IETF 101, London Coordinated Address Space Management (CASM)
10 Slides249.00 KB

IETF 101, London Coordinated Address Space Management (CASM) Architecture draft-li-opsawg-address-pool-management-arch-00 China Telecom : Chen Li , Chongfeng Xie ( Presenter) Juniper Networks : Rakesh Kumar Telecom Italia: Fioccola Giuseppe Huawei : Weiping Xu, Shucheng(Will) Liu ZDNS: Di Ma Tsinghua University : Jun Bi 1

Scope of this Draft A general architecture is defined to meet the requirements of automatic address/pool management and allocation in wide-variety of scenarios. It can help to reduce the workload of the existing manual configuration approaches, and also use the address resource more efficiently. This can be a basic document for further work, such as interface modeling and workflow. 2
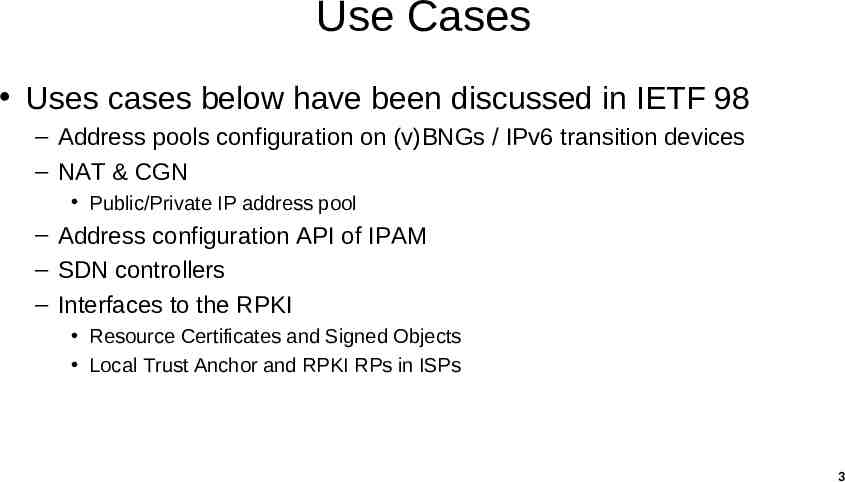
Use Cases Uses cases below have been discussed in IETF 98 – Address pools configuration on (v)BNGs / IPv6 transition devices – NAT & CGN Public/Private IP address pool – Address configuration API of IPAM – SDN controllers – Interfaces to the RPKI Resource Certificates and Signed Objects Local Trust Anchor and RPKI RPs in ISPs 3
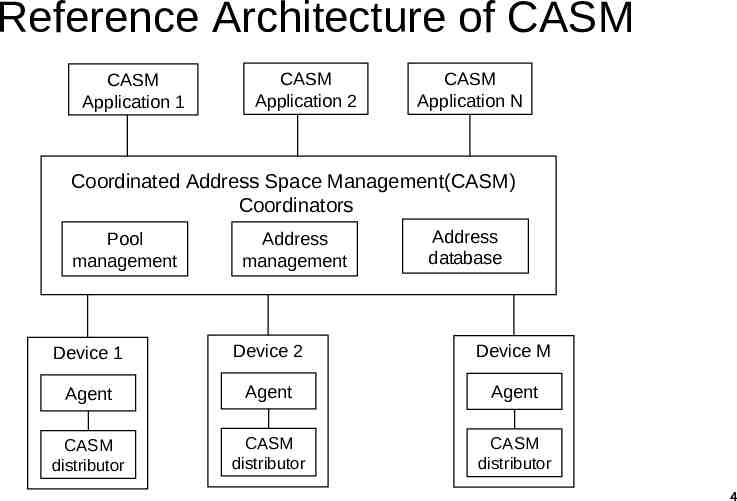
Reference Architecture of CASM CASM Application 1 CASM Application 2 CASM Application N Coordinated Address Space Management(CASM) Coordinators Pool management Address management Address database Device 1 Device 2 Device M Agent Agent Agent CASM distributor CASM distributor CASM distributor 4
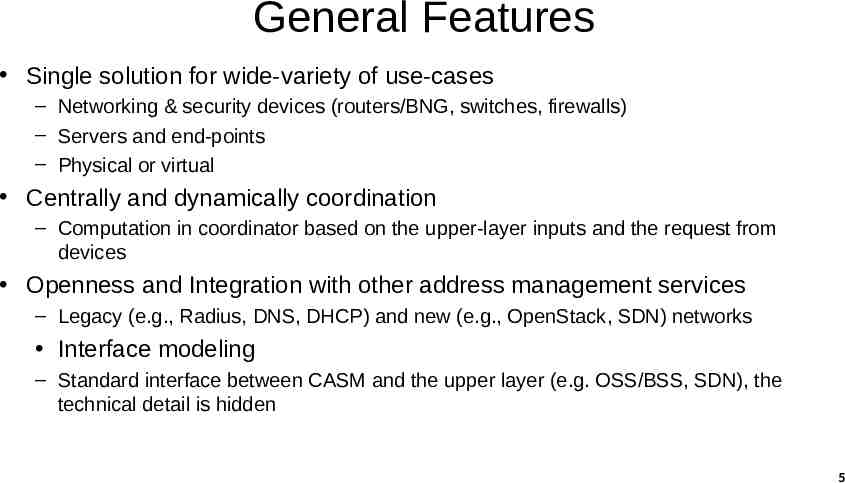
General Features Single solution for wide-variety of use-cases – Networking & security devices (routers/BNG, switches, firewalls) – Servers and end-points – Physical or virtual Centrally and dynamically coordination – Computation in coordinator based on the upper-layer inputs and the request from devices Openness and Integration with other address management services – Legacy (e.g., Radius, DNS, DHCP) and new (e.g., OpenStack, SDN) networks Interface modeling – Standard interface between CASM and the upper layer (e.g. OSS/BSS, SDN), the technical detail is hidden 5

Requirements For the Interfaces Functional requirements – – – – Dynamic allocation and reclaiming Generic address assignment policies Address pools management: Address management: Unicast(Private/Public v4 addresses, v6 addresses), Multicast General operational requirements – – – – Authentication and Authorization Audit Logging Error notification Aggregated view Interface modeling requirements – – – – – Functional attributes such as switch, router, firewall, server, end-point Form-factoral attributes such as physical, virtual Network segment identifier, such as VLAN, VxLAN or other user-defined value Addressing scope attributes, such as private, public, VPN, unicast, multicast Extensible user-defined attributes 6
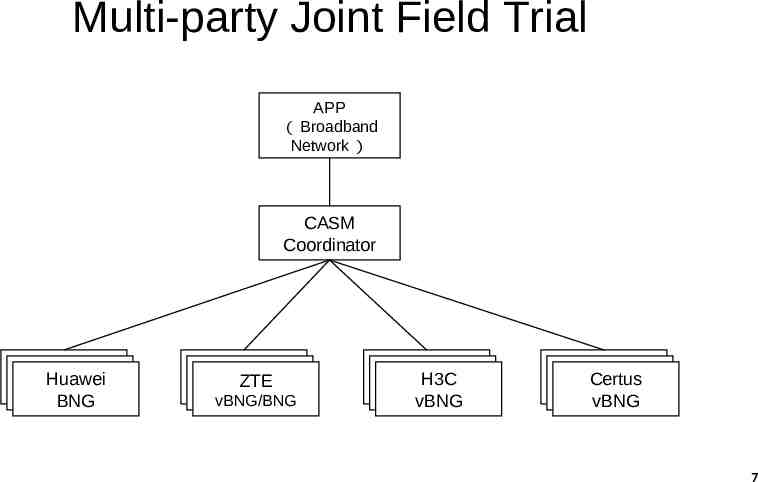
Multi-party Joint Field Trial APP ( Broadband Network ) CASM Coordinator Huawei Huawei Huawei BNG BNG BNG ZTE ZTE ZTE vBNG/BNG vBNG/BNG vBNG/BNG H3C H3C H3C vBNG vBNG vBNG Certus Certus Certus vBNG vBNG vBNG 7

Moving forward Request more reviews and refine the document Interface definition in other new drafts, any contributions are welcome Adopted as a WG doc ? 8

Acknowledgements Comments and suggestions received from Benoit Claise, Fred baker , Andrew Sullivan , Dave Thaler, Sheng Jiang , Brian Carpenter, Georgios Karagiannis, Suresh Krishnan, etc 9
Thank you! Q&A 10