Nurse Residency Programs: A Transition into Practice Deidre
13 Slides191.81 KB

Nurse Residency Programs: A Transition into Practice Deidre Dennison RN NUR 444 – Nursing Leadership SUNYIT

Introduction Purpose: To investigate the efficacy of nurse residency programs (NRPs) on new graduate nurse retention in general by performing literature reviews as well as comparing the overall trends to the outcomes of Albany Medical Center’s NRP Audience: New graduate registered nurses (RNs & GNs) employed at AMC & other institutions nationwide

Preceptor Role/Information I worked with a staff member at the Center for Learning & Development at Albany Medical Center – a separate off-site center dedicated to continued education and extensive orientation/course offerings My experience included multiple NRP sessions, hospital critical care nursing leadership meetings, education & resuscitation committee meetings, follow-up with NRP ‘cohort group’(ICU & cardiovascular)

Significance to Nursing According to Rhodes et. al. (2013), newly licensed registered nurses (NLRNs) make up approximately 10% of the clinical staff in hospitals Turnover rates of NLRNs within the first year averages from 35% to 61% Contributes to increased hospital costs, staffing shortages, and quality of care

Why the High Turnover? Factors that have been shown to add to new graduate nurse turnover include: Stress Ineffective orientation Working ‘short’ Scare resources Group cohesion/support Feelings of being unprepared for the multiple roles associated with nursing

Characteristics of NRPs Focus of NRPs include clinical skills, but the focus is more on professional skills: Critical thinking Time management/organization Prioritization Appropriate delegation Professional/Interdisciplinary communication Effective patient teaching/health literacy Dealing with difficult patients and families Stress management

Benefits of NRPs Provides a ‘cohort group’ to new registered nurses which meets socialization needs & which the new grad can express their successes & frustrations Promotes leadership skills Reduces newly graduated registered nurse turnover from the 30% range into the single digits in some cases (Trepanier, Early, Ulrich, & Cherry 2012) Reduces hospital costs - for every nurse that leaves a position, it costs the hospital between 40,000 - 64,000 (Baggot, et. al. 2013)

Benner’s Novice-to Expert Theory Based on the changes of practice as nurses progress in their field, gain more experience, and develop more effective clinical/professional skills Evolves in five stages throughout the nurse’s career “Movement from reliance on abstract principles to use of past concrete examples as paradigms” (Hood, 2010, p.13)
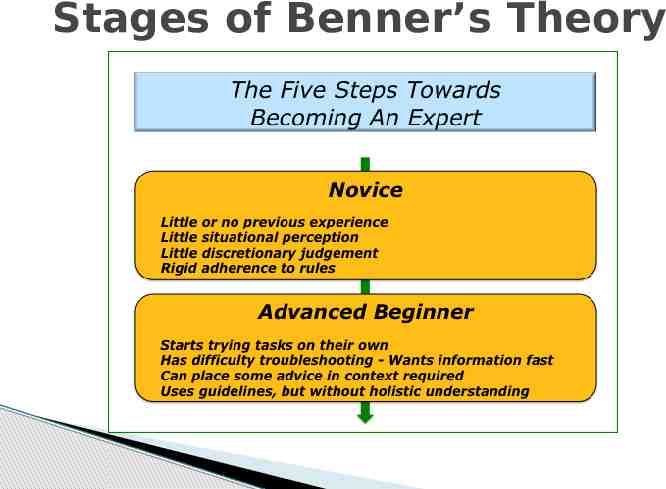
Stages of Benner’s Theory
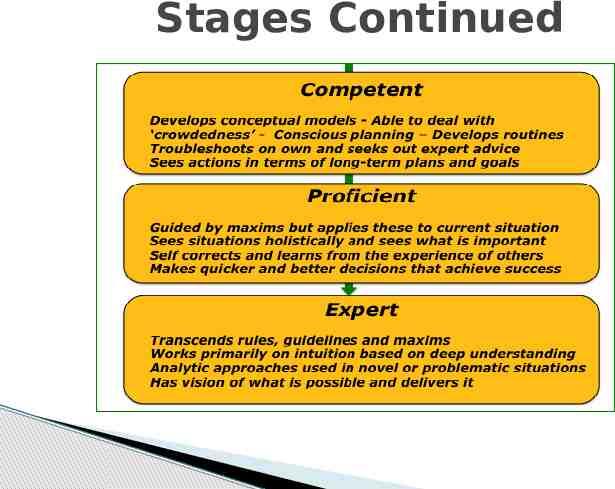
Stages Continued

Experience With NRPs at Albany Medical Center The organization has been using NRPs for almost three years as mandatory orientation for new graduate registered nurses 12 month program Requires research Power Point presentation to nursing leadership at the end of the program by smaller groups based on specialty Improved new grad retention rates beginning the first year and beyond My agreement with Albany Med prohibits me from releasing specific figures as the findings are being prepared for publication in the future

Summary NRPs can be an effective way to reduce new graduate registered nurse turnover along with the associated expenses & other negative results of turnover Cost analysis shows that although NRPs require financial and time investments, they are still less costly than high turnover expenses Provides a more level playing field in regards to practice by nurses with various levels of education/preparation

References Hood, L. J. (2010). Leddy & pepper's conceptual bases of professional nursing. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health. Theisen, J. L., & Sandau, K. E. (2013). Competency of New Graduate Nurses: A Review of Their Weaknesses and Strategies for Success. Journal Of Continuing Education In Nursing, 44(9), 406-414. Trepanier, S., Early, S., Ulrich, B., & Cherry, B. (2012). New Graduate Nurse Residency Program: A Cost-Benefit Analysis Based On Turnover and Contract Labor Usage. Nursing Economic , 30(4), 207214. Rhodes, C., Radziewicz, R., Amato, S., Bowden, V., Hazel, C., McClendon, S., & . McNett, M. (2013). Registered Nurse Perceptions After Implementation of a Nurse Residency Program. Journal Of Nursing Administration, 43(10), 524-529.






