■ Essential Question: – What role did the United States play in
17 Slides4.97 MB

Essential Question: – What role did the United States play in fighting in the Pacific during World War II? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 11.5: – “Fighting World War II in the Pacific” notes
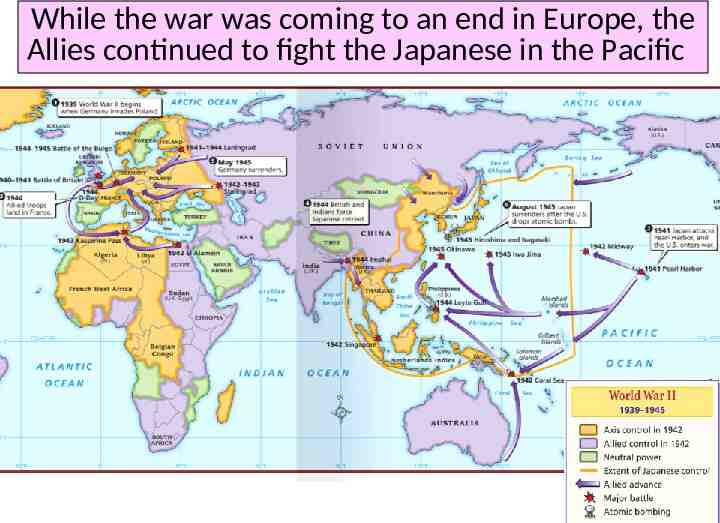
While the war was coming to an end in Europe, the Allies continued to fight the Japanese in the Pacific

After the attack on Pearl Harbor, the USA sent troops to the Pacific theater The Pacific war revealed a new kind of fighting by using aircraft carriers In May 1942, the Battle of Coral Sea was the first time aircraft carriers fired on one another The turning point in the war in the Pacific came at the Battle of Midway After Midway, the Allies began to regain islands controlled by Japan
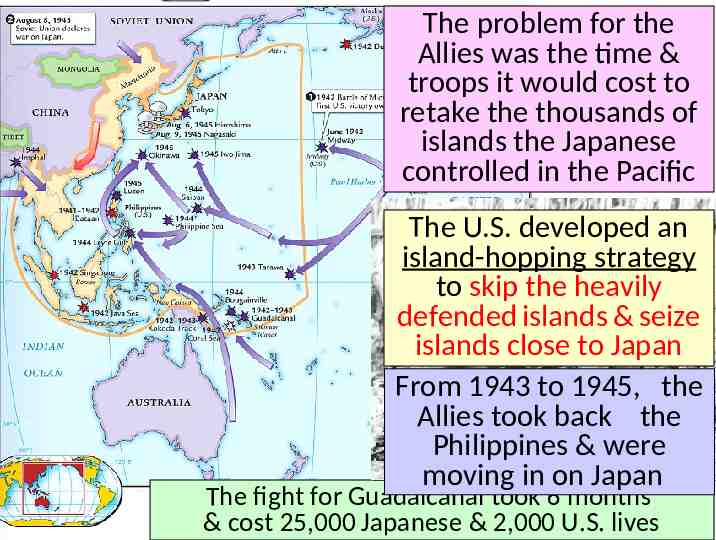
The problem for the Allies was the time & troops it would cost to retake the thousands of islands the Japanese controlled in the Pacific The U.S. developed an island-hopping strategy to skip the heavily defended islands & seize islands close to Japan From 1943 to 1945, the Allies took back the Philippines & were moving in on Japan The fight for Guadalcanal took 6 months & cost 25,000 Japanese & 2,000 U.S. lives
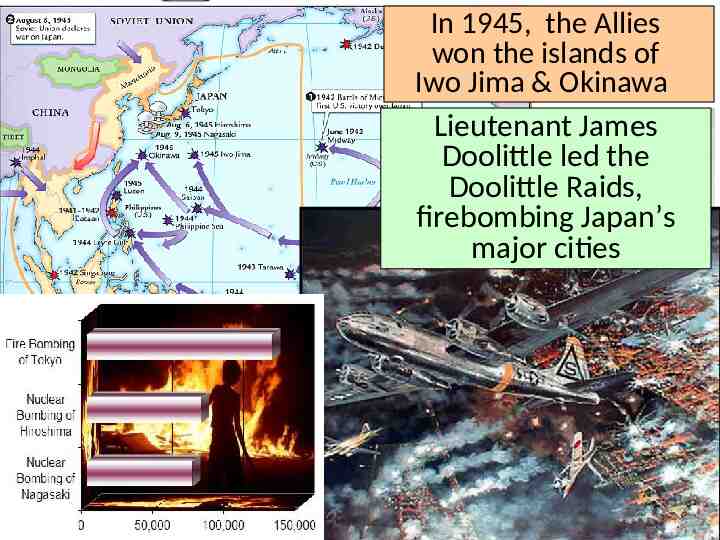
In 1945, the Allies won the islands of Iwo Jima & Okinawa Lieutenant James Doolittle led the Doolittle Raids, firebombing Japan’s major cities
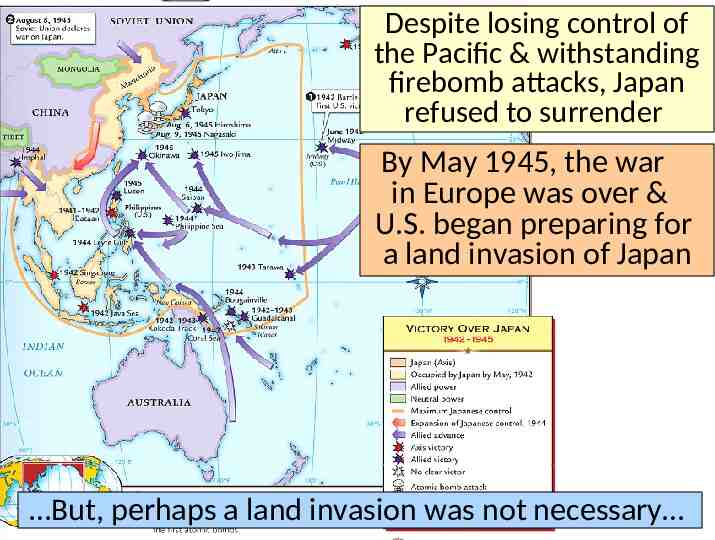
Despite losing control of the Pacific & withstanding firebomb attacks, Japan refused to surrender By May 1945, the war in Europe was over & U.S. began preparing for a land invasion of Japan But, perhaps a land invasion was not necessary

In 1939, Albert Einstein wrote U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt about the potential to build a nuclear weapon FDR created a topsecret program called the Manhattan Project, to construct the atomic bomb

The Manhattan Project Robert Oppenheimer was put in charge of developing the bomb From 1942-1945, a number of secret labs across the country developed & built the bomb

In July 1945, the in bomb was The bomb was constructed tested TN at Los Alamos, a secretsuccessfully city in Oak Ridge, New Mexico during Project Trinity Physicist Enrico Fermi at the University of Chicago developed Nuclear plant in Hanford, WA the nucleardeveloped reaction the plutonium America: Story of Us: The Manhattan Project

In April 1945, FDR died & his VP Harry Truman became president and had to decide how to end the war in the Pacific

In July 1945, the Big Three met at the Potsdam Conference to discuss the end of WWII Truman learned the atomic bomb was ready & issued the Potsdam Declaration to Japan: “surrender or face destruction”

When Japan refused to surrender, Truman ordered the bombing of Hiroshima on August 6, 1945 After 3 days, Japan did not surrender so a 2nd atomic bomb was dropped on Nagasaki After the second atomic bomb, Emperor Hirohito agreed to a surrender
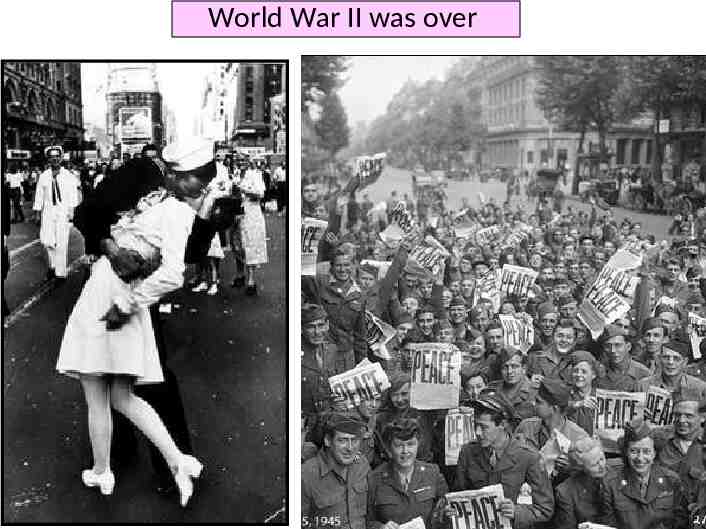

World War II was over

In 1945, the Nuremberg Trials began Prosecution of the members of the political, military and economic leadership of Germany began

The GI Bill of Rights offered returning soldiers cheap loans for new homes & tuition for college
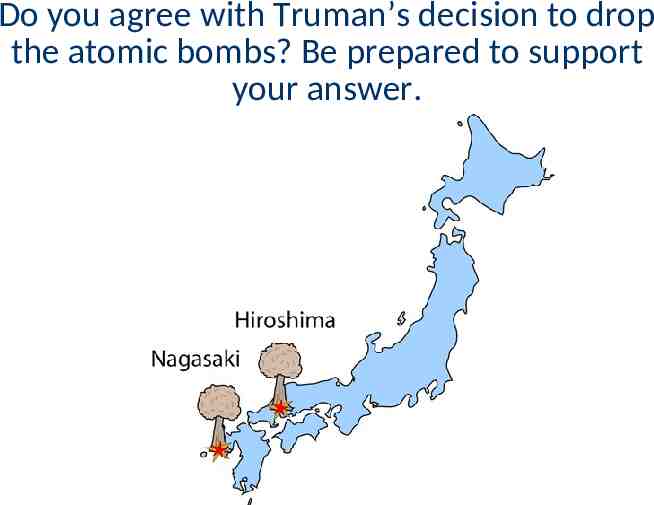
Do you agree with Truman’s decision to drop the atomic bombs? Be prepared to support your answer.

Conclusions: The Impact of World War II World War II was the biggest, most deadly, & most impactful war in world history: – Europe was destroyed by the war & lost its place as the epicenter of power in the world – The USA & USSR emerged as super powers & rivals competing for influence in the world – A United Nations was formed to replace the League of Nations to help promote peace – Colonized nation began to demand independence from Europeans