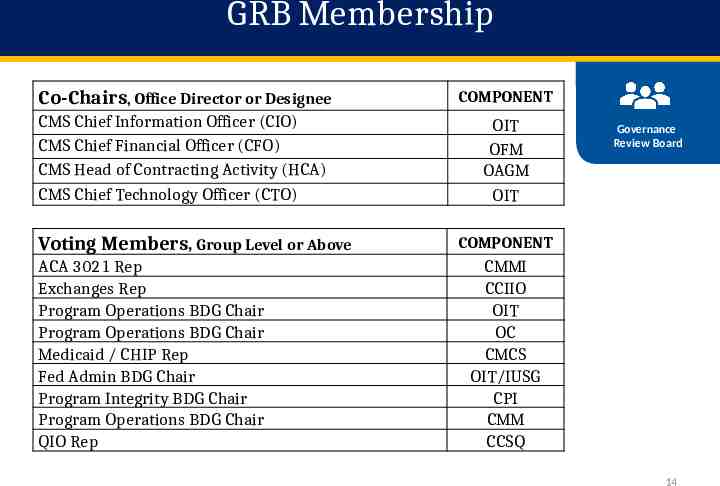
GRB Membership Co-Chairs, Office Director or Designee COMPONENT CMS Chief Information Officer (CIO) CMS Chief Financial Officer (CFO) CMS Head of Contracting Activity (HCA) CMS Chief Technology Officer (CTO) OIT OFM OAGM OIT Voting Members, Group Level or Above ACA 3021 Rep Exchanges Rep Program Operations BDG Chair Program Operations BDG Chair Medicaid / CHIP Rep Fed Admin BDG Chair Program Integrity BDG Chair Program Operations BDG Chair QIO Rep Governance Review Board COMPONENT CMMI CCIIO OIT OC CMCS OIT/IUSG CPI CMM CCSQ 14

Life Cycle ID (LCID) Governance Process If the GRB approves a project, it will be issued a Life Cycle ID (LCID) The LCID signifies that the project/investment has been reviewed and approved by the GRB If projects do not have a valid IT Life Cycle ID: OFM will not allocate funding to the project OAGM will not process contract actions 15

Project Team The Project or Program Team: Project Team Is led by CMS employee(s) as Project Sponsor/ Business Owner/Manager Must have an ISSO (Information Systems Security Officer) Will be responsible for developing and maintaining systems documentation that satisfies governance requirements Is encouraged to maintain the documentation on CMS infrastructure so that it is not lost when contractors change 16

TLC Phases - Section III Section III A brief overview of the Four TLC Phases 17

TLC Phase Summary CMS Target Life Cycle Phase Summary 18

Initiate Phase Fill out an Intake Form to start the TLC Governance process Document your business need Have a brief meeting with Enterprise Architecture and the TLC administrators to kick things off Get on the schedule for a GRT Meeting The GRT will provide guidance and input to the Project Team in crafting the business case and alternatives analysis in preparation for the GRB meeting 19

Initiate Phase (cont’d.) Demonstrate Due Diligence Document your Analysis of Alternatives Pros and cons of each alternative Estimate total life cycle costs for each alternative The Project Team presents the Business Case and Alternatives Analysis to the GRB for review The GRB may approve, disapprove, or ask for changes to the project/investment The GRB does not approve funding for a project, but is a prerequisite for requesting funding. 20

Initiate Phase Summary Key Objectives Clarify business needs Incorporate GRT input on alternatives Present Business Case to GRB Exit Criteria The Business Case and Alternatives Analysis are documented An approved solution is selected by the Project Team A Life Cycle ID is issued 21

Develop Phase When the Project Team has executed a contract action for development, the Develop Phase begins The Project Team defines the chosen project/product management methodology and Systems Development Lifecycle Methodology in their contract and planning documentation The Project Team creates the detailed user stories or requirements, designs and develops the solution, deploys it to a non-production environment, and tests it for compliance with technical and other Federal IT standards and requirements 22

Develop Phase Summary Key Objectives Satisfy information security, privacy, and Section 508 requirements Exit Criteria Obtain an Authorization to Operate (ATO) Successful Testing 23

Operate Phase Once deployed into Production, the Project Team is responsible for maintaining the availability and reliability of the system by ensuring that routine maintenance is performed and sound security practices are followed Most projects will be in Development and Operate phases at the same time for most of their life If major changes or development are needed, the project may have to go back to the Initiate Phase to get approval for the additional scope 24

Operate Phase Summary Key Objectives Maintain solution availability and performance Exit Criteria Decommission Decision 25

Retire Phase The Project Team creates and executes a decommissioning plan that complies with Federal guidelines for data disposition, hardware disposition, and any other considerations that must be met based on the individual system, Records Management (OSORA) must be consulted Other GRT resources are available for consultation on the planning and execution of the plan The Project Manager attests to the completion of the disposition plan when operations cease 26

Retire Phase Summary Key Objectives Properly retain or dispose of any system materials according to the appropriate retention schedule, including but not limited to: System data, software, hardware, and any other necessary system requirements & configurations Close out all related contractual actions and agreements Exit Criteria Project Manager attestation to the completion of the decommissioning checklist The Project Manager/Business Owner sends the attestation to the Governance Team 27
Additional TLC Resources Governance Review Team IT [email protected] Technical Review Board [email protected] TLC Website IT Governance - https://www.cms.gov/TLC Enterprise Architecture [email protected] Navigator [email protected] 28

Questions ? For questions about Governance or more information contact via Mail – IT [email protected] or visit IT Governance - https://www.cms.gov/TLC 29






