Chapter 9: The Client/Server Database Environment 註 : 於 11 版為 Chapter
27 Slides940.00 KB

Chapter 9: The Client/Server Database Environment 註 : 於 11 版為 Chapter 8 楊立偉教授 台灣大學工管系 2014 Fall 1
Client/Server Systems Networked computing model 網路運算模型 Processes distributed between clients and servers 將要處理的工作散在 Client 與 Server Client–Workstation (usually a PC) that requests and uses a service Server–Computer (PC/mini/mainframe) that provides a service For DBMS, server is a database server Chapter 9 2
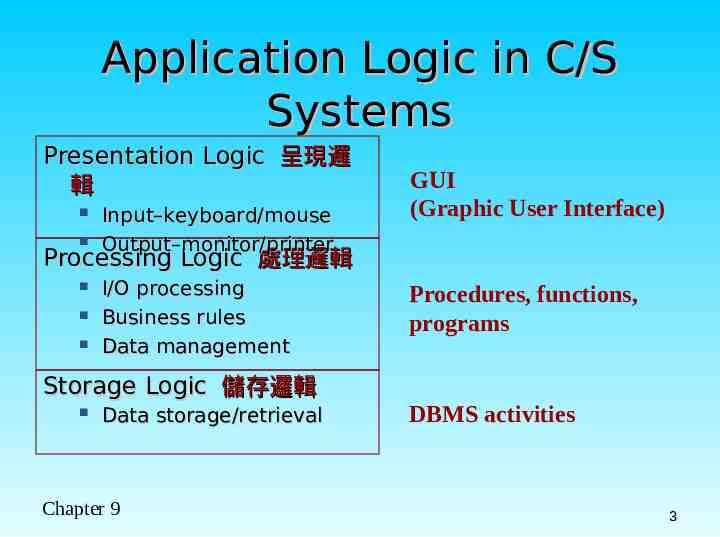
Application Logic in C/S Systems Presentation Logic 呈現邏 輯 Input–keyboard/mouse Output–monitor/printer GUI (Graphic User Interface) Processing Logic 處理邏輯 I/O processing Business rules Data management Storage Logic 儲存邏輯 Data storage/retrieval Chapter 9 Procedures, functions, programs DBMS activities 3
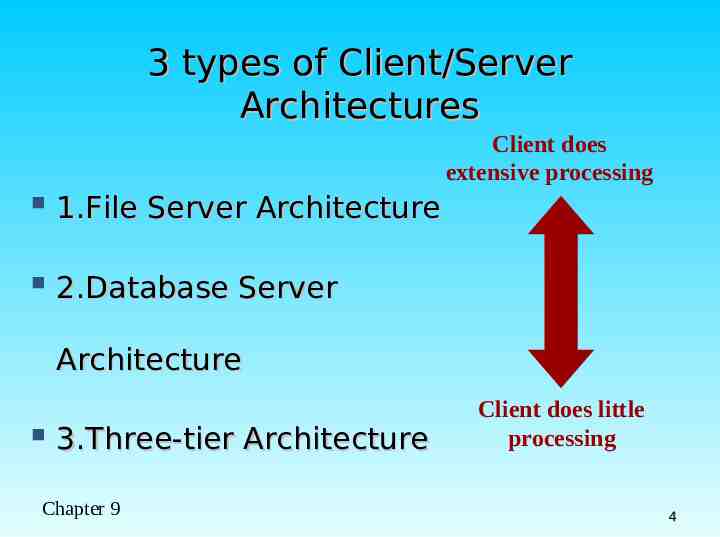
3 types of Client/Server Architectures Client does extensive processing 1.File Server Architecture 2.Database Server Architecture 3.Three-tier Architecture Chapter 9 Client does little processing 4
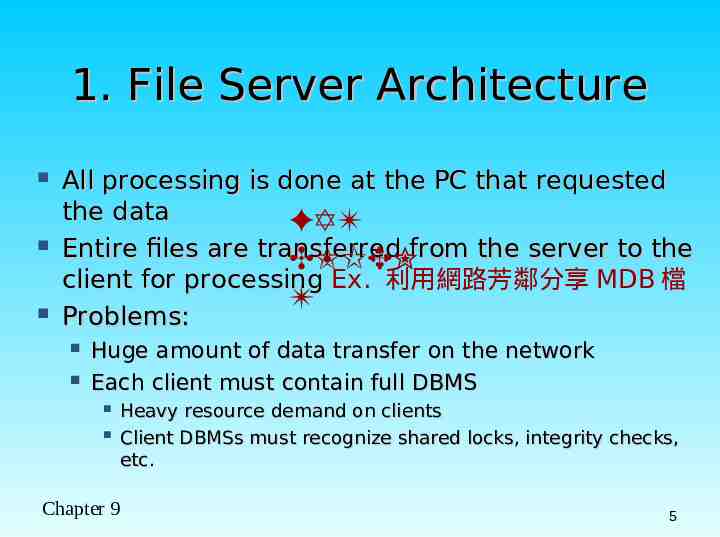
1. File Server Architecture All processing is done at the PC that requested the data FAT Entire files are transferred CLIENfrom the server to the client for processing Ex. 利用網路芳鄰分享 MDB 檔 T Problems: Huge amount of data transfer on the network Each client must contain full DBMS Heavy resource demand on clients Client DBMSs must recognize shared locks, integrity checks, etc. Chapter 9 5
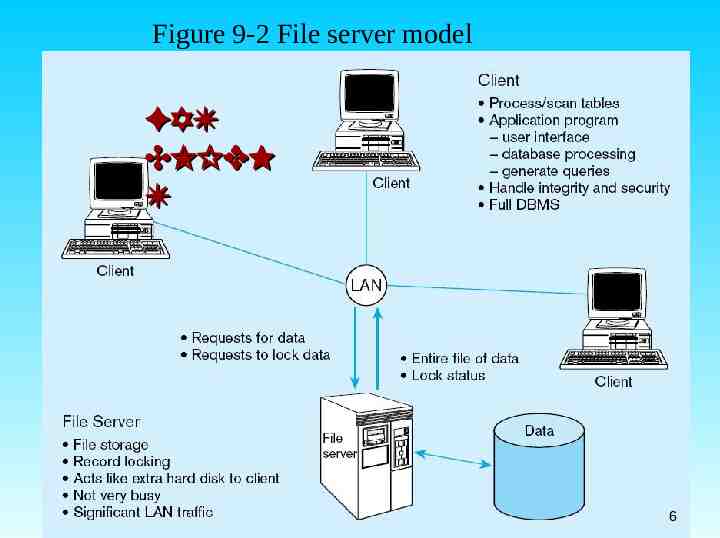
Figure 9-2 File server model FAT CLIEN T Chapter 9 6
2. Two-Tier Database Server Architectures Client is responsible for I/O processing logic Some business rules logic Server performs all data storage and access processing DBMS is only on server Chapter 9 7

Advantages of Two-Tier Approach Clients do not have to be as powerful Greatly reduces data traffic on the network Improved data integrity since it is all processed centrally Stored procedures : performs some business rules done on server 把較常用或重要的程序預先寫好放在 DBMS 內 Chapter 9 8

Advantages of Stored Procedures Compiled SQL statements 編譯後執行 快 Reduced network traffic 佔較少的網路 流量 Improved security 安全性較高 Improved data integrity 資料完整性較 高 Thinner clients 前端運算量較少 Chapter 9 9
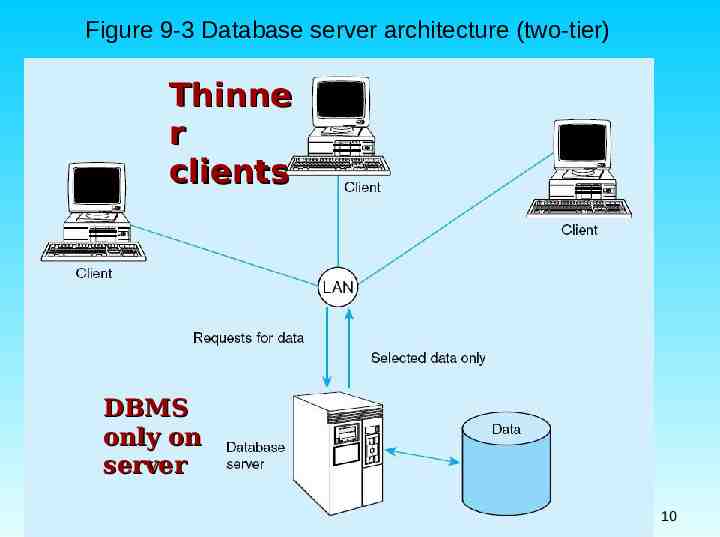
Figure 9-3 Database server architecture (two-tier) Thinne r clients DBMS only on server Chapter 9 10
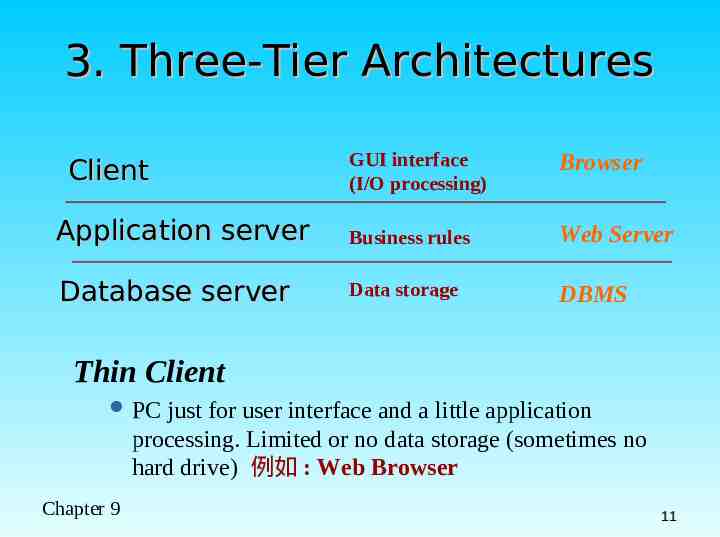
3. Three-Tier Architectures GUI interface (I/O processing) Browser Application server Business rules Web Server Database server Data storage DBMS Client Thin Client PC just for user interface and a little application processing. Limited or no data storage (sometimes no hard drive) 例如 : Web Browser Chapter 9 11
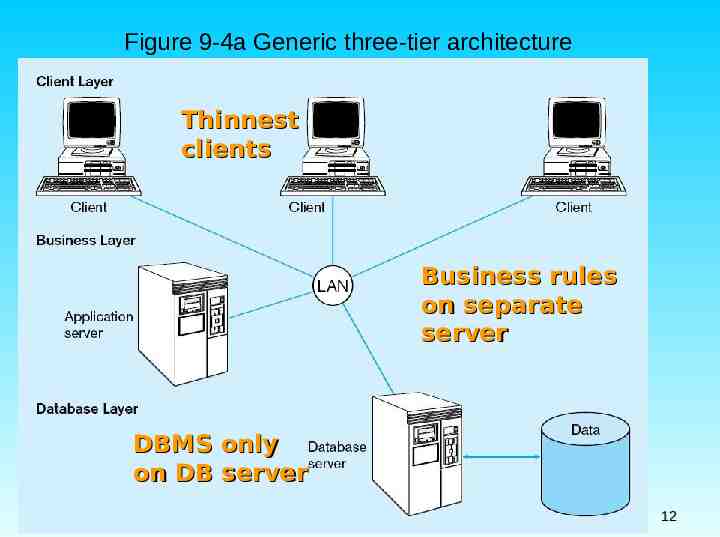
Figure 9-4a Generic three-tier architecture Thinnest clients Business rules on separate server DBMS only on DB server Chapter 9 12
Advantages of Three-Tier Architectures Scalability ( 在佈署與效能上 ) 具擴充性 Technological flexibility 具技術彈性 Long-term cost reduction 長期低本降 低 Better match of systems to business needs 較符合企業所需 Reduced risk 風險降低 Chapter 9 13

Application Partitioning Placing portions of the application code in different locations (client vs. server) AFTER it is written 重新切分程式執行的位 置 Advantages Improved performance Improved interoperability Balanced workloads Chapter 9 14
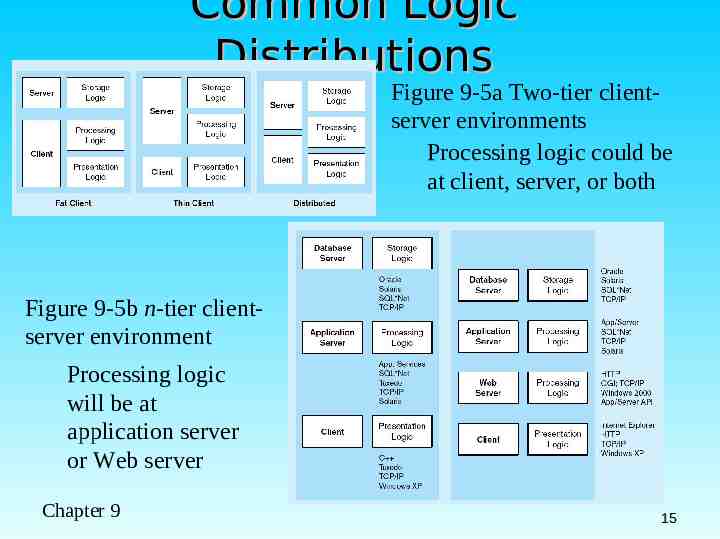
Common Logic Distributions Figure 9-5a Two-tier clientserver environments Processing logic could be at client, server, or both Figure 9-5b n-tier clientserver environment Processing logic will be at application server or Web server Chapter 9 15

Role of the Mainframe 大型 主機 Mission-critical legacy systems tend to remain on mainframes When moving mission critical systems from mainframe to distributed client/server systems 例如 : 銀行核心系統的移轉 Determining which code belongs on server vs. client Identifying potential conflicts with code from other applications Ensuring sufficient resources exist for anticipated load Rule of thumb 移轉的經驗法則 Mainframe for centralized data that does not need to be moved Client for data requiring frequent user access, complex graphics, and user interface Chapter 9 16

Benefits of Moving to Client/Server Architecture Staged delivery of functionality speeds deployment 功能可分階段完成 GUI ease application use 將使用者界面與應用分 離 Flexibility and scalability facilitates business process reengineering 更容易擴充 具有彈性 Reduced network traffic 只傳處理過的資料 Facilitation of Web-enabled applications 易於轉為 Web 或行動應用 Chapter 9 17

Middleware 中介軟體 Software that allows an application to interoperate with other software No need for programmer/user to understand internal processing Accomplished via Application Program Interface (API) The “glue” that holds client/server applications together Chapter 9 18
Database Middleware ODBC–Open Database Connectivity Most DB vendors support this JDBC–Java Database Connectivity 可視為 Java 版的 ODBC Special Java classes that allow Java applications/applets to connect to databases OLE-DB Microsoft enhancement of ODBC Chapter 9 19

Using ODBC to Link External Databases Stored on a Database Server Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) Required parameters: API provides a common language for application programs to access and process SQL databases independent of the particular RDBMS that is accessed ODBC driver Back-end server name Database name User id and password Additional information: Data source name (DSN) Windows client computer name Client application program’s executable name Chapter 9 20
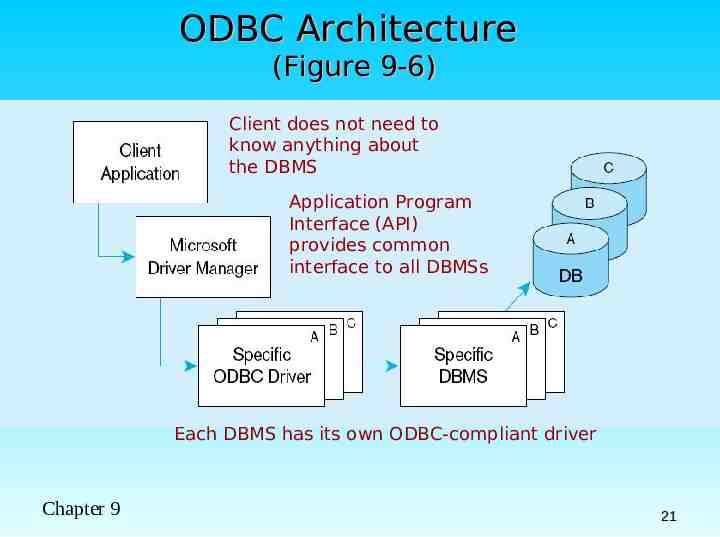
ODBC Architecture (Figure 9-6) Client does not need to know anything about the DBMS Application Program Interface (API) provides common interface to all DBMSs Each DBMS has its own ODBC-compliant driver Chapter 9 21
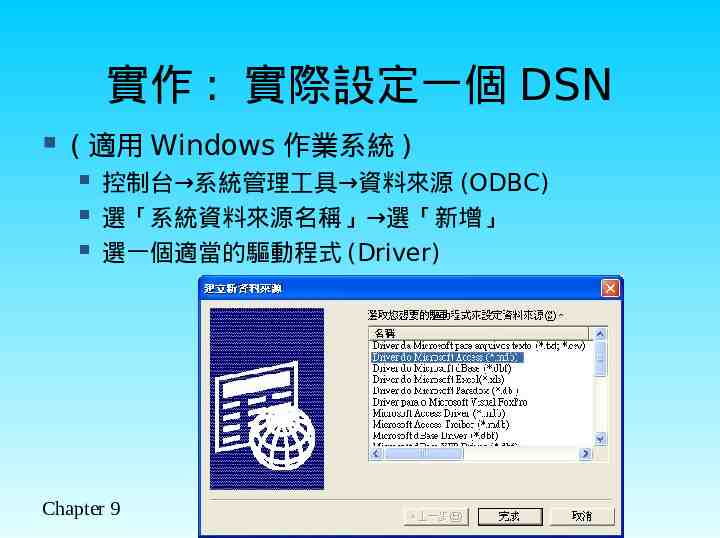
實作 : 實際設定一個 DSN ( 適用 Windows 作業系統 ) 控制台 系統管理工具 資料來源 (ODBC) 選「系統資料來源名稱」 選「新增」 選一個適當的驅動程式 (Driver) Chapter 9
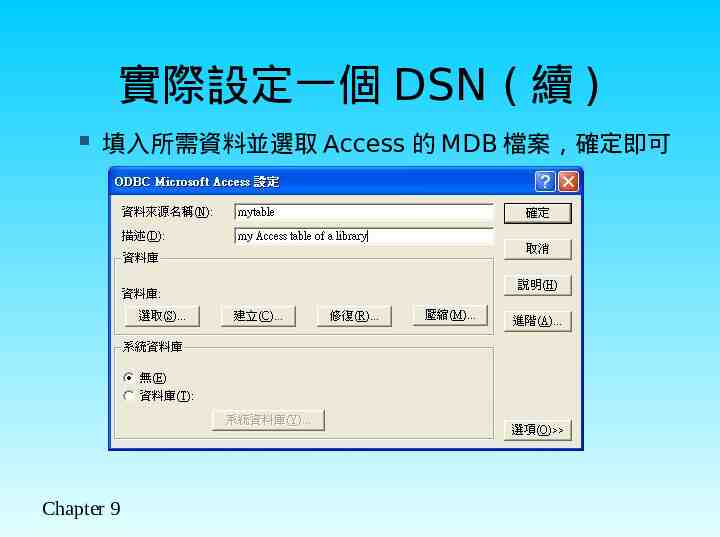
實際設定一個 DSN ( 續 ) 填入所需資料並選取 Access 的 MDB 檔案,確定即可 Chapter 9
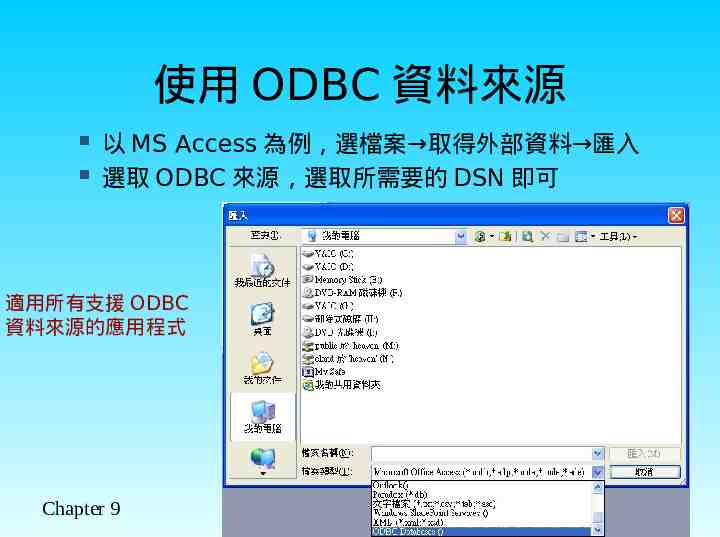
使用 ODBC 資料來源 以 MS Access 為例,選檔案 取得外部資料 匯入 選取 ODBC 來源,選取所需要的 DSN 即可 適用所有支援 ODBC 資料來源的應用程式 Chapter 9
Web/DB Application Components Database server – hosts the DBMS Web server – receives and responds to browser requests using HTTP protocol e.g. Apache, MS IIS (Internet Information Services) Application server – software for creating dynamic web sites e.g. Oracle, MS SQL Server, MS Access, MySQL e.g. MS ASP .NET framework, Java EE, PHP Web browser – client program that sends web requests and receives web pages e.g. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Safari, Google Chrome Chapter 9 25

Static page requests .htm or .html requests handled by the Web server Dynamic page requests .jsp, .aspx, and .php requests are routed to the application server Server-side processing by JSP servlet, ASP .NET application, or PHP Database access via JDBC, ODBC, ADO .NET, or other database middleware Chapter 9 26
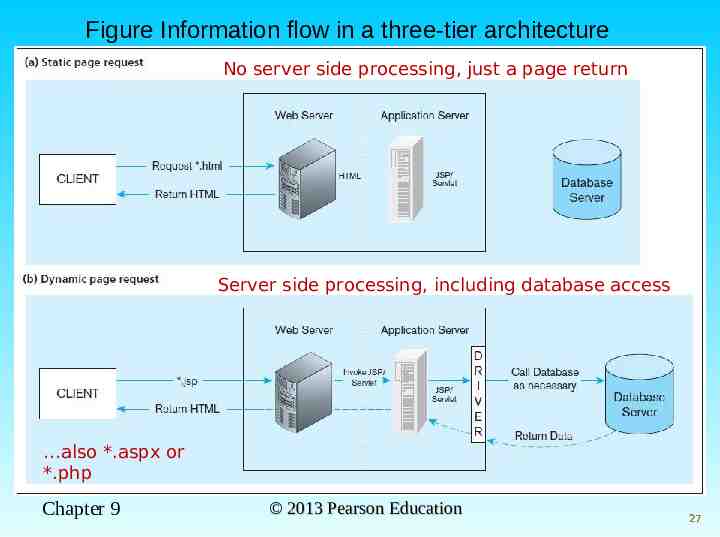
Figure Information flow in a three-tier architecture No server side processing, just a page return Server side processing, including database access also *.aspx or *.php Chapter 9 2013 Pearson Education 27






