An Introduction to Data Warehousing Presented by Joseph M. Wilson EPA
34 Slides1.50 MB

An Introduction to Data Warehousing Presented by Joseph M. Wilson EPA Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 1
In the Beginning, life was simple Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 2
But Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 3
Our information needs Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 4
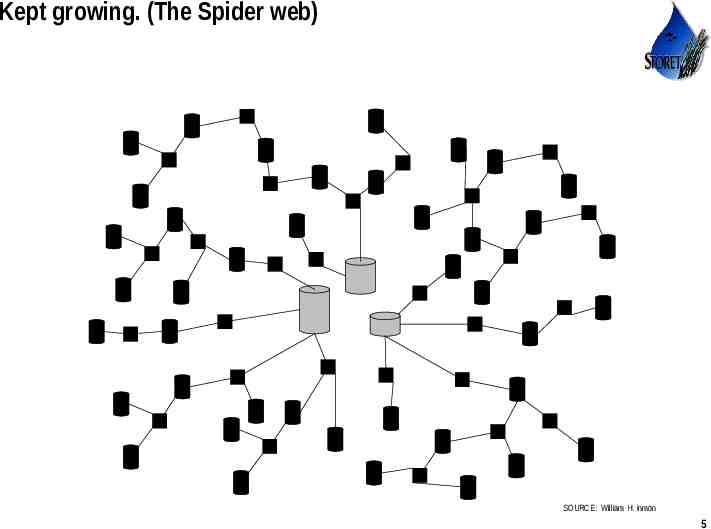
Kept growing. (The Spider web) SOURCE: William H. Inmon Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 5

Purpose To explore and discuss the purpose and principles of data warehousing. Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 6

Briefing Contents Data Warehouse Concepts Building a Data Warehouse STORET Warehouse Example Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 7

So What Is a Data Warehouse? Definition: A data warehouse is the data repository of an enterprise. It is generally used for research and decision support. By comparison: an OLTP (on-line transaction processor) or operational system is used to deal with the everyday running of one aspect of an enterprise. OLTP systems are usually designed independently of each other and it is difficult for them to share information. Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 8

Why Do We Need Data Warehouses? Consolidation of information resources Improved query performance Separate research and decision support functions from the operational systems Foundation for data mining, data visualization, advanced reporting and OLAP tools Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 9

What Is a Data Warehouse Used for? Knowledge discovery Making consolidated reports Finding relationships and correlations Data mining Examples Banks identifying credit risks Insurance companies searching for fraud Medical research Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 10

How Do Data Warehouses Differ From Operational Systems? Goals Structure Size Performance optimization Technologies used Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 11
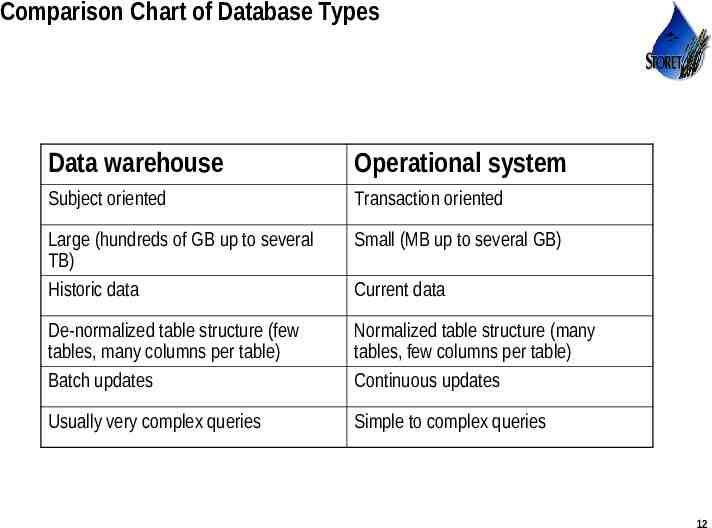
Comparison Chart of Database Types Data warehouse Operational system Subject oriented Transaction oriented Large (hundreds of GB up to several TB) Historic data Small (MB up to several GB) De-normalized table structure (few tables, many columns per table) Batch updates Normalized table structure (many tables, few columns per table) Continuous updates Usually very complex queries Simple to complex queries Current data Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 12
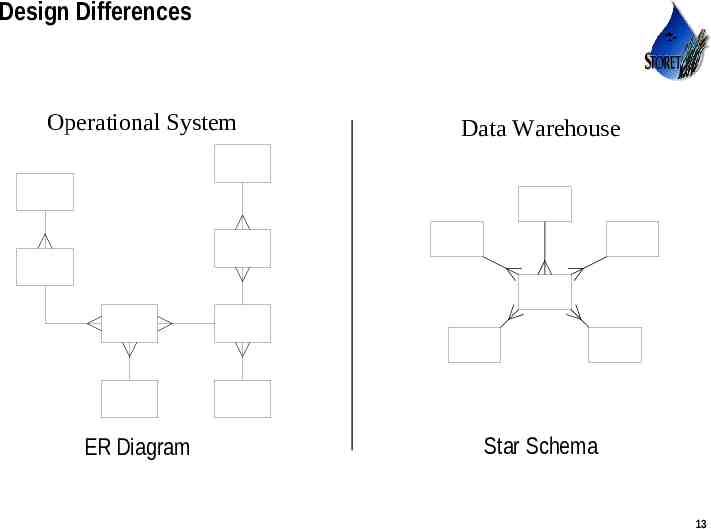
Design Differences Operational System Data Warehouse ER Diagram Star Schema Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 13
Supporting a Complete Solution Operational SystemData Entry Data WarehouseData Retrieval Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 14

Data Warehouses, Data Marts, and Operational Data Stores Data Warehouse – The queryable source of data in the enterprise. It is comprised of the union of all of its constituent data marts. Data Mart – A logical subset of the complete data warehouse. Often viewed as a restriction of the data warehouse to a single business process or to a group of related business processes targeted toward a particular business group. Operational Data Store (ODS) – A point of integration for operational systems that developed independent of each other. Since an ODS supports day to day operations, it needs to be continually updated. SOURCE: Ralph Kimball Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 15

Briefing Contents Data Warehouse Concepts Building a Data Warehouse STORET Warehouse Example Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 16
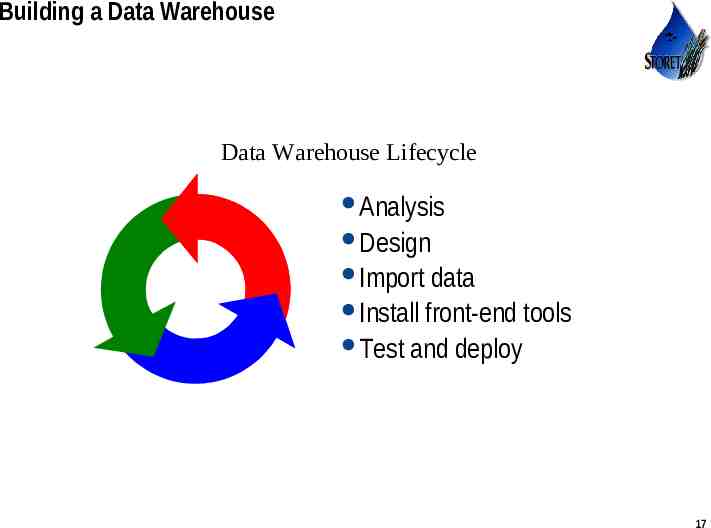
Building a Data Warehouse Data Warehouse Lifecycle Analysis Design Import data Install front-end tools Test and deploy Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 17
Stage 1: Analysis Identify: Target Questions Data needs Timeliness of data Granularity – – – – Analysis Design Import data Install front-end tools Test and deploy Create an enterprise-level data dictionary Dimensional analysis Identify facts and dimensions Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 18
Stage 2: Design Star schema Data Transformation Aggregates Pre-calculated Values HW/SW Architecture – Analysis Design – Import data – Install front-end tools – Test and deploy Dimensional Modeling Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 19
Dimensional Modeling Fact Table – The primary table in a dimensional model that is meant to contain measurements of the business. Dimension Table – One of a set of companion tables to a fact table. Most dimension tables contain many textual attributes that are the basis for constraining and grouping within data warehouse queries. SOURCE: Ralph Kimball Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 20
Stage 3: Import Data Identify data sources Extract the needed data from existing systems to a data staging area Transform and Clean the data – Analysis – Design Import data – Install front-end tools – Test and deploy Resolve data type conflicts Resolve naming and key conflicts Remove, correct, or flag bad data Conform Dimensions Load the data into the warehouse Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 21
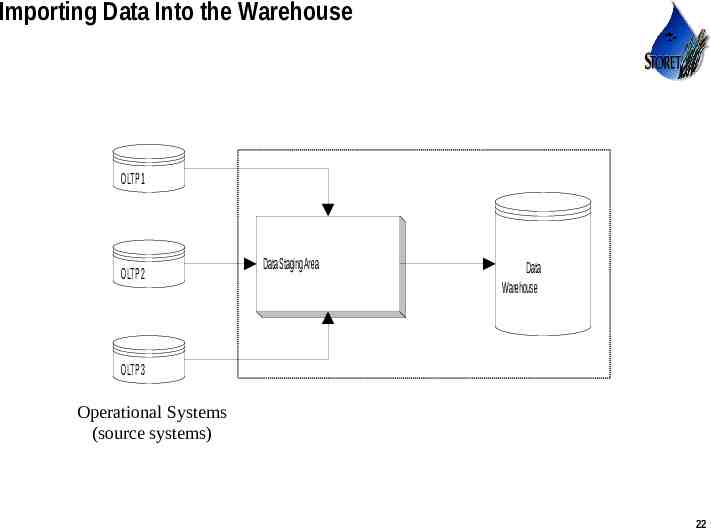
Importing Data Into the Warehouse OLTP 1 Data Staging Area OLTP 2 Data Warehouse OLTP 3 Operational Systems (source systems) Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 22
Stage 4: Install Front-end Tools Reporting tools Data mining tools GIS Etc. Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. – Analysis – Design – Import data Install front-end tools – Test and deploy 23
Stage 5: Test and Deploy – – – – Usability tests Software installation User training Performance tweaking based on usage Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. Analysis Design Import data Install front-end tools Test and deploy 24
Special Concerns Time and expense Managing the complexity Update procedures and maintenance Changes to source systems over time Changes to data needs over time Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 25

Briefing Contents Data Warehouse Concepts Building a Data Warehouse STORET Warehouse Example Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 26

Goals of the STORET Central Warehouse Improved performance and faster data retrieval Ability to produce larger reports Ability to provide more data query options Streamlined application navigation Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 27
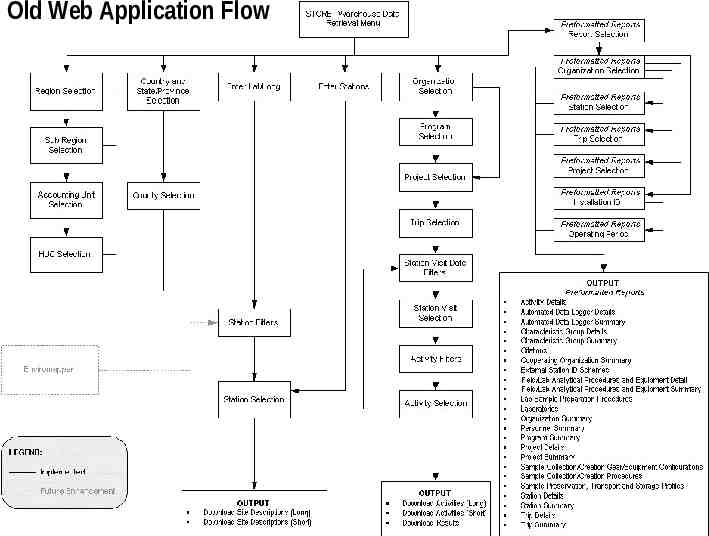
Old Web Application Flow Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 28
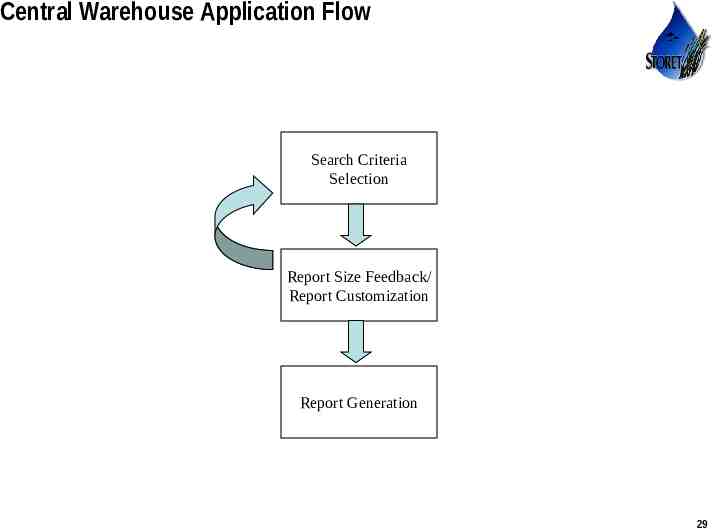
Central Warehouse Application Flow Search Criteria Selection Report Size Feedback/ Report Customization Report Generation Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 29
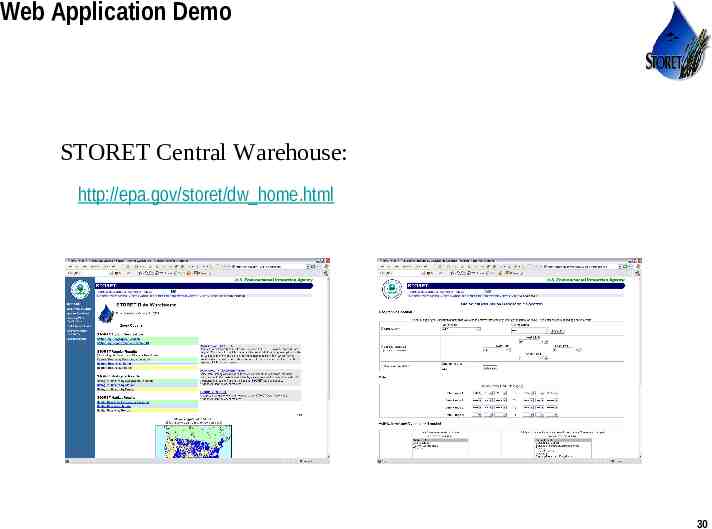
Web Application Demo STORET Central Warehouse: http://epa.gov/storet/dw home.html Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 30
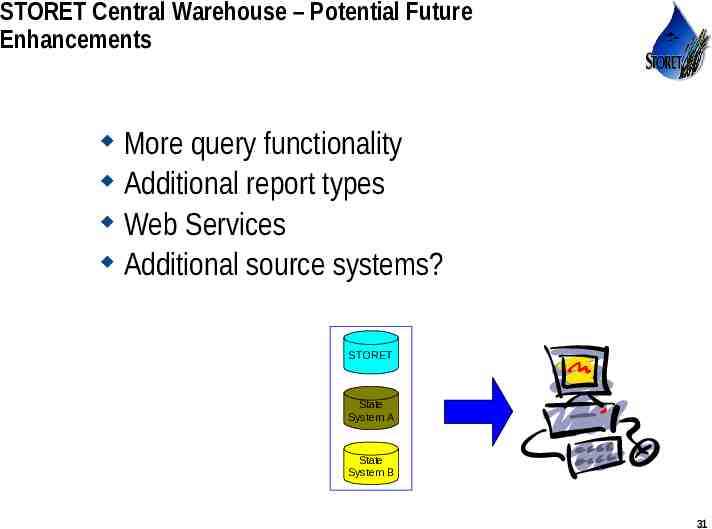
STORET Central Warehouse – Potential Future Enhancements More query functionality Additional report types Web Services Additional source systems? STORET State System A State System B Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 31
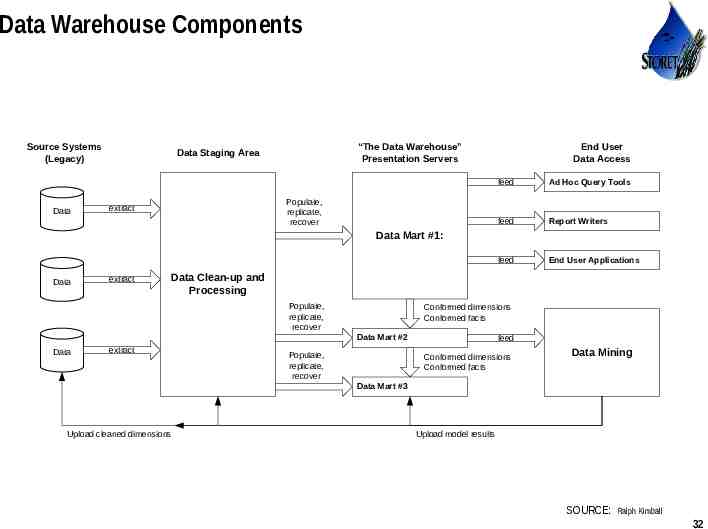
Data Warehouse Components Source Systems (Legacy) Data “The Data Warehouse” Presentation Servers Data Staging Area Populate, replicate, recover extract End User Data Access feed Ad Hoc Query Tools feed Report Writers feed End User Applications Data Mart #1: Data extract Data Clean-up and Processing Populate, replicate, recover Conformed dimensions Conformed facts Data Mart #2 Data extract Populate, replicate, recover feed Conformed dimensions Conformed facts Data Mining Data Mart #3 Upload cleaned dimensions Upload model results SOURCE: Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. Ralph Kimball 32
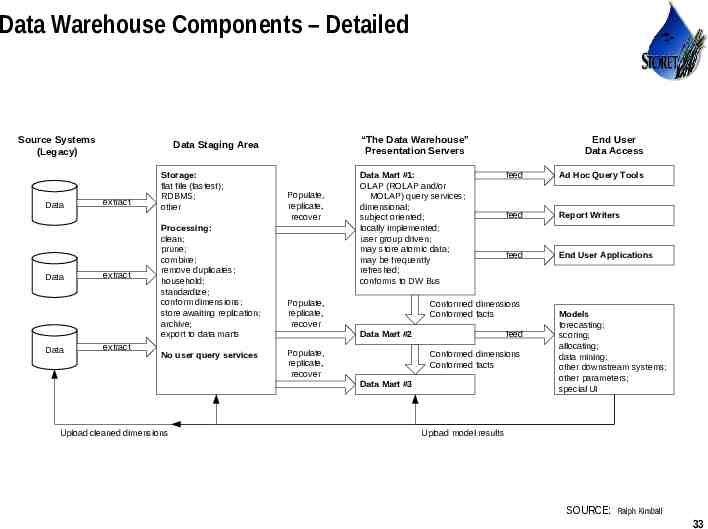
Data Warehouse Components – Detailed Source Systems (Legacy) Data Data Data “The Data Warehouse” Presentation Servers Data Staging Area extract extract extract Storage: flat file (fastest); RDBMS; other Processing: clean; prune; combine; remove duplicates; household; standardize; conform dimensions; store awaiting replication; archive; export to data marts No user query services Populate, replicate, recover Data Mart #1: OLAP (ROLAP and/or MOLAP) query services; dimensional; subject oriented; locally implemented; user group driven; may store atomic data; may be frequently refreshed; conforms to DW Bus Populate, replicate, recover feed Ad Hoc Query Tools feed Report Writers feed End User Applications Conformed dimensions Conformed facts Data Mart #2 Populate, replicate, recover feed Conformed dimensions Conformed facts Data Mart #3 Upload cleaned dimensions End User Data Access Models forecasting; scoring; allocating; data mining; other downstream systems; other parameters; special UI Upload model results SOURCE: Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. Ralph Kimball 33

Briefing Contents Data Warehouse Concepts Building a Data Warehouse STORET Warehouse Example Use or disclosure of data contained on this sheet is subject to the restriction on the title page of this proposal or quotation. 34






