Open Coding Presented by Shahedul Huq Khandkar 1
24 Slides560.67 KB

Open Coding Presented by Shahedul Huq Khandkar 1

Outline Overview Building Concepts When to stop coding? Research Group Size Open Coding in DQA Exercise Critics 2

Qualitative Data Analysis (QDA) Notice, Collect and think about interesting things[1] QDA is a non-linear process Notice things Analyze Data [1] Qualitative Data Analysis. John V. Seidel Collect Data 3

Introduction Express your thoughts Analyze and share ideas Compare with existing theories Choose the right name 4

Building Concepts Break down the data Find relations, similarities & Dissimilarities Mark important sections with labels or “codes” rebellious act Interviewer: Tell me about teens and drug use. Respondent: I think teens use drugs as a release from their parents. Well, I don’t know. I can only talk for myself. Experience 5

Abstracting Concepts In vivo codes – Words taken from data Constructed Codes – Created by researcher Interviewer: Tell me about teens and drug use. Respondent: Well, I don’t know. I can only talk for myself. For me, it was an experience. You hear a lot about drugs. Experience Drag Talks 6

Record Concepts Thoughts that can’t be expressed with few words Interviewer: Tell me about teens and drug use. Respondent: I think teens use drugs as a release from their parents Memo: The first thing that strikes me in this sentence is the work “use”. This is a strange term because, when taken out of the context of drug taking, the work means that an object or a person is being employed for some purpose. It implies a willful and directed act. In making a comparison, when I think about a computer, I think about employing it to accomplish a task. I think of it as being at my disposal. Source: Basics of Qualitative Research, Second Edition by Anselm Strauss & Juliet Corbin 7

Guidelines for Memo Glaser’s (1978) guidelines for effective memos: – Keep memos separate from data – Stop coding when an idea for memo occurs – Collapse codes when similar memos found – When you have two ideas, add two separate memos 8

Defining Categories When you have pages of codes – Find similarities & group them in categories Example: – Communication: { Email, Telephone Conversation, Text Message, Voice Mail} 9

When to Stop Coding? When you are not really finding any new concepts – Go to the next level (i.e. Selective Coding) – Use analytic tools to collect more information 10

Levels of Detail in Coding Line by line coding Code against – Sentences or Paragraphs – Chapters or Documents 11

Doing Open Coding with peers Concept definitions become more exact Data perspective is maintained more consistently Generally, more number of phenomena are discovered and processed Source: A Coding Scheme Development Methodology Using Grounded Theory for Qualitative Analysis of Pair Programming. Stephan Salinger, Laura Plonka, Lutz Prechelt. Berlin 12
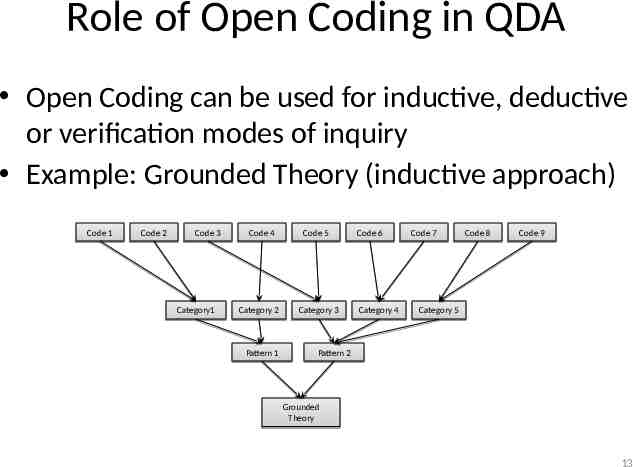
Role of Open Coding in QDA Open Coding can be used for inductive, deductive or verification modes of inquiry Example: Grounded Theory (inductive approach) Code 1 Code 2 Code 3 Category1 Code 4 Category 2 Pattern 1 Code 5 Category 3 Code 6 Category 4 Code 7 Code 8 Code 9 Category 5 Pattern 2 Grounded Theory 13

Exercise 14

Sample Data An interview with a woman in her 20s – Its about drug use by teens – The interviewer didn’t have preset questions – It was recorded and later transcribed 15
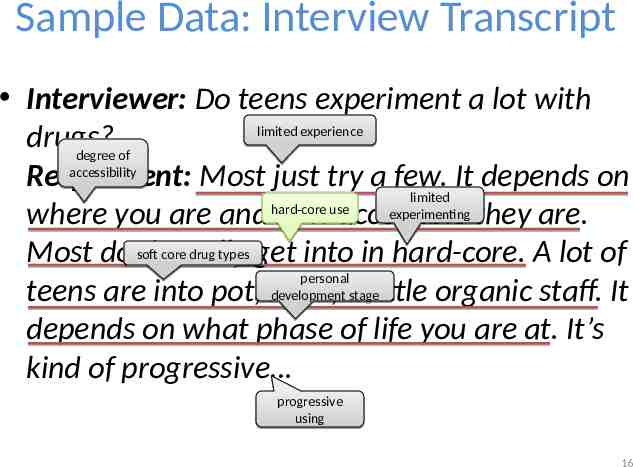
Sample Data: Interview Transcript Interviewer: Do teens experiment a lot with limited experience drugs? degree of accessibility Respondent: Most just try a few. It depends on limited hard-core use experimenting they are. where you are and how accessible soft core drug types get into in hard-core. A lot of Most don’t really personal developmenta stage teens are into pot, hash, little organic staff. It depends on what phase of life you are at. It’s kind of progressive progressive using 16

Open Coding using Pen & Paper Source: http://www.flickr.com/photos/jepoirrier/376900808/sizes/o/ 17
Automated Tools Atlas.ti – Desktop application – Commercial License – Supports different Coding styles (i.e. invivo, constructed) 18

Automated Tools (2) Saturate – Web Application – Free – Supports: constructed coding and memo. Source: http://www.saturateapp.com. Developed by Dr. Sillito 19

Do Open Coding using Saturate http://vimeo.com/6736972 20

Benefits Hard to miss any critical information Instead of assumption, theories emerge from data 21

Critics Tedious and time consuming process Often difficult to decide when to stop If missed something, may need to restart 22

Resources Books: – Basics of Qualitative Research, Second Edition by Anselm Strauss & Juliet Corbin – Nursing research: principles and methods by Denise F. Polit, Cheryl Tatano Beck – Symbolic Interactionism. Bulmer H. Publications: – Qualitative Data Analysis. John V. Seidel – A Coding Scheme Development Methodology Using Grounded Theory for Qualitative Analysis of Pair Programming. Institut für Informatik, Freie Universität Berlin – Building Inductive Theory of Collaboration in Virtual Teams: An Adapted Grounded Theory Approach. S. Sarker, F. Lau, S. Sahay 23

Question? 24






