1. First Americans—–Pre-Columbian
53 Slides9.24 MB

1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian
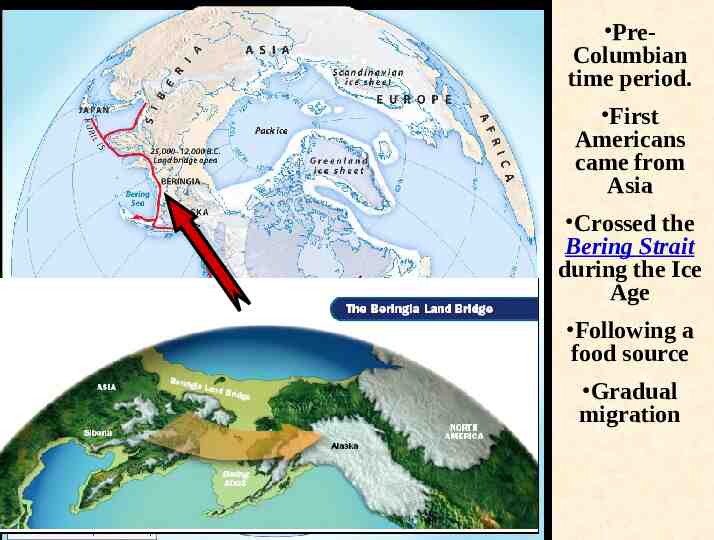
PreColumbian time period. First Americans came from Asia Crossed the Bering Strait during the Ice Age Following a food source Gradual migration
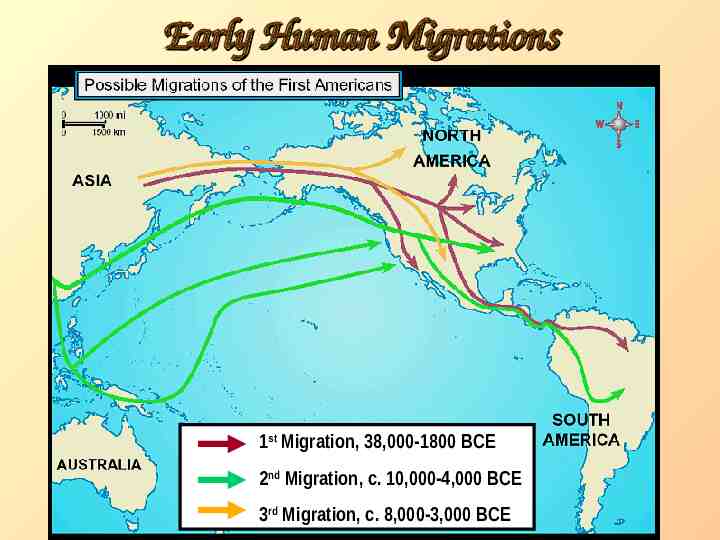
Early Human Migrations 1st Migration, 38,000-1800 BCE 2nd Migration, c. 10,000-4,000 BCE 3rd Migration, c. 8,000-3,000 BCE
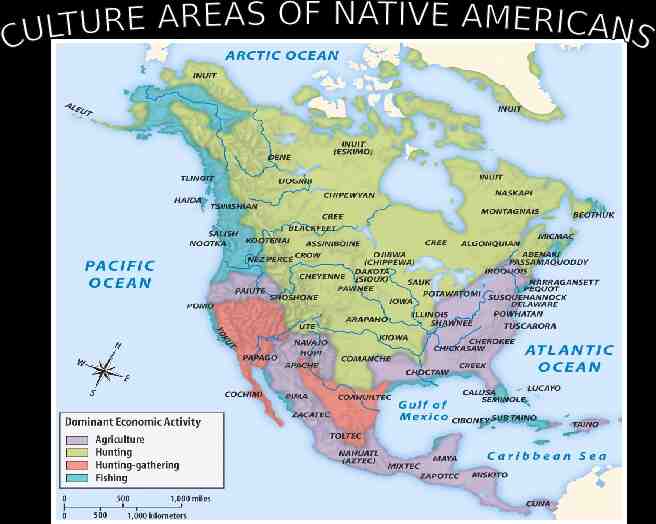
Culture area
WHITE EUROPEANS Used the land for economic needs Clearing the land, destroying hunting areas and fencing it off into private property Divided the land and selling it for monetary value. NATIVE AMERICANS Relationship with environment as part of their religion Need to hunt for survival Ownership meant access to the things the land produced, not ownership of the land itself.

1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian 2. Europe Exploration Causes Indirect Direct Effects notes

Earlier Explorations 1. Islam & the Spice Trade Silk Road 2. New Player Europe Nicolo, Maffeo, & Marco Polo, 1271 Expansion becomes a state enterprise monarchs had the authority & the resources. Better seaworthy ships.

Motives for European Exploration 1. Crusades by-pass intermediaries to get to Asia. 2. Renaissance curiosity about other lands and peoples. 3. Reformation refugees & missionaries. 4. Monarchs seeking new sources of revenue. 5. Technological advances. 6. Fame and fortune.

New Maritime Better Maps Technologies Hartman Astrolabe (1532) Mariner’s Compass Sextant

New Weapons Technology

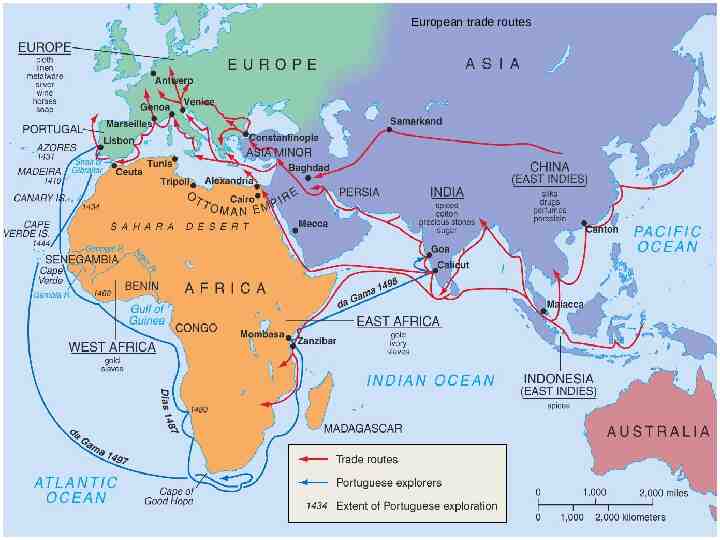
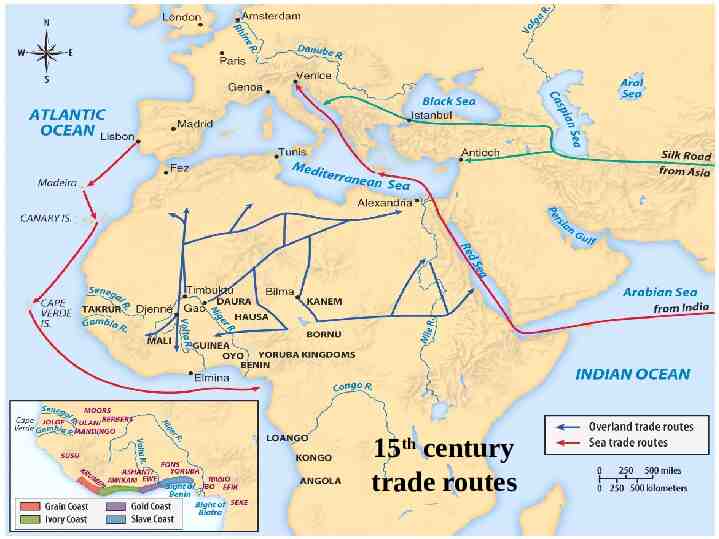
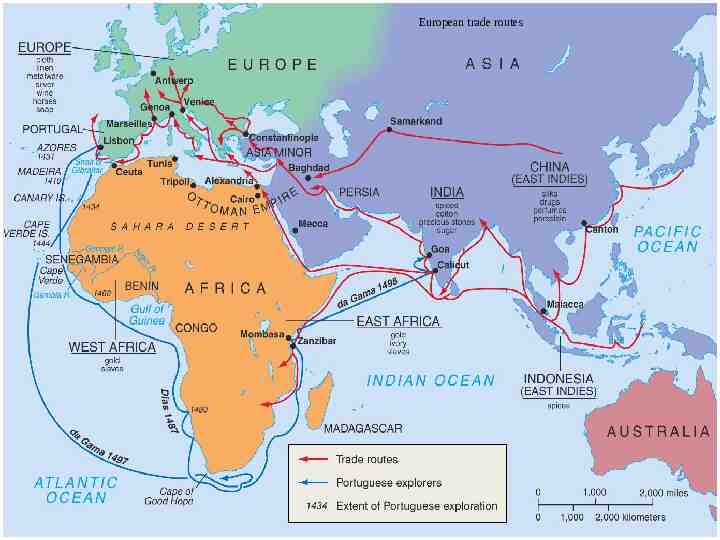
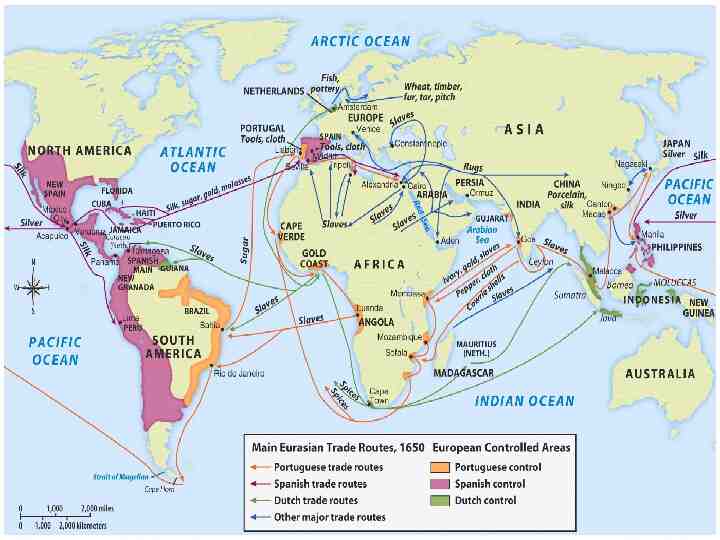
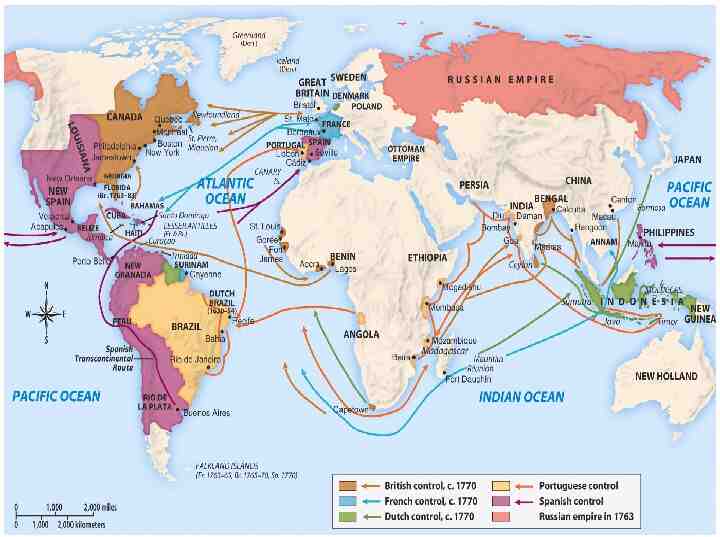
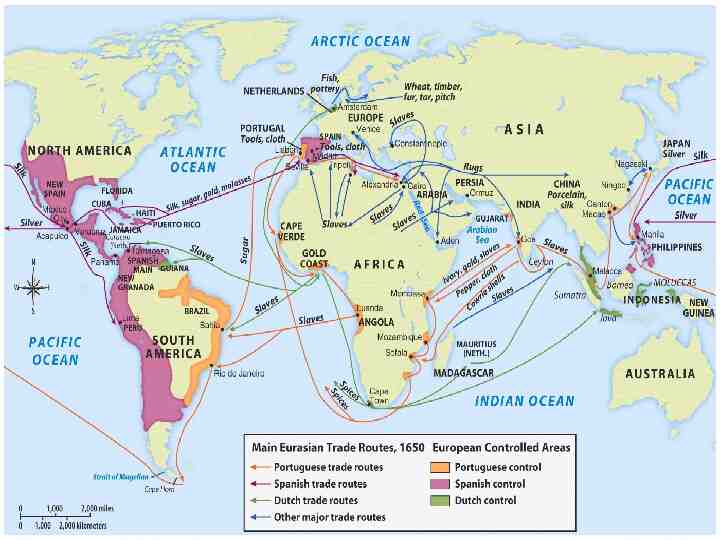
15th century trade routes

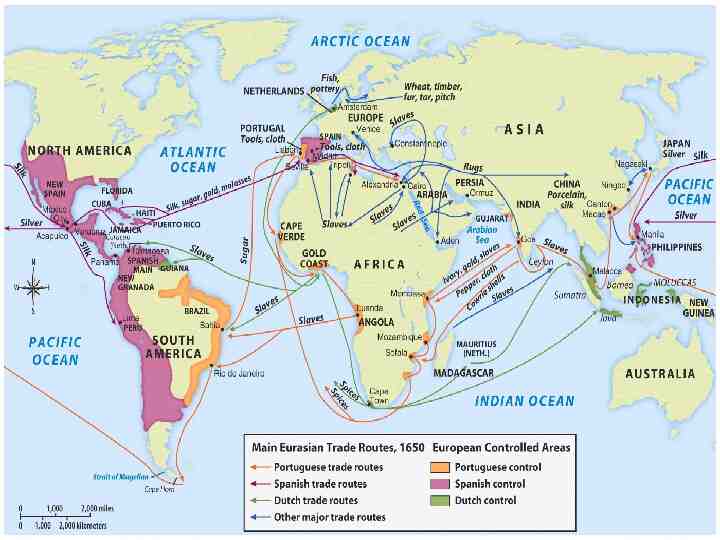
European trade routes
Direct Causes 3 G’s Political: Become a world power through gaining wealth and land. (GLORY) Economic: Search for new trade routes with direct access to Asian/African luxury goods would enrich individuals and their nations (GOLD) Religious: spread Christianity and weaken Middle Eastern Muslims. (GOD) The 3 motives reinforce each other
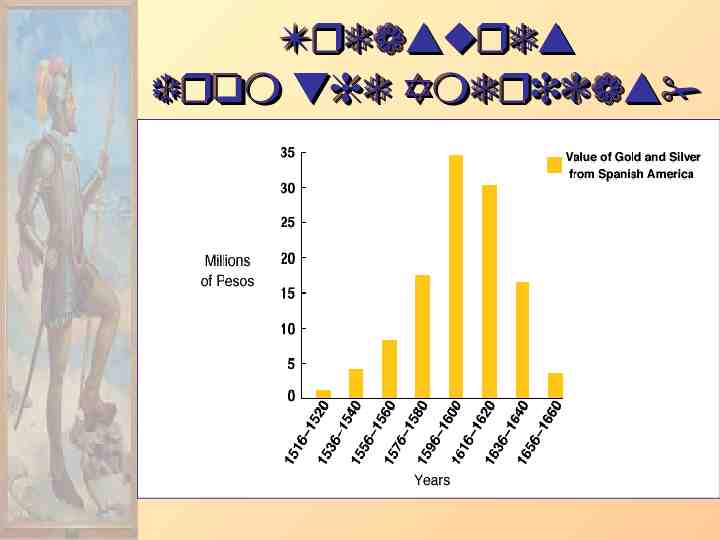
Treasures from the Americas!

EFFECTS Europeans reach and settle Americas Expanded knowledge of world geography Growth of trade, mercantilism and capitalism Indian conflicts over land and impact of disease on Indian populations Introduction of the institution of slavery Columbian Exchange
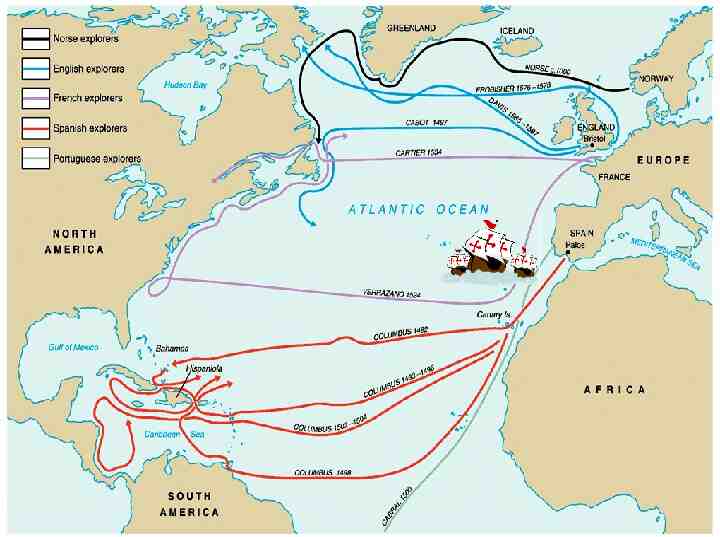
explorers
Columbian Exchange or the transfer of goods involved 3 continents, Americas, Europe and Africa * Squash * Turkey * Cocoa * Peanut * Avocado * Pumpkin * Pineapple * Tomato * Peppers * Tobacco * Cassava * Vanilla * Olive * Onion * Grape * Citrus Fruits * Cattle * Flu * Diptheria * Coffee Beans * Banana * Turnip * Honeybee * Peach * Sugar Cane * Pear * Wheat * Sheep * Pig * Typhus * Measles * Whooping Cough * Sweet Potatoes * Quinine * POTATO * MAIZE * Syphilis * Rice * Barley * Oats * HORSE * Smallpox * Malaria
1. First Americans-----Pre-Columbian 2. Europe Exploration Causes Indirect Direct Effects 3. European Colonization Spain Portugal France Dutch
European Colonization European Colonization Once the New World is discovered, the Big 4 four European countries begin competing for control of North America and the world . – Spain – England – France – Portugal This power struggle ultimately leads to several wars.
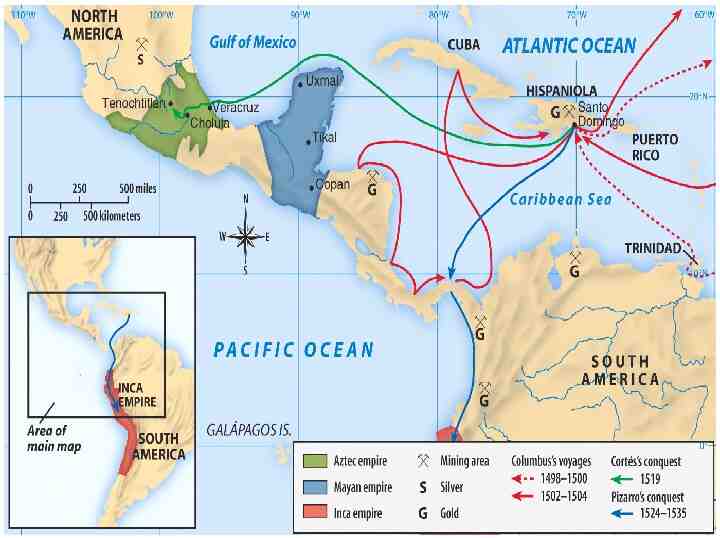
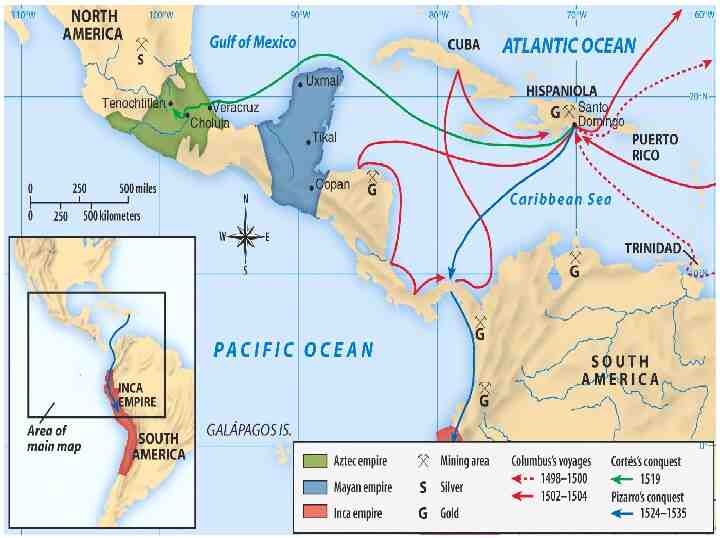
Spanish first to pursue colonization Start in Caribbean, then Central and South America—most important was conquest of Aztecs by Cortez (1521) and Incas by Pizzaro (1531) First permanent colonies in what will become United States are founded by Spain – St. Augustine (Florida) is founded (1565) to protect Spanish treasure fleets
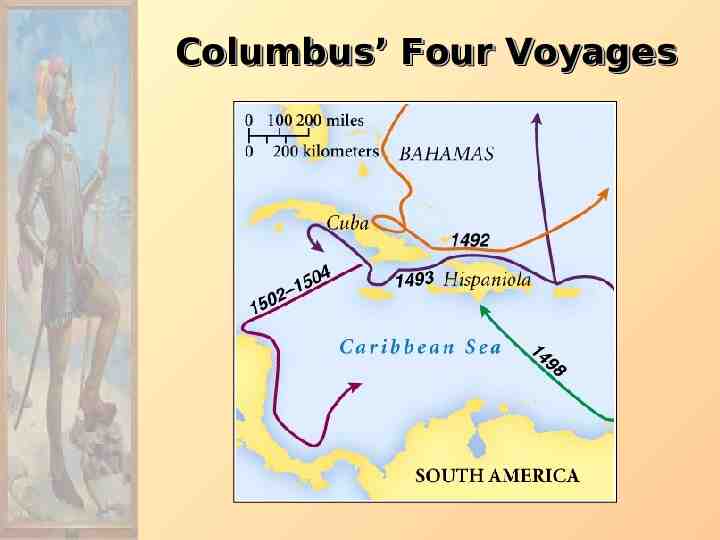
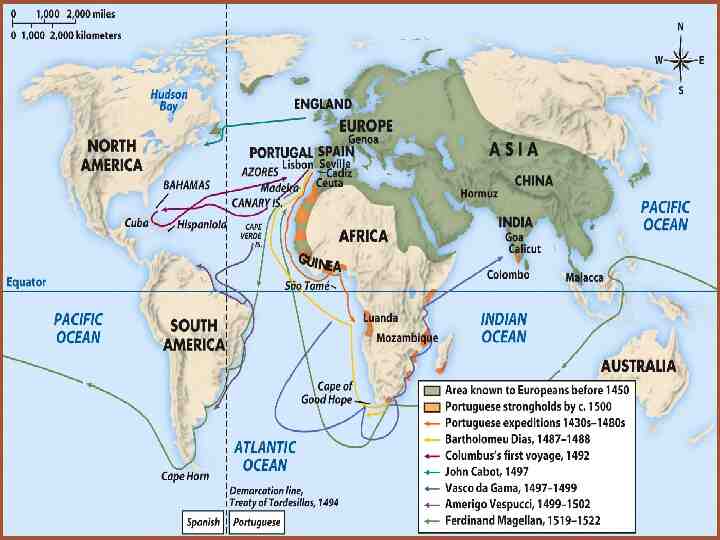
Explorers Sailing For Spain Columbus - Italian sailing for Spain Landed in the “West Indies” - 1492 Magellan - Portuguese sailing for Spain - 1st to circumnavigate the world - 1522

Columbus’ Four Voyages
Ferdinand Magellan & the First Circumnavigation of the World
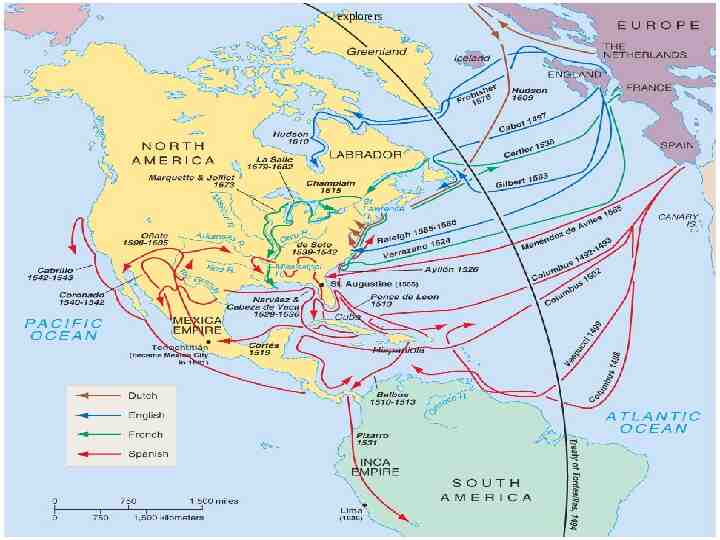
Explorers Sailing From Hispaniola De Leon - colonist of Hispaniola - Established colony at Puerto Rico - Sailed north looking for Fountain of Youth - Discovered Florida - 1508 Balboa - colonist of Hispaniola - Established settlement in Panama - 1st European to see Pacific Ocean - 1513 de Coronado - Spain - Explored north from Mexico; up Colorado River; saw Grand Canyon -1540 de Soto - Spain - Explored Florida into Carolina’s and west to the Mississippi River - 1541

Explorers Sailing For Spain & Portugal Vespucci - Italian sailing for both Spain and Portugal - Sailed to the America’s Amerigo is his first name (where we get “America”) - 1501

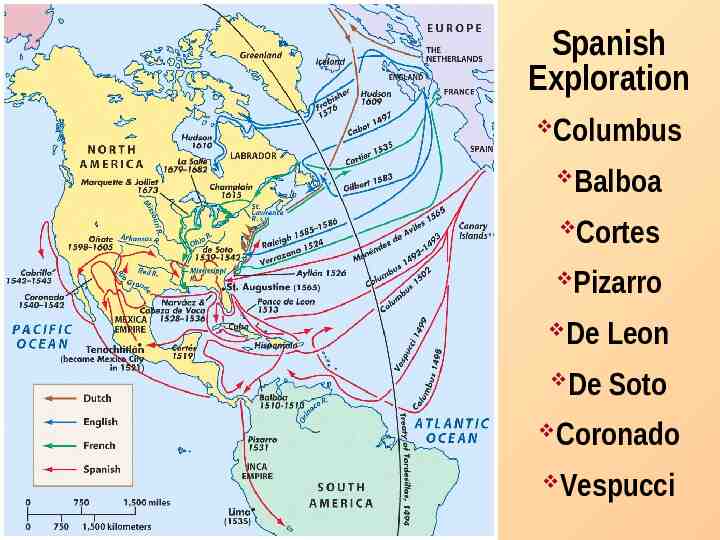
Spanish Exploration Columbus Balboa Cortes Pizarro De Leon De Soto Coronado Vespucci

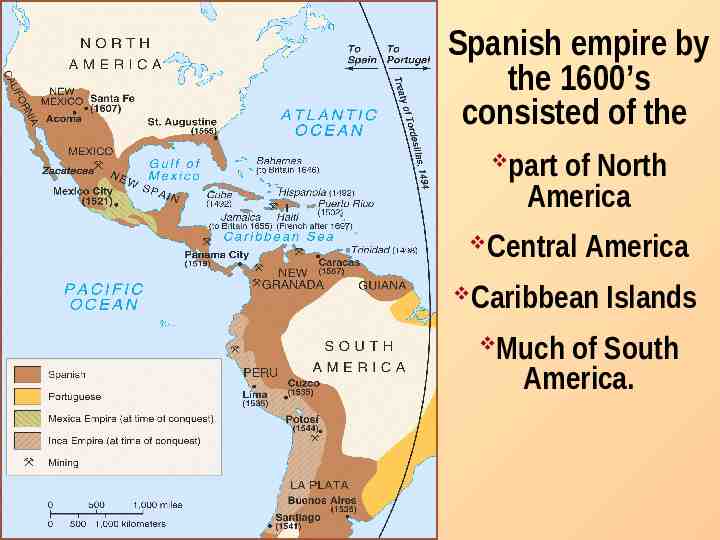
Spanish empire by the 1600’s consisted of the part of North America Central America Caribbean Islands Much of South America.

First Spanish Conquests: The Aztecs Cortes conquered Aztec Empire in 1519 and took control of modern day Mexico. vs. Hernando Cortés Montezuma Montezuma II II

Mexico Surrenders to Cortés
First Spanish Conquests: The Incas Pizarro conquered Incan Empire in modern day Peru in 1532 vs. Francisco Francisco Pizarro Atahualpa Atahualpa
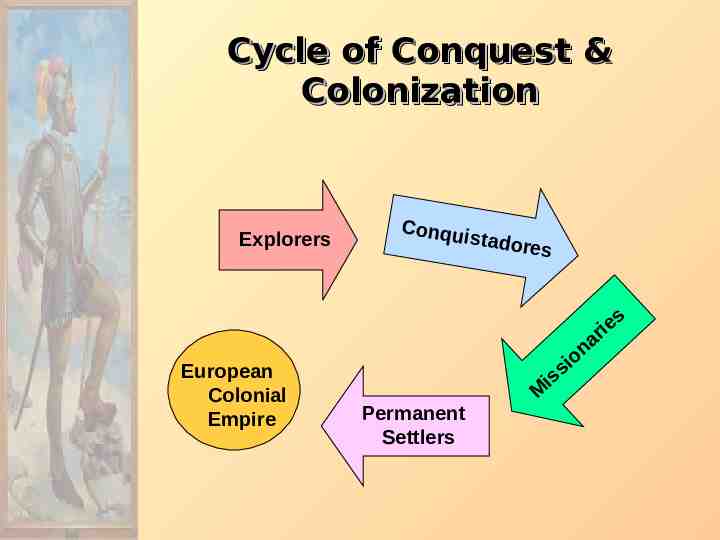
Cycle of Conquest & Colonization Explorers European Colonial Empire Co n q u i stadore Permanent Settlers s a n io s is M ri e s

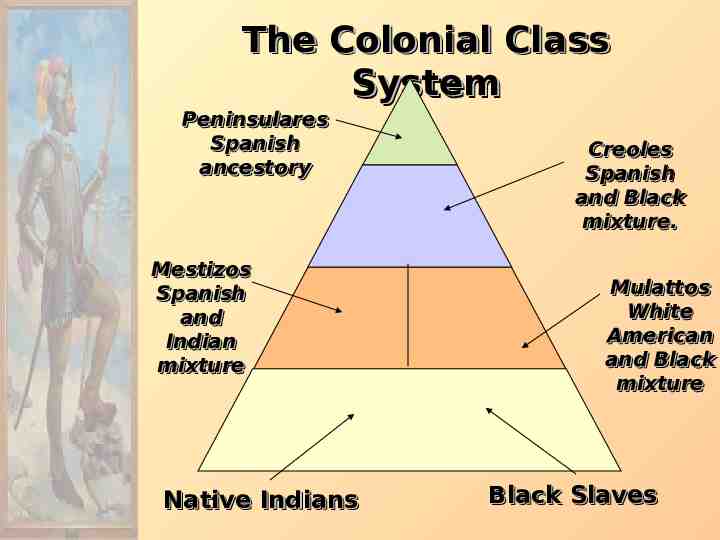
The Colonial Class System Peninsulares Spanish ancestory Mestizos Spanish and Indian mixture Native Indians Creoles Spanish and Black mixture. Mulattos White American and Black mixture Black Slaves

The Influence of the Colonial Catholic Church Our Lady of Guadalupe Guadalajara Cathedral Spanish Mission
Father Bartolomé de Las Casas Believed Native Americans had been treated harshly by the Spanish. Indians could be educated and converted to Christianized. Believed Indian culture was advanced as European but in different ways. New Laws -- 1542
1. Spanish practice of securing an adequate and cheap labor supply FEUDALISM “granted” to deserving subjects of the King 2. Conquistador controlled Indian populations Required Indians to pay tribute from their lands Indians often rendered personal services as well. 3. In return the conquistador was obligated to protect his wards instruct them in the Christian faith defend their right to use the to live off the land 4. Encomienda system eventually decimated Indian population. 5. The King prevented the encomienda with the New Laws (1542) supported by de Las Casas, the system gradually died out.

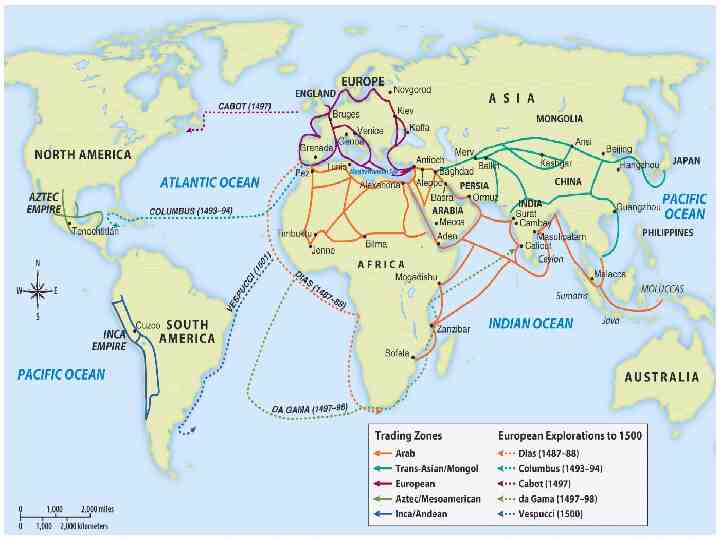
European Colonization The Portuguese were the first to begin searching for an all water route to Asia . – Prince Henry the Navigator – 1450’s Colonized the South America in the area of what would become Brazil

Explorers Sailing For Portugal Prince Henry the Navigator - Portugal - Funded Exploration down coast of Africa - 1419-1460 Dias - Portugal - Rounded the Cape of Good Hope 1488 da Gama - Portugal - Opened trade with India - Placed Portugal in position to dominate trade with India - 1498 Cabral - Portugal - Claimed present day Brazil for Portugal - 1500

European trade routes
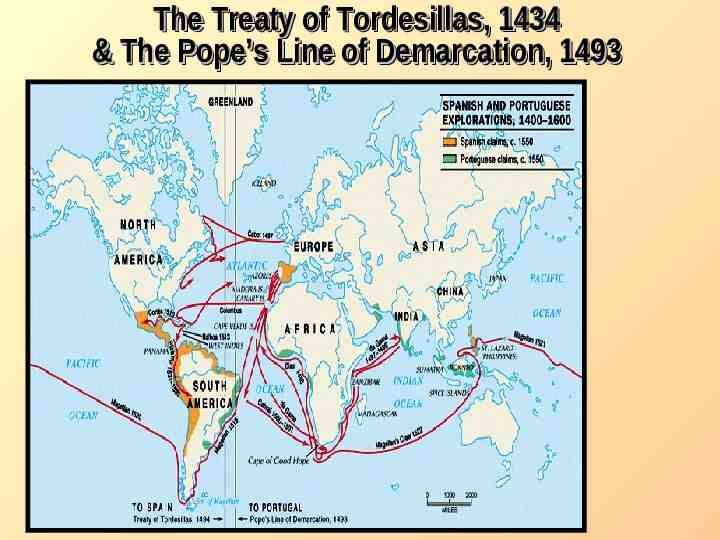
The Treaty of Tordesillas, 1434 & The Pope’s Line of Demarcation, 1493
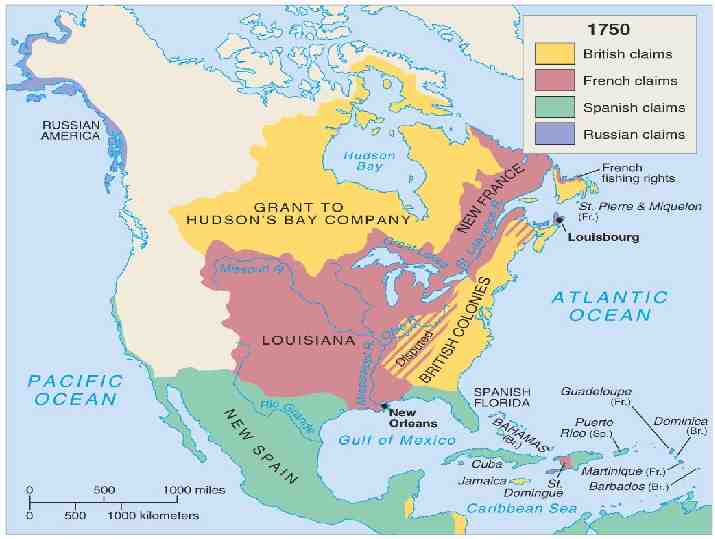
COLONIAL PERIOD COLONIZATION IS A NATURAL OUTGROWTH OF EXPLORATION MERCANTILISM - COLONIES EXIST TO BENEFIT THE MOTHER COUNTRY 3 MAJOR COUNTRIES TOOK THE LEAD IN COLONIZING THE NEW WORLD SPAIN FRANCE ENGLAND
SPAIN IN AMERICA SPANISH OBJECTIVES IN THE NEW WORLD o WEALTH o POWER & GLORY o EXPAND BOUNDARIES o SPREAD RELIGION COLONIES LOCATED IN SOUTH AMERICA, CENTRAL AMERICA & SOUTHERN NORTH AMERICA

SPAIN IN AMERICA SPANISH SOCIETY IN THE NEW WORLD PENINSULARIE - PURE SPANISH S CREOLES - PART SPANISH / PART EUROPEAN EUROPEAN MESTIZO - PART SPANISH / PART INDIAN MULATTO - PART SPANISH / PART AFRICAN INDIAN AFRICAN ZAMBO - PART INDIAN / PART AFRICAN

SPAIN IN AMERICA SPANISH GOVERNMENT DOMINATED COLONIAL AFFAIRS SPANISH WERE SEEKERS OF WEALTH SPANISH ENSLAVED THE INDIANS RELIGION (ROMAN CATHOLIC) PLAYS A BIG ROLE