Chapter 5: Principles of ServiceOriented Computing Service-Oriented
10 Slides515.00 KB

Chapter 5: Principles of ServiceOriented Computing Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents – Munindar P. Singh and Michael N. Huhns, Wiley, 2005

Highlights of this Chapter Chapter 5 Use Cases Service-Oriented Architectures Major Benefits Composing Services Spirit of the Approach Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 2
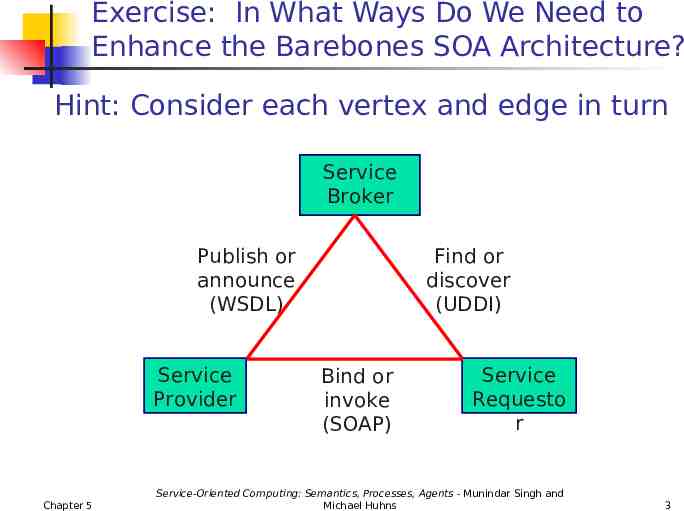
Exercise: In What Ways Do We Need to Enhance the Barebones SOA Architecture? Hint: Consider each vertex and edge in turn Service Broker Publish or announce (WSDL) Service Provider Chapter 5 Find or discover (UDDI) Bind or invoke (SOAP) Service Requesto r Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 3

Description The description should be unambiguous, formal representations of A service’s functionality A service’s nonfunctional attributes A user’s needs and preferences Chapter 5 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 4

Engagement Chapter 5 Architecture: P2P, messaging Transactions: replications, recovery Coordination Workflows and processes Choreographies Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 5

Collaboration Chapter 5 Reasoning Consistency maintenance Negotiation Organizational modeling Business protocols, interaction patterns Contracts, monitoring, and compliance Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 6

Discovery and Selection Finding the right services Semantic matchmaking Team matchmaking: creating functioning collaborations (organizations) Economic selection Reputation and recommendation Distributed architectures Accommodating domain-specific or idiosyncratic qualities of service Trust Chapter 5 Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 7
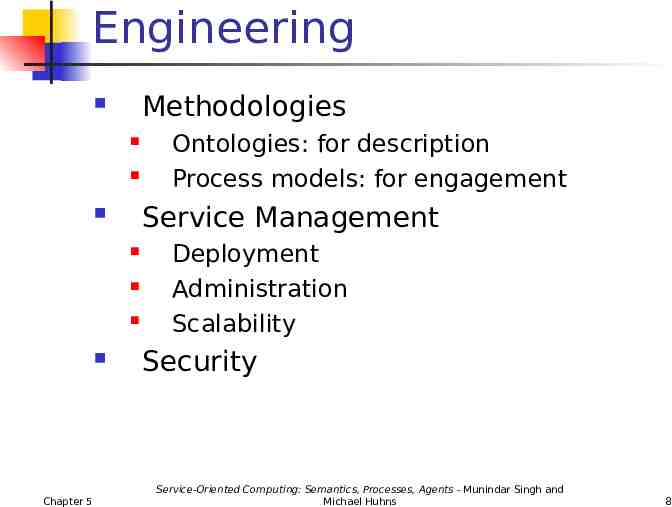
Engineering Methodologies Service Management Chapter 5 Ontologies: for description Process models: for engagement Deployment Administration Scalability Security Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 8

Key Concepts for an SOA Chapter 5 Loose coupling Implementation neutrality Flexible configurability Persistence Granularity Teams Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 9

Chapter 5 Summary Does moving to services create so many problems? No, these are the needs of open environments As computing moves from closed to open environments, virtually every technical aspect is up for grabs Chapter 5 Services merely highlight them Great research and practical opportunities Think of real-life service engagements Service-Oriented Computing: Semantics, Processes, Agents - Munindar Singh and Michael Huhns 10