CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Chapter 8 State Government Section 1:
36 Slides1.02 MB
CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Chapter 8 State Government Section 1: The States Section 2: State Legislature Section 3: The State Executive Branch Section 4: State Courts 1 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 1: Key Terms Delegated Powers Reserved Powers Concurrent Powers Full Faith and Credit Clause Extradition 2 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT State Government Powers The Main Idea When the founding fathers wrote the Constitution, they did not want to hand too much power to the Federal Government. Delegated Powers were given to the federal government. Ex. Foreign Policy, Printing Money, Maintaining a Post Office, Defending the Country 3 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Powers Reserved for the States 10th Amendment of the Constitution states that any power not delegated to the federal govt. belongs to the people and the states. Also known as reserved powers. Est. Rules for health, safety, and welfare Marriage, Traffic regulations, and maintain education systems Have control over all govts. within their boundaries. (Cities, Towns, Townships, Counties) 4 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Law 101 Education is funded at many levels, mainly from taxes. Some states look towards alternatives to fund education, such as the lottery or slot machines. Is it fair that everyone should pay taxes to fund schools? Even if you have no children attending the school. What is your opinion about using lotteries or slot machines to pay for education? 5 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Concurrent Powers Powers shared by both the federal and state governments Examples of Concurrent Powers: Taxation Federal Income Tax, State income and property taxes Making and Enforcing Laws 6 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Powers of the State State Powers 7 Establish and Maintain Schools Establish local Governments Regulate business within the state Make marriage laws Provide for public safety Oversee elections Assume other powers not delegated to the national government nor prohibited to the states Shared Powers Maintain law and order Levy taxes Borrow money Charter banks Establish Courts Oversee public health and safety Enforce laws HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT State Constitutions Many states have their own Constitutions Most state constitutions have the following elements: Preamble State Affairs Bill of Rights Management Provisions Amendment Process Organization of Govt. Election Provisions 8 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT States Work Together Full Faith and Credit Clause ensures that each state will accept the decisions of civil courts in other states Ex. Marriage and birth certificates, wills, contracts, property deeds, etc. States also work together when it comes to criminals Extradition is the process of returning fugitives to another state for trial 9 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 1 Assessment Why might states amend their constitutions? Is it important for state governments to retain control of affairs within their own boarders? How might our federal system be different if states did not work together with the national government? 10 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 2 STATE LEGISLATURES 11 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 2: Key Terms 12 Bicameral Initiative Unicameral Referendum Constituents Recall HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT State Legislatures The Main Idea Although it may go by a different name in some states, every state has a lawmaking body. Legislators are elected officials that pass laws on the citizens behalf. They are organized to represent all state citizens equally. 13 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Organization 49 of the 50 states have a bicameral legislature. This means they have 2 houses. House of Representatives (larger house) Senate (smaller house) Which state has a unicameral legislature? Meaning one house called the senate Hint: These people are nicknamed the cornhuskers 14 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Organization (cont’d) State legislatures vary in size Alaska has the smallest with 40 reps and 20 senators New Hampshire has the largest with 400 reps and 24 senators States divide up the state into legislative districts. Each legislator represents the people within their district 15 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT PA Legislature 253 total Members 203 Representatives 50 Senators 16 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Your PA Legislators Rep. Phyllis Mundy (D) Swoyersville Pringle Luzerne Kingston Forty-Fort Courtdale 17 Sen. Lisa Baker (R) Swoyersville Pringle Kingston Forty-Fort Rep. Gerald Mullery(D) Plymouth Larksville Edwardsville Sen. John Yudichak(D) Luzerne Courtdale Plymouth Edwardsville HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Qualifications and Terms Every states’ qualifications vary by state Generally state senators must be 25 years old State reps must be 21 years old However there are some states that have lowered that age 18 for both reps and senators Terms Most states senators serve 4 year terms while reps serve 2 year terms 18 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON
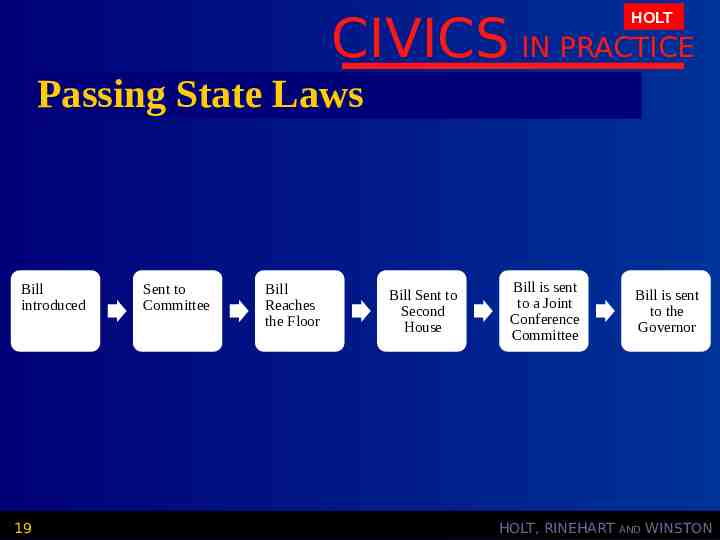
CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Passing State Laws Bill introduced 19 Sent to Committee Bill Reaches the Floor Bill Sent to Second House Bill is sent to a Joint Conference Committee HOLT, RINEHART Bill is sent to the Governor AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT How Citizens Participate in Lawmaking Legislators and Governors represent the people within their state It is these constituents that provide the input needed for legislators to help make the state better and run more efficiently 20 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Bypassing the Legislature Citizens can start a process called an initiative. Process by which citizens can start new legislation Citizens write a petition called a proposition. Once a required number of votes/signatures is reached it then appears on the ballot of the next general election. If the majority of people vote in favor, it then becomes law 21 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Bypassing the Legislature (cont’d) In many states the voters must approve certain bills passed by the legislature before it becomes law. This is a called a referendum. Some states allow for voters to remove elected officials from office. This process is known as a recall, it begins when a number voters sign a petition. 22 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 2: Assessment How might unequal representation harm certain citizens or areas of a state? What role do committees play in passing laws? Why are initiative, referendum, and recall important tools for citizens? 23 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 3 THE STATE EXECUTIVE BRANCH 24 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 3: Key Terms Governor Patronage Lieutenant Governor 25 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT The State’s Chief Executive The governor is the chief executive in each state. Leads the state govt., set priorities, make govt. appointments, and implement laws to meet the needs of their states 26 Tom Corbett (R) Governor HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Qualifications, Terms, and Compensation Most states require a governor to be 30 years old. Except California and Ohio the age is 18. Most governors serve 4 year terms. Except NH and VT which is 2 year terms. Salaries vary from state to state. Range from 105,000- 183,255(PA) 27 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Powers and Duties of the Governor 28 Chief Executive Power of the Budget Chief Legislator Political Party Leader Power to Make Head of State Police Appointments Power to Supervise State Employees (Some jobs are filled through patronage, people recommended by political leaders and National Guard Judicial Power to pardon certain prisoners HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Other State executive Officials Lieutenant Governor- similar to 29 vice president Secretary of State Attorney General State Treasurer State Auditor Superintendent of Public Instruction (Secretary or Education) Lt. Gov. Jim Cawley PA (R) HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 3: Assessment What are the primary powers and duties of most governors? How does the governor’s legislative power influence the types of bills legislators introduce? How are a the responsibilities of the lt. gov and the VP of US similar? How are they different? 30 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 4 STATE COURTS 31 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 4: Key Terms Penal Code- set of criminal laws Missouri Plan- method of selecting judges in which a committee prepares a list of qualified judges, the governor appoints a judge from the list, and the judge faces voters in next election 32 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT State Court Cases States are free to set up their own court system to meet its states needs Each state creates its on set of criminal laws or penal code State judges hear the case and make the final decision on punishment They also hear civil cases Civil cases do not determine guilt or innocence but how much money or property is owed. 33 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON
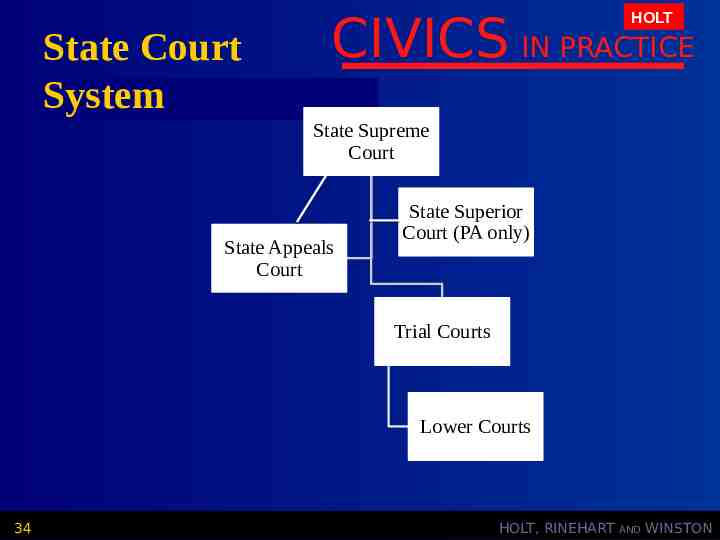
State Court System CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT State Supreme Court State Appeals Court State Superior Court (PA only) Trial Courts Lower Courts 34 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Election of Judges & Terms of Service People that support elected judges argue that elections make judges responsible to the people who will be affected by their decisions. The counter point is that judges may make decision based on what the people will like so they can be re-relected. Terms of service vary by state This is why some states have adopted the Missouri Plan 35 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON

CIVICS IN PRACTICE HOLT Section 4: Assessment What are the 4 levels of the state court system? Why do most states have low level courts such as small claims and traffic courts? Do you think that electing judges is the best way to select state court judges? Why or why not? 36 HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON






